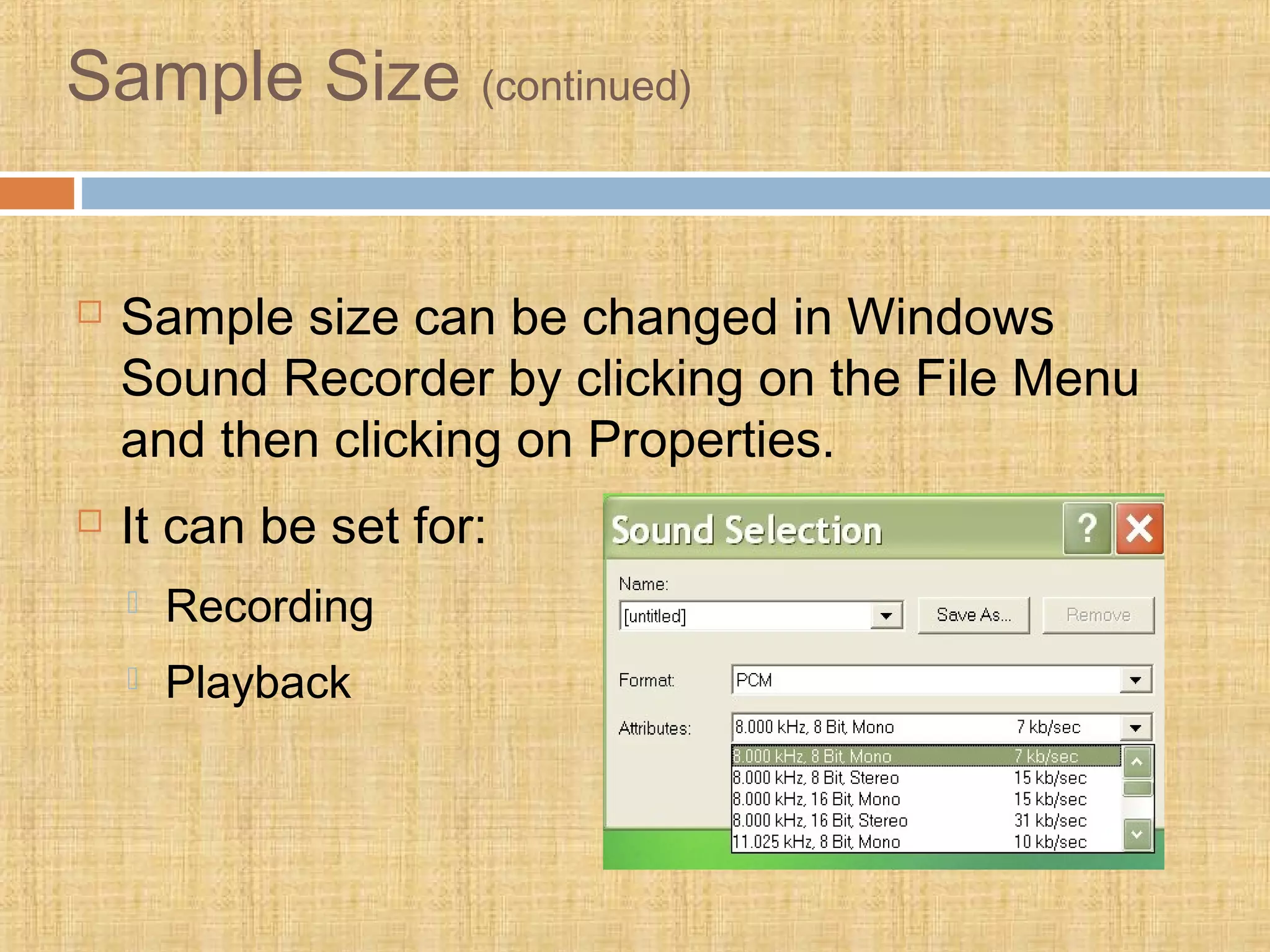
The document discusses multimedia elements and their uses. It describes the main multimedia elements as text, graphics, animation, audio, video, menus, hyperlinks, and virtual reality. It provides details on how to effectively use each element, such as using serif fonts for printed text and sans serif for screens. Graphics should balance size and quality for the intended purpose and audience. Animation and video can simplify illustrations or simulations. Sound is digitized through sampling and formats include MP3, WAV and MIDI. Video formats include AVI, MOV, MPEG and RM. Multimedia has various uses including education, entertainment, advertising and medicine.