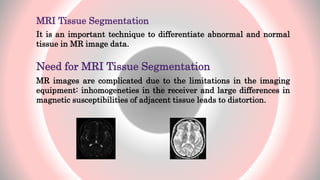
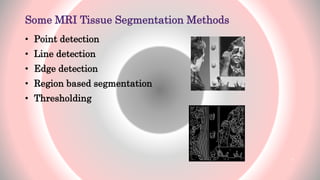
The document presents an overview of MRI tissue segmentation, covering image types, processing applications, and segmentation methods to differentiate normal and abnormal tissues. It discusses the challenges with MRI, including noise, inhomogeneities, and the need for bias field correction in image acquisition. Various algorithms and methods used in MRI tissue segmentation are reviewed, highlighting their development over recent years.


![Magnetic Resonance Image[MRI]
It is a tomographic imaging technique that produces images of internal
physical and chemical characteristics of an object from externally measured
nuclear magnetic resonance(NMR) signals.
Applications of MRI
• Diagnosing multiple sclerosis, brain tumours, spinal infections and
strokes in their earliest stages.
• Visualizing torn ligaments in the wrist, knee, and ankle, shoulder injuries.
• Evaluating bone tumors and herniated discs in the spine .
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/preview1-150324075401-conversion-gate01/85/MRI-Tissue-Segmentation-basics-5-320.jpg)