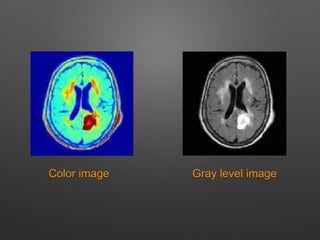
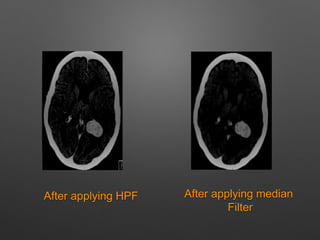
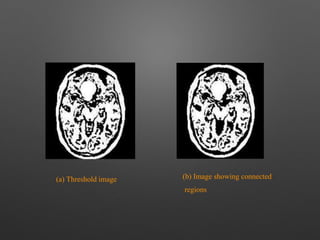
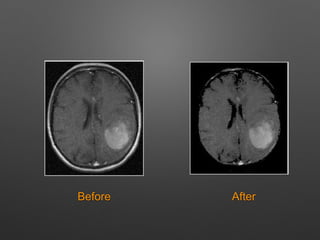
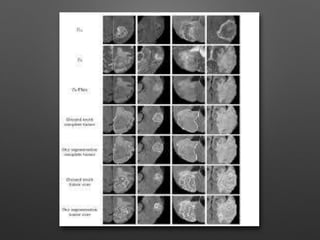
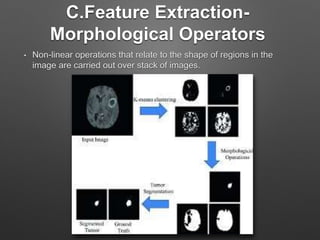
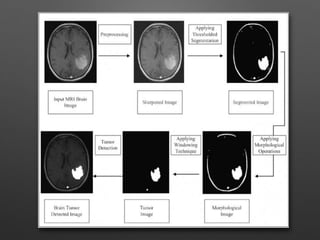
The document outlines the methodology for brain tumor detection from MRI images. It involves four main stages: pre-processing, skull stripping, segmentation, and feature extraction. In pre-processing, MRI images are converted to grayscale and filters are applied to remove noise. Skull stripping removes non-brain tissues. Segmentation uses Otsu's thresholding and watershed methods to separate brain regions. Feature extraction uses morphological operators to extract the tumor region by subtracting it from the original grayscale image.