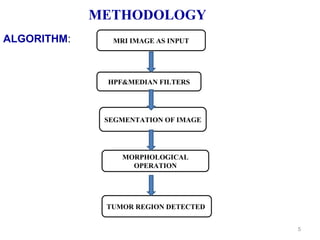
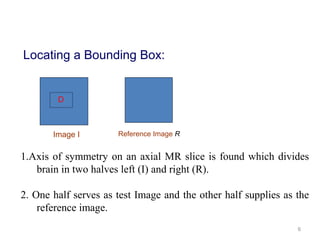
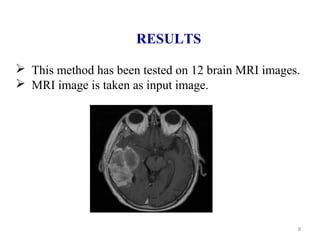
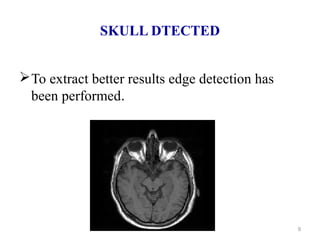
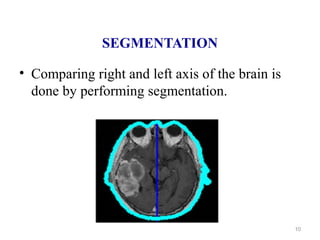
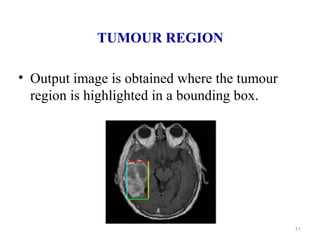
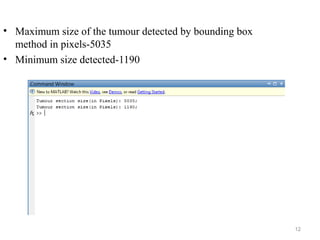
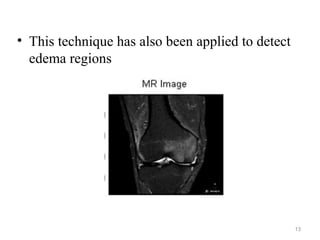
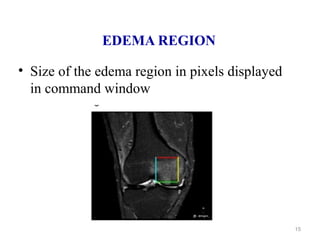
This document describes a methodology for detecting brain tumors and edema from magnetic resonance images (MRI) using bounding box symmetry. The methodology involves segmenting the brain from MRI images, applying filters, and using a novel score function based on Bhattacharya coefficient to detect a rectangle representing the region of interest by comparing the left and right sides of the brain. The method was tested on 12 brain MRI images and was able to accurately detect tumor and edema regions and their sizes.