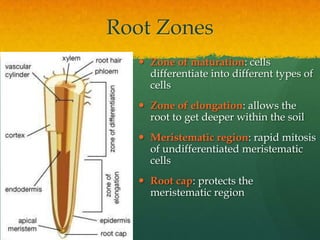
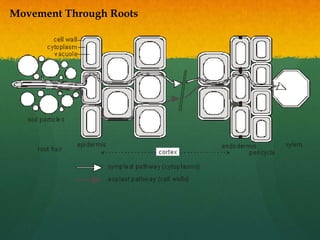
Roots take up water and minerals from the soil. They have branches and root hairs that increase their surface area for absorption. Water enters roots through osmosis as root cells have a higher solute concentration than the soil. Minerals enter through active transport against their concentration gradient. Water moves through the root via two pathways - through the cell walls (apoplast pathway) or through the cytoplasm and plasmodesmata between cells (symplast pathway). Most water is drawn up through transpiration and replaced through the roots.