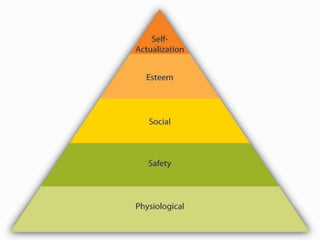
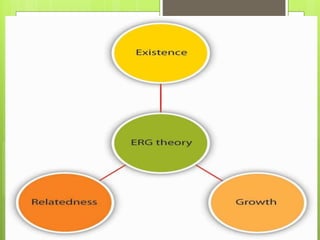
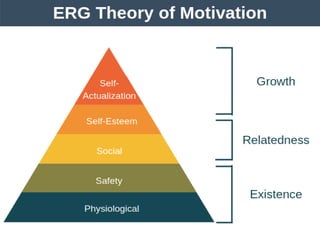
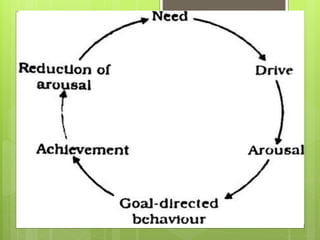
This document discusses motivation and related concepts. It defines motivation as the internal state that causes an organism to strive toward a goal, often in response to external stimuli. Motivation arises from needs, drives, incentives, and motives. It discusses various theories of motivation including instinct theory, drive theory, Maslow's hierarchy of needs, ERG theory, and Herzberg's two-factor theory. Motivation involves a cycle from needs and drives being aroused, to goal-directed behavior, achievement of the goal, and relief.