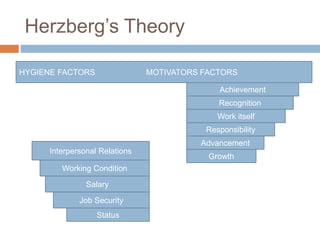
This presentation discusses motivation and related concepts and theories. Motivation comes from the Latin word "movere" meaning to move and is defined as an inner state that activates and directs behavior. There are intrinsic and extrinsic types of motivation. Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory proposes that needs must be met in a certain order, while Herzberg's theory separates motivators like achievement from hygiene factors like salary. Maslow focuses on unsatisfied needs driving motivation, whereas Herzberg argues hygiene factors only prevent dissatisfaction and not motivate. Motivated employees contribute more and are remunerated in return, fueling continued motivation within the organization.