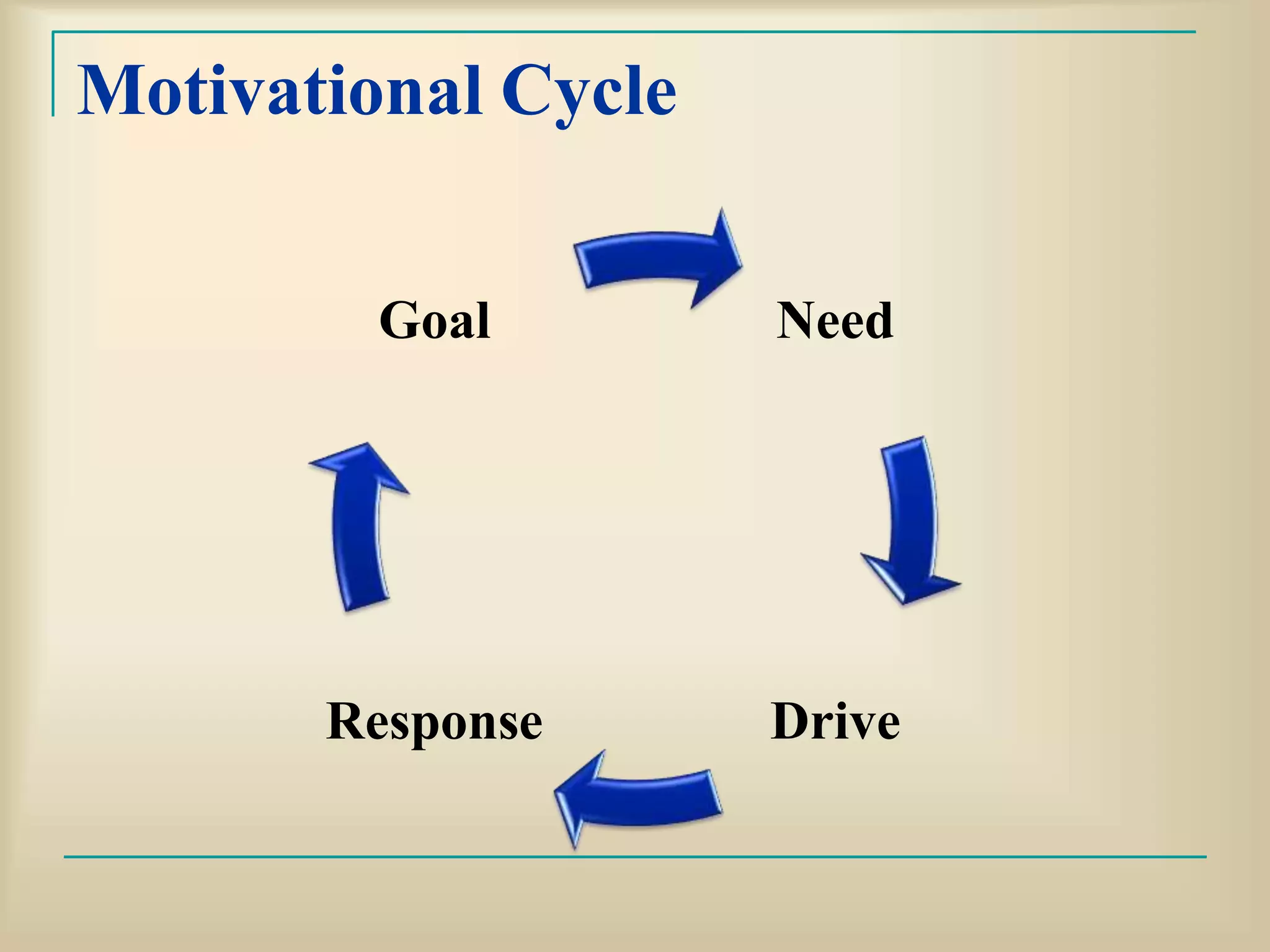
The document discusses motivation and its key components. Motivation refers to internal driving forces that compel behavior and goal attainment. It arises from basic needs and is influenced by incentives. Motivation involves deciding on goals, effort toward goals, and persistence. Several theories attempt to explain motivation, such as reinforcement, cognitive, humanistic, and social learning theories. Understanding motivation can help nurses in learning, job performance, and understanding patient behavior.