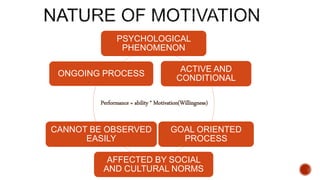
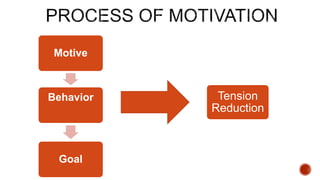
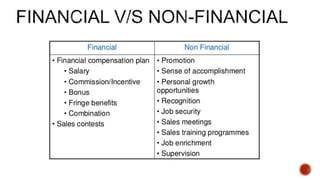
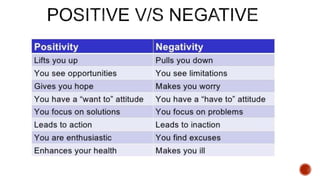
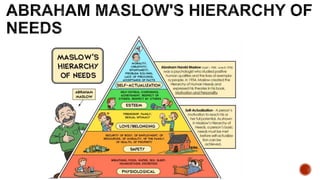
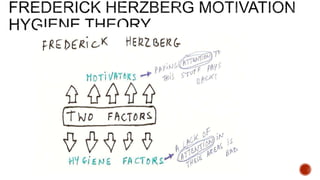
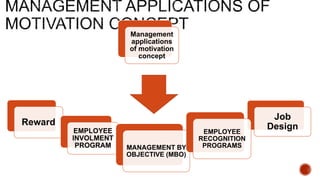
This document defines motivation and discusses its nature, process, types, major theories, importance, and managerial applications. It defines motivation as inspiring goal-oriented behavior and discusses Abraham Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory, Frederick Herzberg's motivator-hygiene theory, and Douglas McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y. Motivation is important for increased productivity, efficiency, goal achievement, and workforce stability. Managers can apply motivation concepts through rewards, employee involvement programs, job design, and employee recognition.