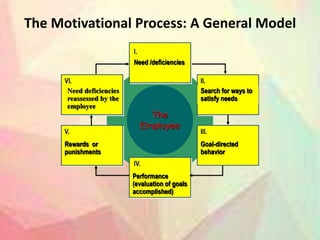
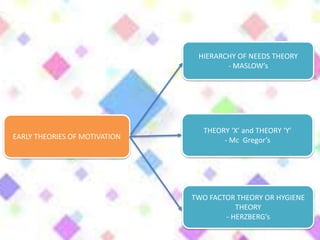
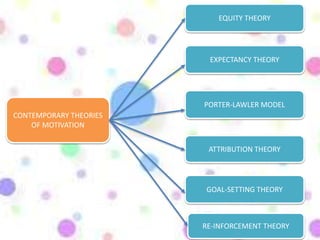
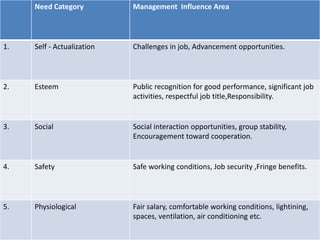
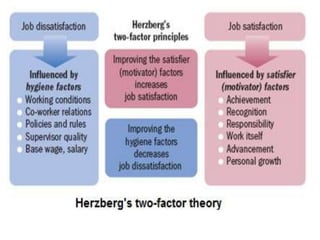
Here are a few key points on the role of money in motivating Indian employees:
- For most Indian employees, basic financial security and needs are important motivating factors given the country's developing economy. Meeting basic needs like paying bills, supporting a family, saving for the future etc. are priorities. So money does play an important role in motivation.
- However, money alone may not be a long-term sustaining motivator. While pay is important, Indian employees also want meaningful work, growth opportunities, recognition from managers/leaders, an engaging workplace culture etc. Non-monetary factors become increasingly important over time.
- In jobs that are more mundane or repetitive, money could be a stronger motivator