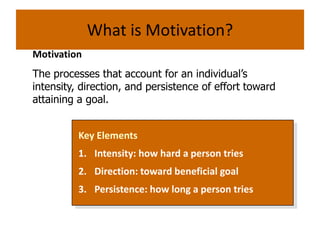
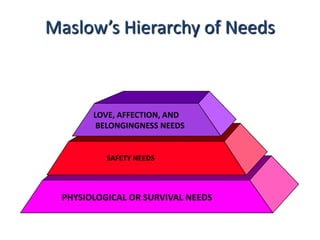
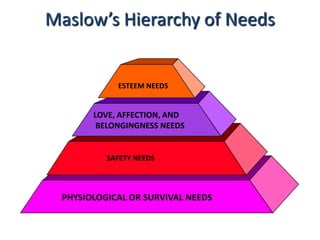
Abraham Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory proposes that people are motivated to fulfill basic needs before moving on to other needs. The hierarchy consists of physiological needs, safety needs, love and belonging needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs. Physiological needs are basic survival needs like food and water. Safety needs include security and stability. Once these are met, people seek love, friendship, and sense of belonging. Esteem and self-respect needs then motivate people. Finally, self-actualization involves fulfilling one's full potential. The theory assumes lower needs must be met before progressing to higher needs, though some criticisms note the order may not always apply rigidly.