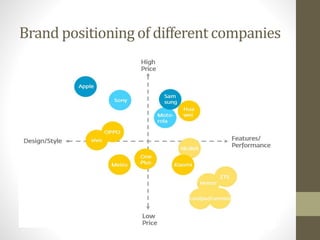
This presentation discusses brand positioning. It defines brand positioning as creating a brand offer that occupies a distinctive place in the target customer's mind. It notes that positioning involves identifying similarities and differences to develop knowledge and perceptions among customers. The presentation discusses determining the target consumer, competitors, and how the brand is similar or different. It also covers developing a positioning statement, issues in implementation, and types and approaches to positioning, including potential errors.