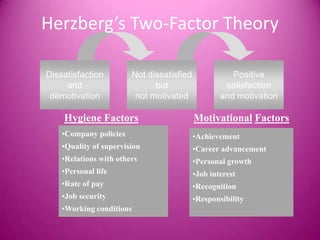
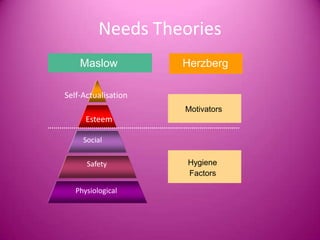
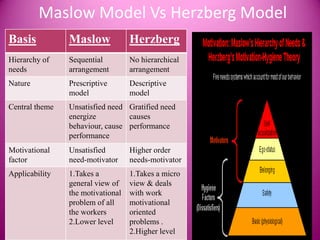
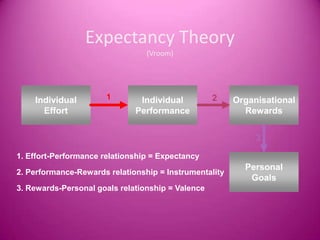
Motivation is defined as stimulating someone to action and providing an incentive or motive. It comes from internal or external factors that encourage goal-directed behavior. Effective motivation leads to benefits like increased job satisfaction, lower absenteeism and turnover, and higher productivity. Motivation theories include Maslow's hierarchy of needs and Herzberg's two-factor theory. Managers can use motivational strategies like training, feedback, job rotation, and appealing to needs, wants, emotions and expertise to encourage employee performance.