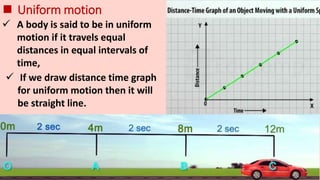
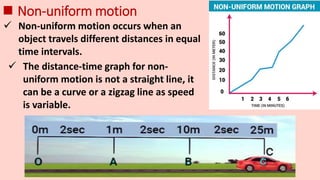
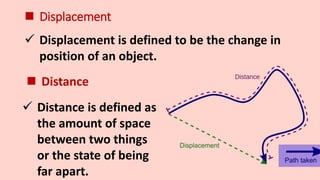
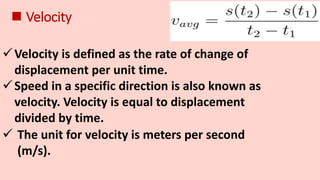
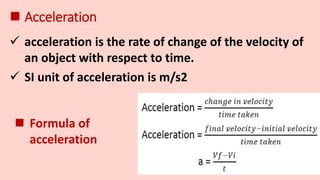
Motion refers to the phenomenon where an object changes position over time. It is described mathematically using terms like displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, speed, and time. Uniform motion occurs when an object travels equal distances in equal time intervals, resulting in a straight line on a distance-time graph. Non-uniform motion involves traveling different distances in equal times, shown as a curve on the graph. Key terms discussed include displacement as a change in position, speed as the rate of motion, velocity as speed in a direction, and acceleration as the rate of change of velocity over time. Uniform and non-uniform variations are described for acceleration as well.