Embed presentation
Downloaded 17 times

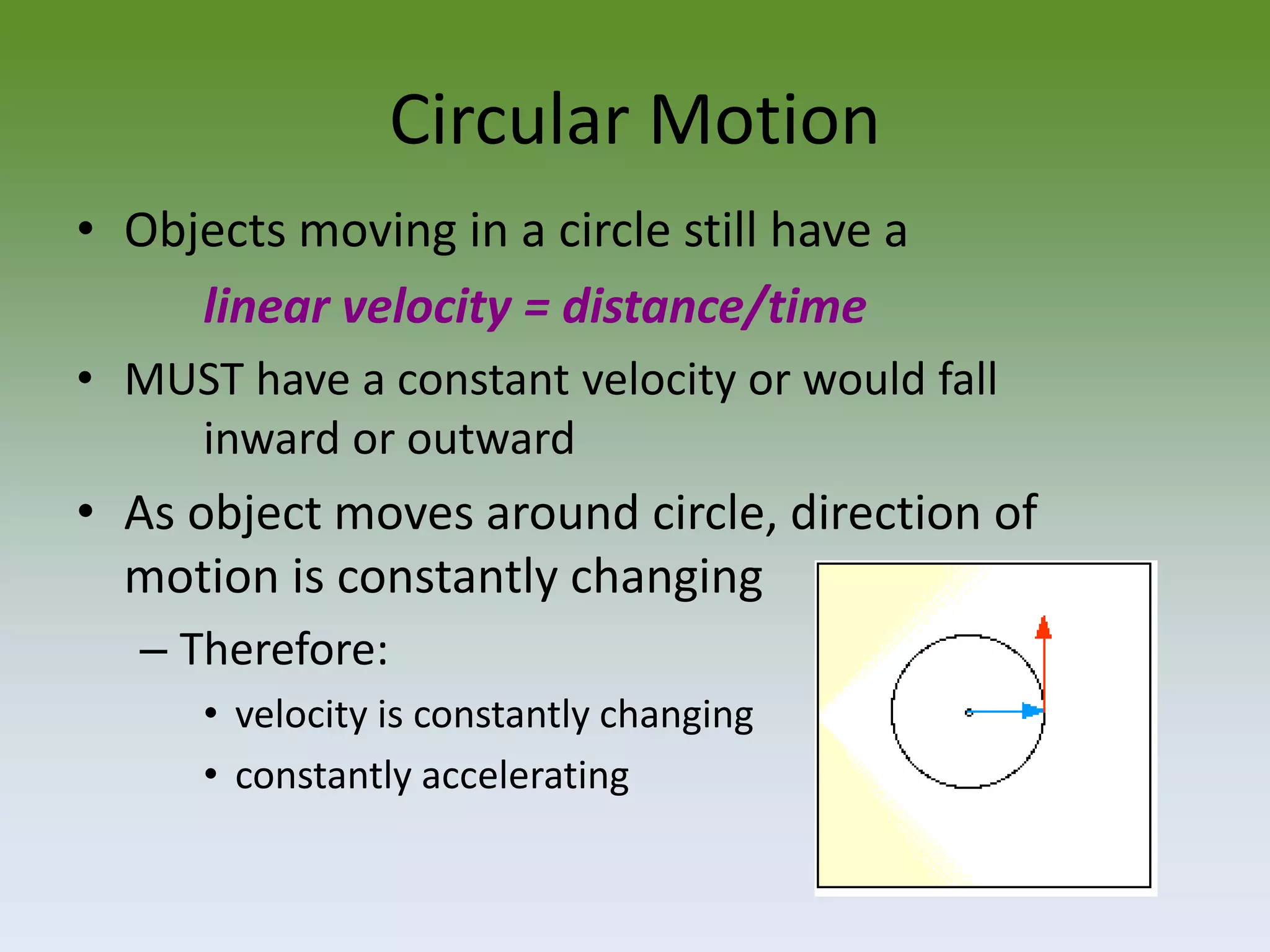


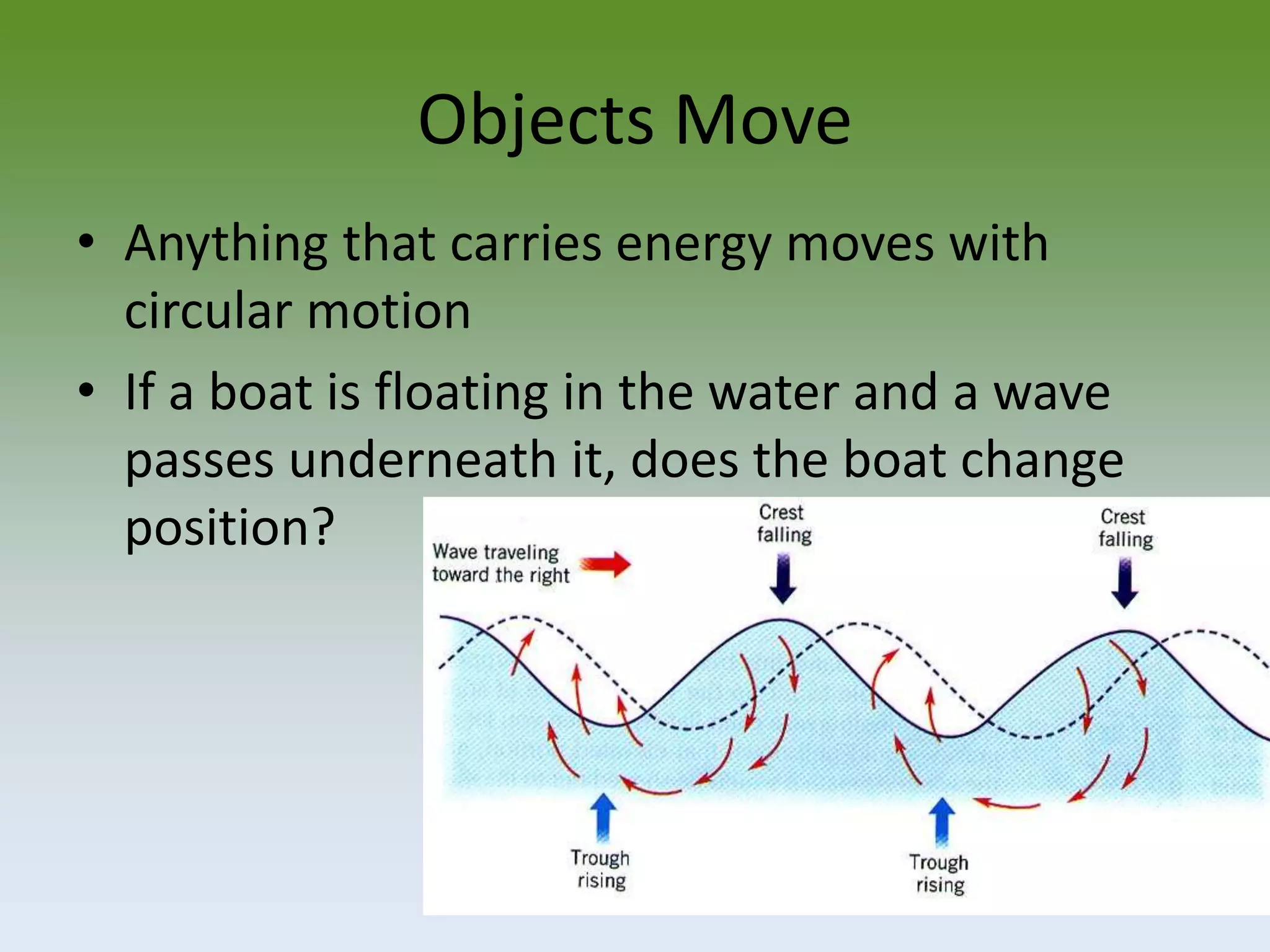
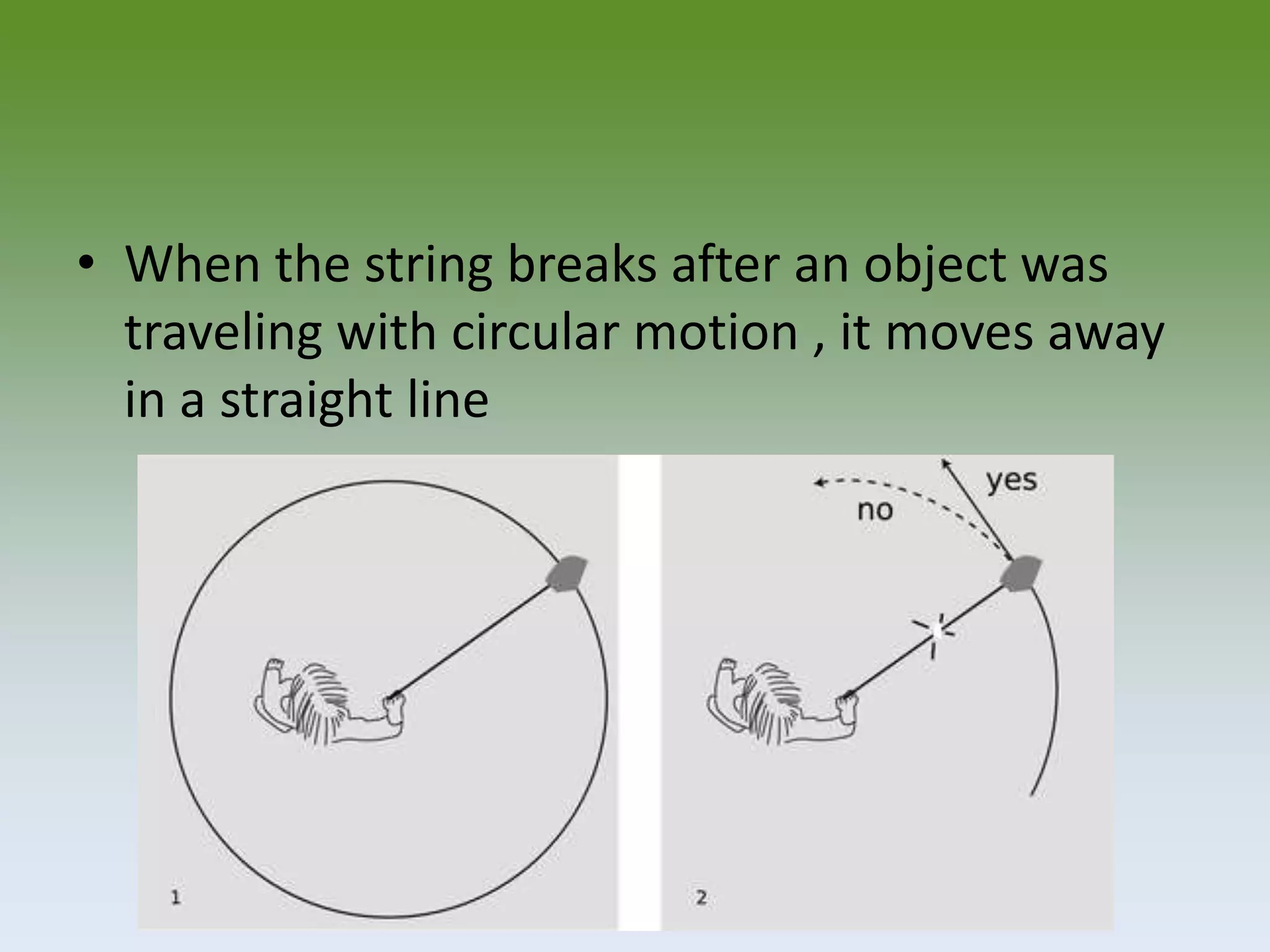
Objects moving in a circular path have a constant linear velocity but are constantly accelerating because their direction of motion is continuously changing. Centripetal acceleration points toward the center of the circle and depends on an object's speed and the radius of the circle. For an object to travel in a circular path, a net centripetal force pointing toward the center of the circle must be applied to overcome the object's inertia. Examples of circular motion include boats on waves, objects on strings, orbital motion of planets, and the rotation and revolution of Earth.







