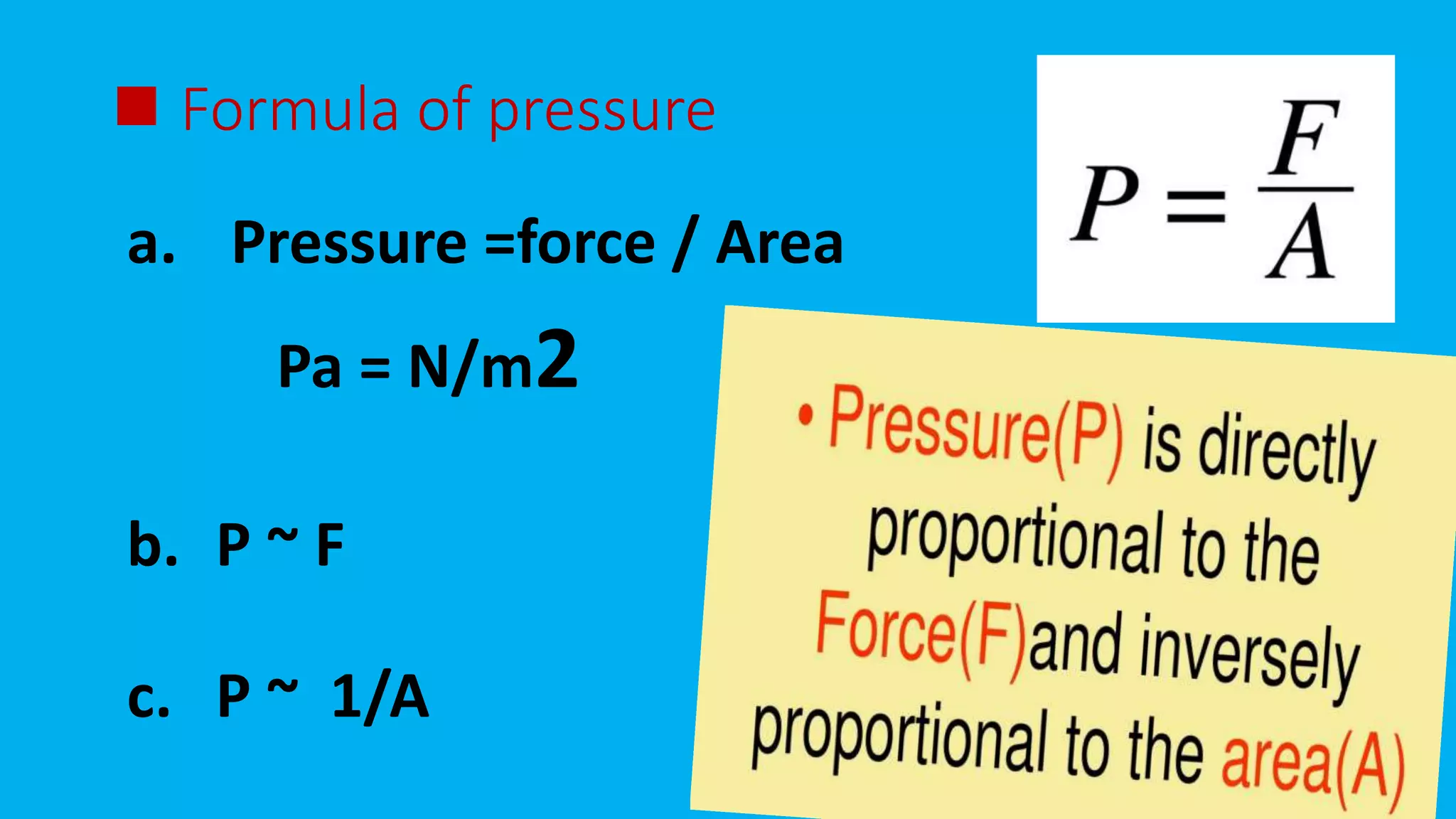
Pressure is defined as the force per unit area, with the formula f/a and measured in pascals. It varies based on the force and area involved, and fluid pressure is proportional to both the specific gravity and height of the fluid. Atmospheric pressure, which decreases with altitude, is typically measured with a barometer.