Embed presentation
Download to read offline



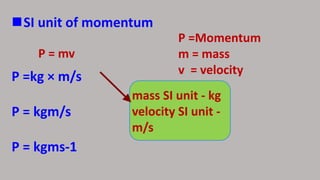



Momentum is defined as the product of a particle's mass and its velocity, and it is a vector quantity with both magnitude and direction. According to Newton's second law of motion, the rate of change of momentum is proportional to the force applied to the particle, and the formula for momentum is represented as p = mv. The SI unit for momentum is kg·m/s, emphasizing that momentum also has a directional component.






