Embed presentation
Downloaded 370 times








![Morphs, the actual forms used to realize
morphemes.
Example:
cats
[cat + (-s)]
bus
[bus + (-es)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/morphsandallomorphs-131120203352-phpapp02/85/Morphs-and-allomorphs-11-320.jpg)
![Allomorphs, any of the different forms of
a morpheme.
Example:
Past Tense: called [-d], talked [-t],
glided [-ed]
Morpheme: [-d]
Allomorphs /-d/ /-t/ /-ed/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/morphsandallomorphs-131120203352-phpapp02/85/Morphs-and-allomorphs-12-320.jpg)
![Example:
Plural Formation: desks [-s], cars [-z],
buses [-ez]
Morpheme: [-s]
Allomorphs /-s/ /-z/ /-ez/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/morphsandallomorphs-131120203352-phpapp02/85/Morphs-and-allomorphs-13-320.jpg)

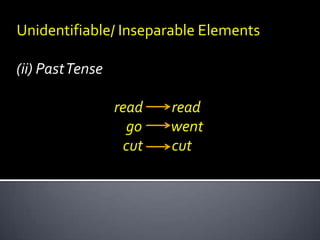
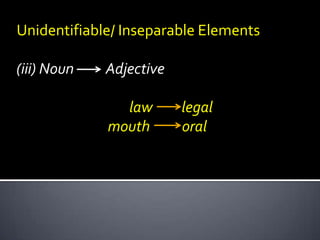
This document discusses morphological concepts including: - Inflectional morphemes change grammatical categories like number or tense, while derivational morphemes can change word class. - Affix order is important, with derivational suffixes coming before inflectional ones. - Some words have irregular or unidentifiable elements like plural sheep or past tense went. - Morphemes are realized through morphs, with allomorphs being variant forms of a single morpheme like plural -s, -z, or -es.










![Morphs, the actual forms used to realize
morphemes.
Example:
cats
[cat + (-s)]
bus
[bus + (-es)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/morphsandallomorphs-131120203352-phpapp02/85/Morphs-and-allomorphs-11-320.jpg)
![Allomorphs, any of the different forms of
a morpheme.
Example:
Past Tense: called [-d], talked [-t],
glided [-ed]
Morpheme: [-d]
Allomorphs /-d/ /-t/ /-ed/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/morphsandallomorphs-131120203352-phpapp02/85/Morphs-and-allomorphs-12-320.jpg)
![Example:
Plural Formation: desks [-s], cars [-z],
buses [-ez]
Morpheme: [-s]
Allomorphs /-s/ /-z/ /-ez/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/morphsandallomorphs-131120203352-phpapp02/85/Morphs-and-allomorphs-13-320.jpg)