1) Morphemes are the smallest units of meaning in morphology. They include both bound morphemes like suffixes and prefixes, as well as free morphemes like root words.
2) Morphemes can have allomorphs, where the same meaning unit has different phonological forms depending on context. Regular allomorphs are predictable, while irregular forms must be memorized.
3) The internal structure of words is analyzed by breaking words into their constituent morphemes. This reveals the meaning of complex words like "unlockable". Compounding also combines morphemes, and can create new words with ambiguous structures.







![Connections between Sound and
Meaning
• Remember that a phoneme sometimes has
more than one sound form, while being the
same abstract unit: /p/ with [p] and [ph]
• A related thing happens with morphemes as
well
• In order to see this, we have to look at slightly
more complex cases](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/morphologicalstructure-190914193709/85/Morphological-structure-8-320.jpg)
![Morphemes and Allomorphs
• We will say in some cases that a morpheme has
more than one allomorph
• This happens when the same meaning unit like [past]
for past tense or [pl] for plural has more than one
sound form
– Past: one feature [past]
• kick / kick-ed
• leave / lef-t
• hit / hit-Ø
• The last example shows a case in which the
phonological form of the morpheme past is zero, i.e.
it is not pronounced](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/morphologicalstructure-190914193709/85/Morphological-structure-9-320.jpg)
![Allomorphy, cont.
• In the case of phonology, we said that the different
allophones of a phoneme are part of the same
phoneme, but are found in particular contexts
• The same is true of the different allomorphs of a
morpheme
• Which allomorph of a morpheme is found depends on
its context; in this case, what it is attached to:
– Example: consider [pl] for English plural. It normally has the
pronunciation –s (i.e. /z/), but
• moose / moose- Ø
• ox / ox-en
• box/*box-en/box-es
• So, the special allomorphs depend on the noun](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/morphologicalstructure-190914193709/85/Morphological-structure-10-320.jpg)





![Content and Function Words
Another distinction:
• Content Morphemes: morphemes that have a
referential function that is independent of
grammatical structure; e.g. dog, kick, etc.
– Sometimes these are called “open-class” because speakers
can add to this class at will
• Function morphemes: morphemes that are bits of
syntactic structure– e.g. prepositions, or morphemes
that express grammatical notions like [past] for past
tense.
– Sometimes called “closed-class” because speakers cannot
add to this class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/morphologicalstructure-190914193709/85/Morphological-structure-16-320.jpg)





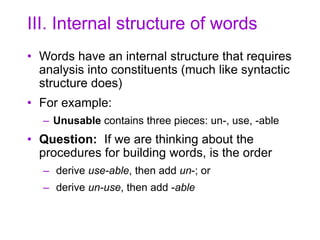
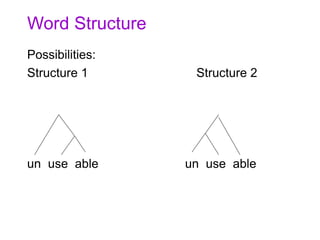
![Word Structure, Cont.
• Consider:
– With –able, we create adjectives meaning
‘capable of being V-ed’, from verbs V
• Break/break-able; kick/kick-able
– There is no verb un-use
– This is an argument that Structure 1 is correct:
[un [use able]]
– This analysis fits well with what the word means
as well: not capable of being used. Structure two
would mean some thing like ‘capable of not being
used’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/morphologicalstructure-190914193709/85/Morphological-structure-24-320.jpg)

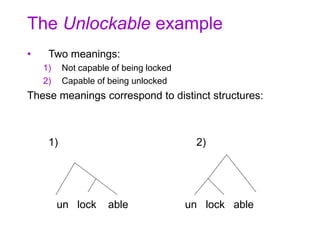



![Internal structure
• Like with other complex words, the internal
structure of compounds is crucial
• There are cases of ambiguities like that with
unlockable
• Example: obscure document shredder
1) Person who shreds obscure documents
[[obscure document] shredder]
2) Obscure person who shreds documents
[obscure [document shredder]]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/morphologicalstructure-190914193709/85/Morphological-structure-30-320.jpg)
