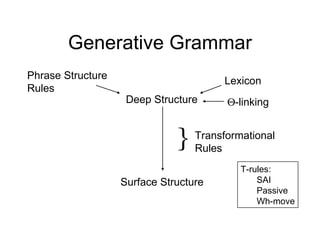
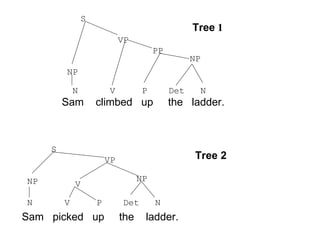
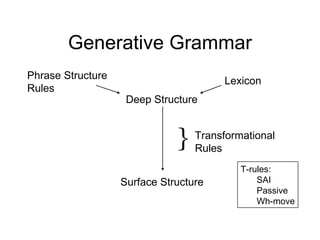
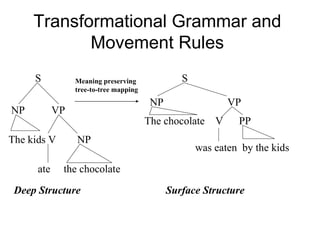
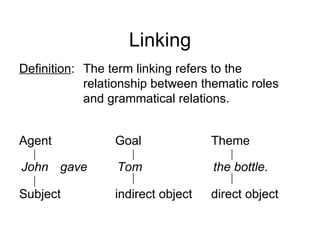
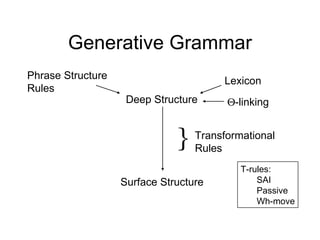
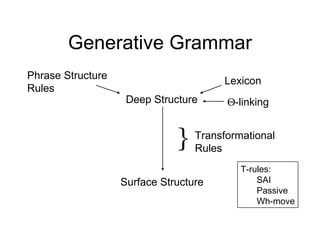
The document discusses several topics in generative grammar including phrase structure rules, transformational rules like passive and wh-movement, theta roles, and particle shift. It provides examples and definitions of concepts like deep structure, surface structure, subjects playing different semantic roles, and constraints on transformations like the passive requiring an object that is a patient.


![Subcategorization frames Verbs come in different flavors: V i : The woman walked V t : John loves Mary V dt : Mary gave Peter flowers V s : I know that she likes you This can be expressed as a kind of frame associated with the lexical entry for each verb: walked , V i , [ ___ ] love , V t , [ ___ NP] put , V dt , [ ___ NP NP] know , V s , [ ___ S]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntaxstylistics5-091104145615-phpapp02/85/Syntax-Stylistics5-4-320.jpg)
![Connecting PS and V frames S NP VP V put [ ___ NP PP] the The boys PP P NP on the porch NP dinner The frame puts selectional restrictions on where a particular verb can appear.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntaxstylistics5-091104145615-phpapp02/85/Syntax-Stylistics5-5-320.jpg)





















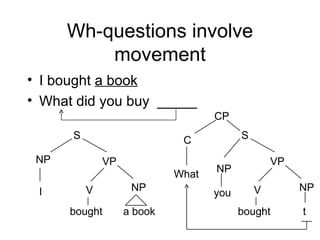
![Where from? What did you say [ was hit ______ ]? gets theta role here cf. John hit the ball Ends up here](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntaxstylistics5-091104145615-phpapp02/85/Syntax-Stylistics5-32-320.jpg)
![How Far away? What did you say Joel dreamed Kyra thought Ayla said [ was hit ______ ]? still gets theta role here](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntaxstylistics5-091104145615-phpapp02/85/Syntax-Stylistics5-33-320.jpg)