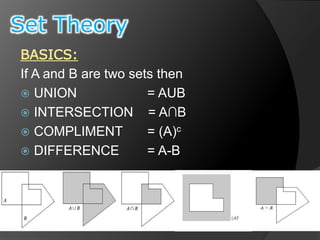
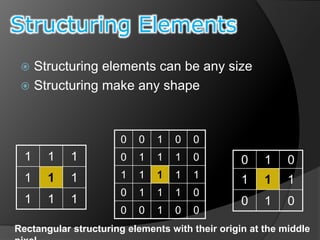
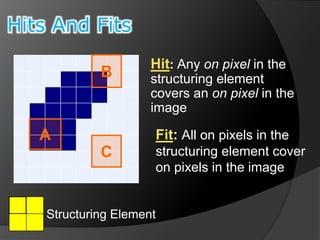
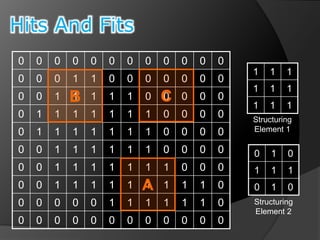
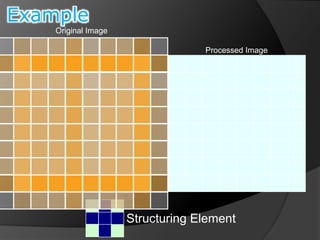
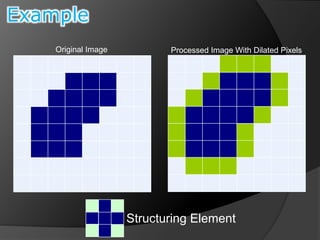
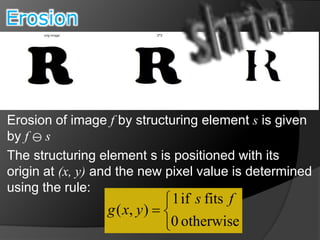
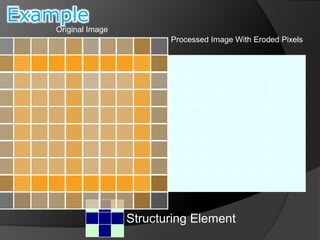
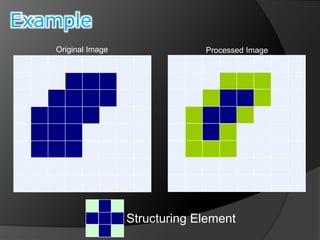
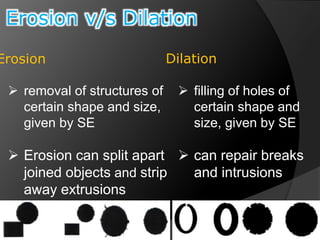
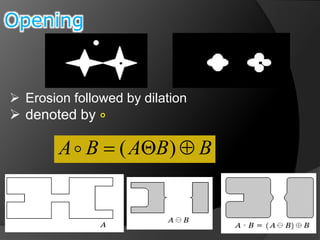
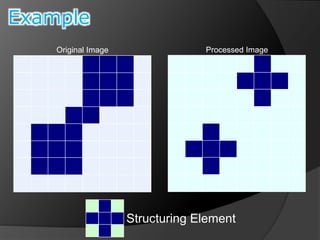
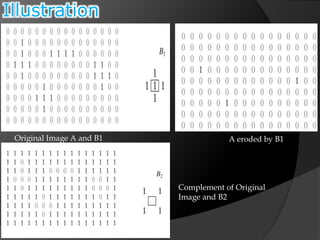
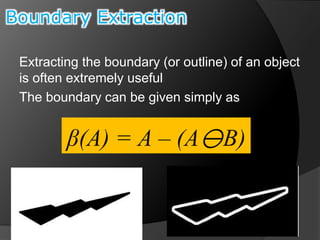
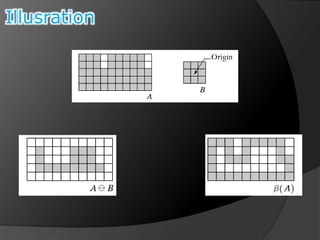
This document summarizes key concepts in morphological image processing including dilation, erosion, opening, closing, and hit-or-miss transformations. Morphological operations manipulate image shapes and structures using structuring elements based on set theory operations. Dilation adds pixels to the boundaries of objects in an image, while erosion removes pixels on object boundaries. Opening can remove noise and smooth object contours, while closing can fill in small holes and fill gaps in object shapes. Hit-or-miss transformations are used to detect specific patterns of on and off pixels. These operations form the basis for morphological algorithms like boundary extraction.