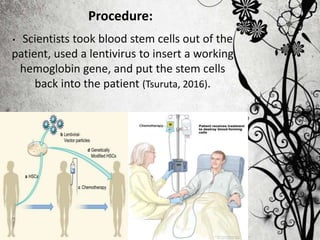
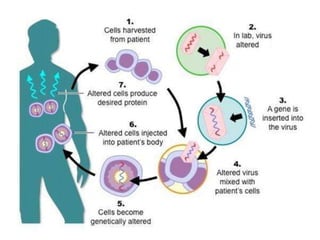
Thalassemia is a genetically transmitted blood disorder caused by mutations in genes that produce hemoglobin. It affects approximately 7% of the global population and causes 50,000 to 100,000 deaths annually. There are two primary types - alpha thalassemia affects alpha globin genes and beta thalassemia affects beta globin genes. Current treatments include blood transfusions, iron chelation therapy, and bone marrow transplants, but these have complications. Gene therapy is a promising new treatment that involves using a lentiviral vector to insert a normal globin gene into a patient's stem cells and could potentially cure thalassemia without lifelong treatments. The first successful human trial occurred in 2007 in France and showed sustained