Molecular chaperones are proteins that assist in the folding of other proteins but are not part of the final folded structure. They help prevent misfolding and aggregation of proteins. The first observations of molecular chaperones date back to the 1970s but their function was not fully understood until the 1980s and 1990s when it was discovered that they play a key role in protein folding and homeostasis. Molecular chaperones are found in all compartments of the cell where protein folding occurs and help protect proteins from misfolding, especially under stressful conditions.









![12
Group II
Group II chaperonins, found in the eukaryotic cytosol and in archaea, are more poorly
characterized.
TRiC (TCP-1 Ring Complex, also called CCT for chaperonin containing TCP-1), the eukaryotic
chaperonin, is composed of two rings of eight different though related subunits, each thought to
be represented once per eight-membered ring. TRiC was originally thought to fold only the
cytoskeletal proteins actin and tubulin but is now known to fold dozens of substrates.
Mm cpn (Methanococcus maripaludis chaperonin), found in the archaea Methanococcus
maripaludis, is composed of sixteen identical subunits (eight per ring). It has been shown to fold
the mitochondrial protein rhodanese; however, no natural substrates have yet been identified.[3]
Group II chaperonins are not thought to utilize a GroES-type cofactor to fold their substrates.
They instead contain a "built-in" lid that closes in an ATP-dependent manner to encapsulate its
substrate.
. Chaperones in prokaryotes and eukaryotes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/molecularchaperones-171022075539/85/Molecular-chaperones-13-320.jpg)


![16
The sign of ΔG depends on the signs of the changes in enthalpy (ΔH) and entropy (ΔS), as well
as on the absolute temperature (T, in kelvin). Notice that ΔG changes from positive to negative
(or vice versa) where T = ΔH/ΔS.
When ΔG is negative,
The process or chemical reaction proceeds spontaneously in the forward direction.
When ΔG is positive, the process proceeds spontaneously in reverse.
When ΔG is zero, the process is already in equilibrium, with no net change taking place over
time.
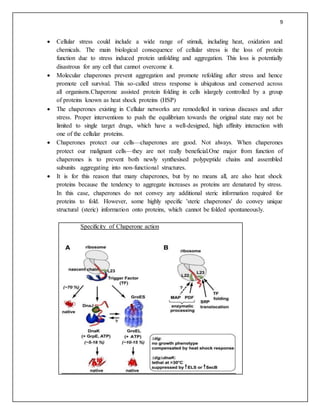
In molecular biology, molecular chaperones are proteins that assist the non-covalent folding or
unfolding and the assembly or disassembly of other macromolecular structures. Chaperones are
not present when the macromolecules perform their normal biological functions and have
correctly completed the processes of folding and/or assembly. The common perception that
chaperones are concerned primarily with protein folding is incorrect. The first protein to be
called a chaperone assists the assembly of nucleosomes from folded histones and DNA and such
assembly chaperones, especially in the nucleus, are concerned with the assembly of folded
subunits into oligomeric structures.
Example
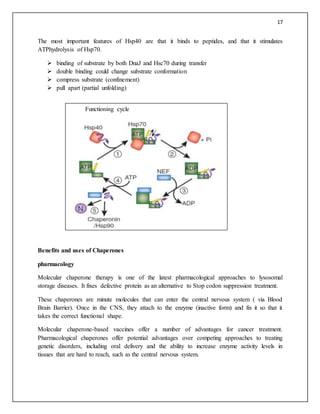
The Hsp70 System
The Hsp70 proteins constitute the central part of an ubiquitous chaperone system that is present
in most compartments of eukaryotic cells, in eubacteria, and in many archaea.
Hsp70 is comprised of two functional entities: an N-terminal ATPase domain, and a smaller C-
terminal peptide-binding domain.
Hsp70 proteins are involved in a wide range of cellular processes, including protein folding and
degradation of unstable proteins The common function of Hsp70 in these processes appears to be
the binding of short hydrophobic segments in partially folded polypeptides, thereby preventing
aggregation and arresting the folding process DnaK and many other Hsp70 chaperones interact
in vivo with two classes of partner proteins that regulate critical steps of its functional cycle,
Partner Proteins of Hsp70–Modulation of the Functional Cycle
Hsp40 belongs to a diverse class of proteins that consist of multiple functional domains. One of
the domains, the amino-acid J domain, is conserved in all Hsp40 chaperones. Mutational
analysis revealed that this domain is essential forthe interaction between Hsp40 and Hsp70.[82]
Its name is derived from DnaJ, the Hsp40 protein from E. coli that cooperates with DnaK.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/molecularchaperones-171022075539/85/Molecular-chaperones-17-320.jpg)