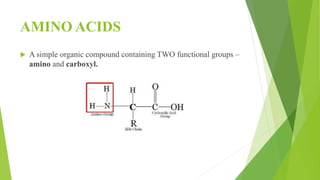
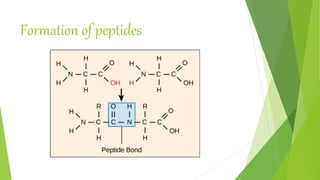
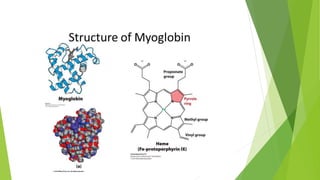
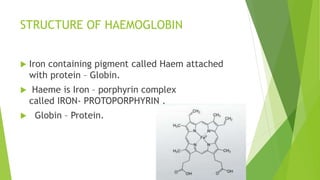
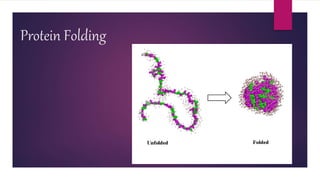
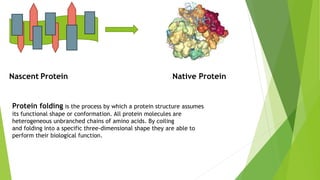
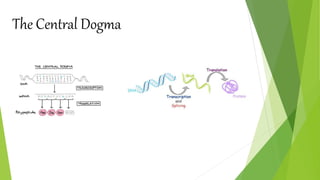
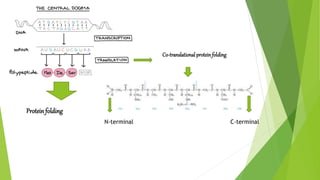
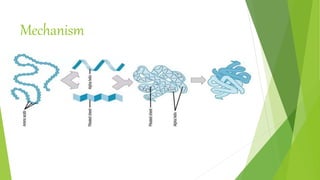
1. Proteins are complex organic macromolecules composed of amino acids arranged in a linear chain. They fold into complex three-dimensional shapes determined by their amino acid sequence.
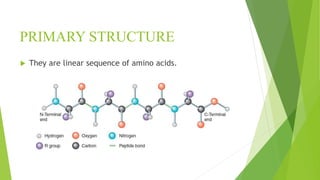
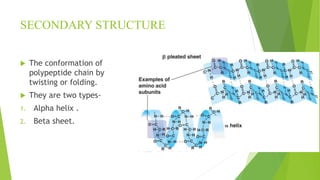
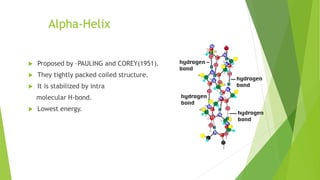
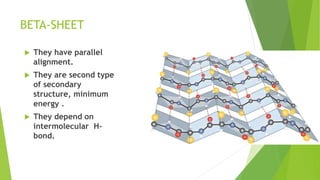
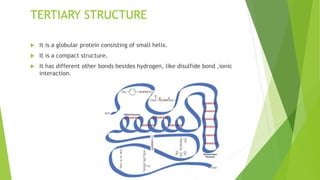
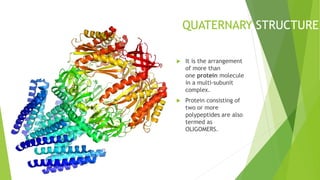
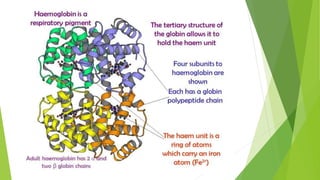
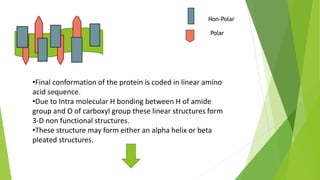
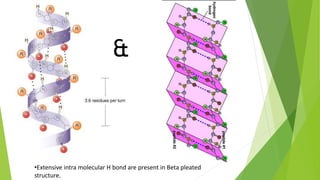
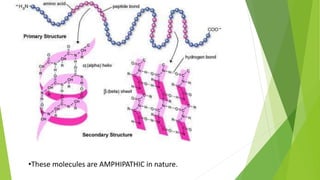
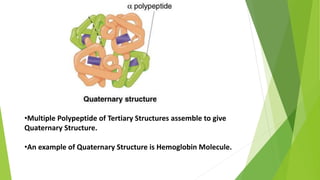
2. There are four levels of protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. Secondary structures include alpha helices and beta sheets formed by hydrogen bonding. Tertiary structure involves folding into a compact 3D shape.
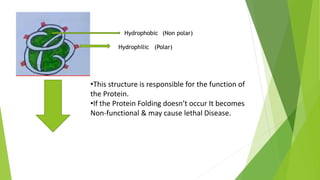
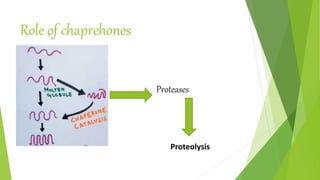
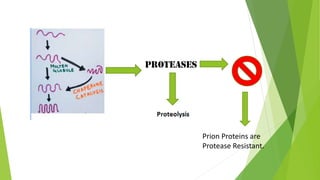
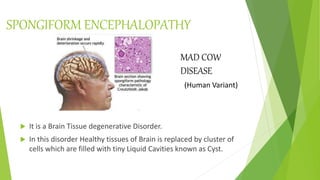
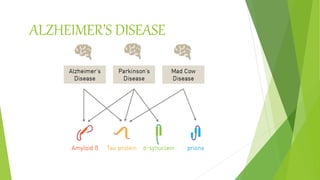
3. Misfolding of proteins can cause neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and prion diseases. Chaperone proteins assist the normal folding process to prevent misfolding.