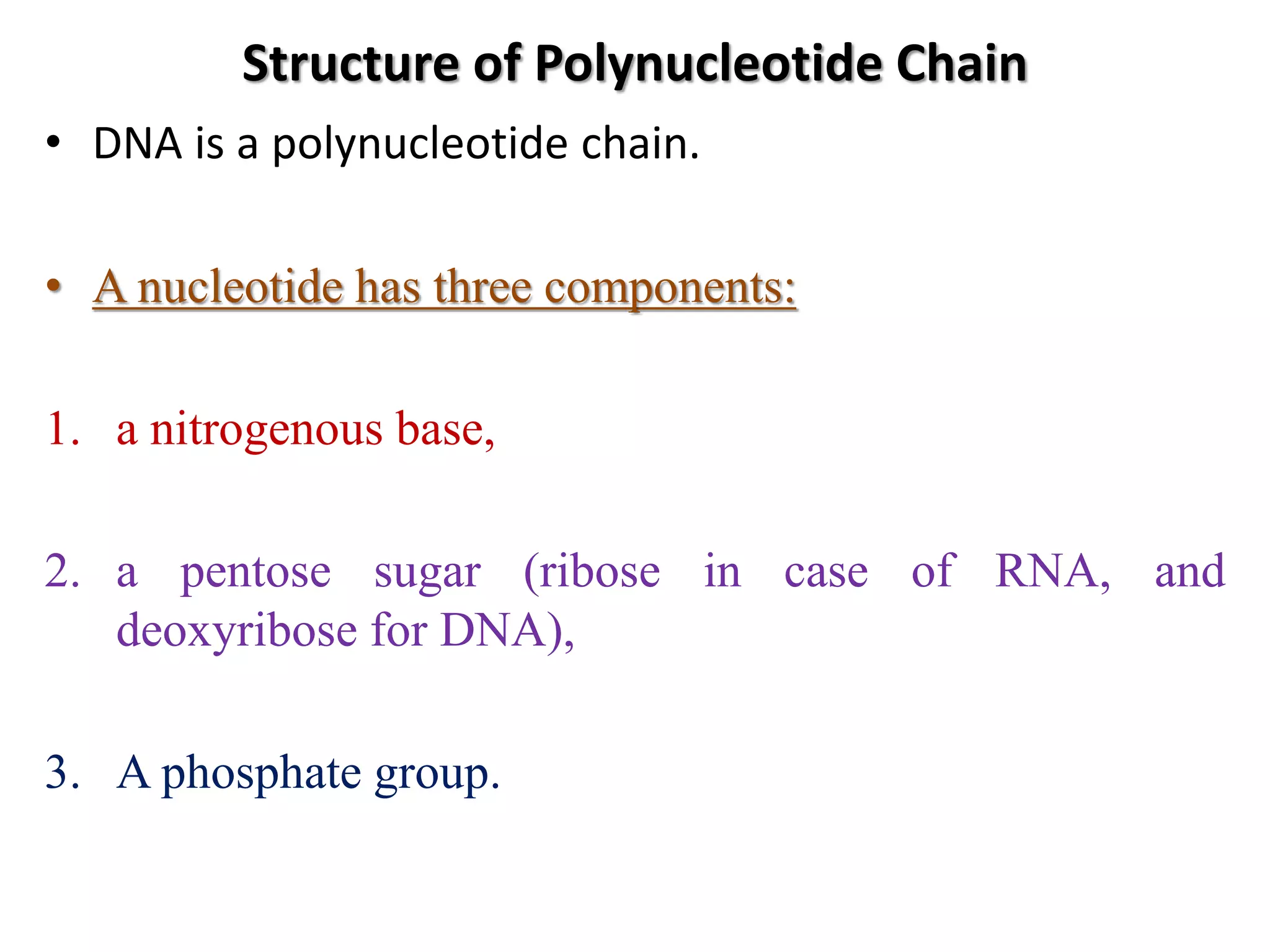
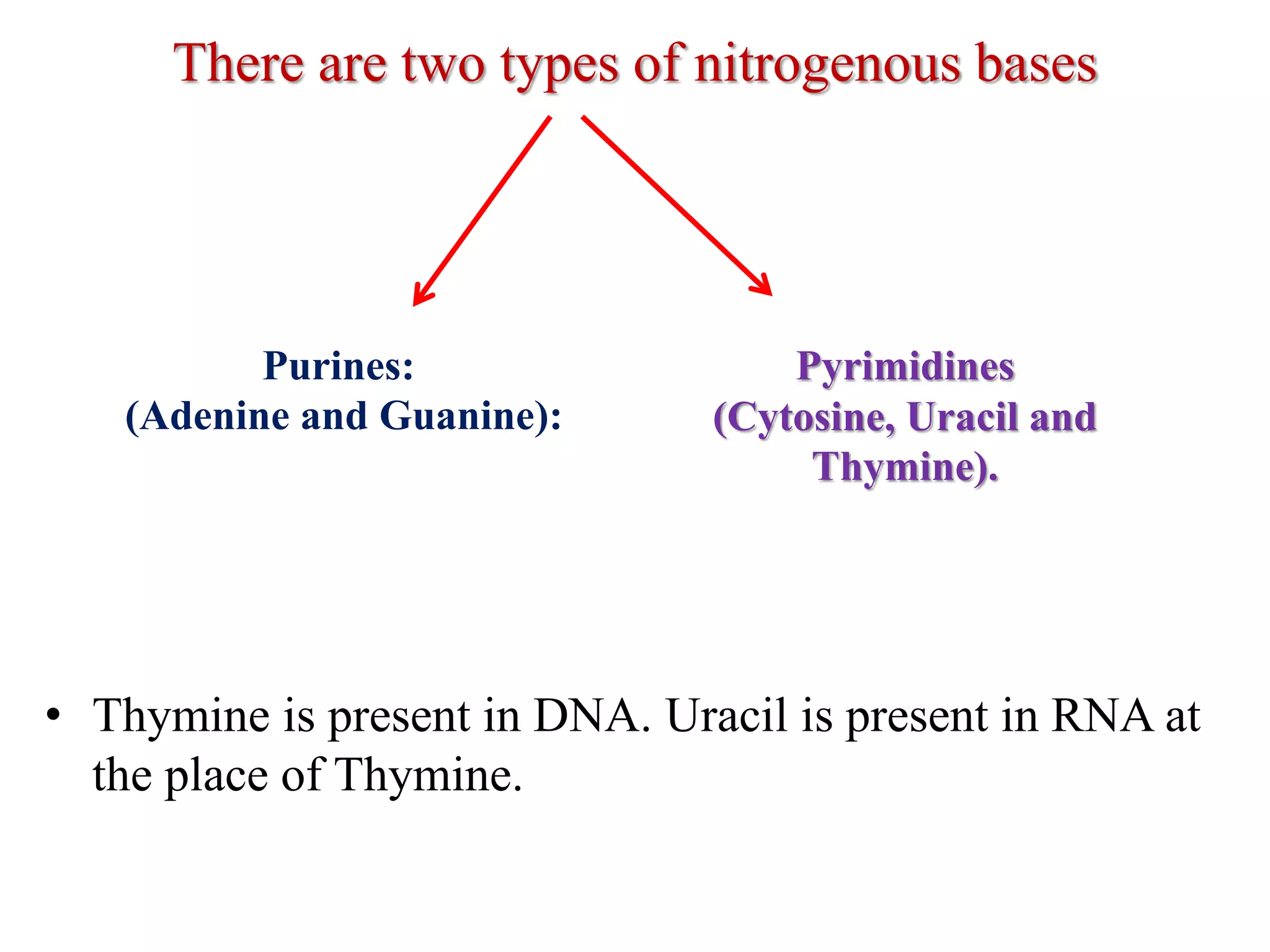
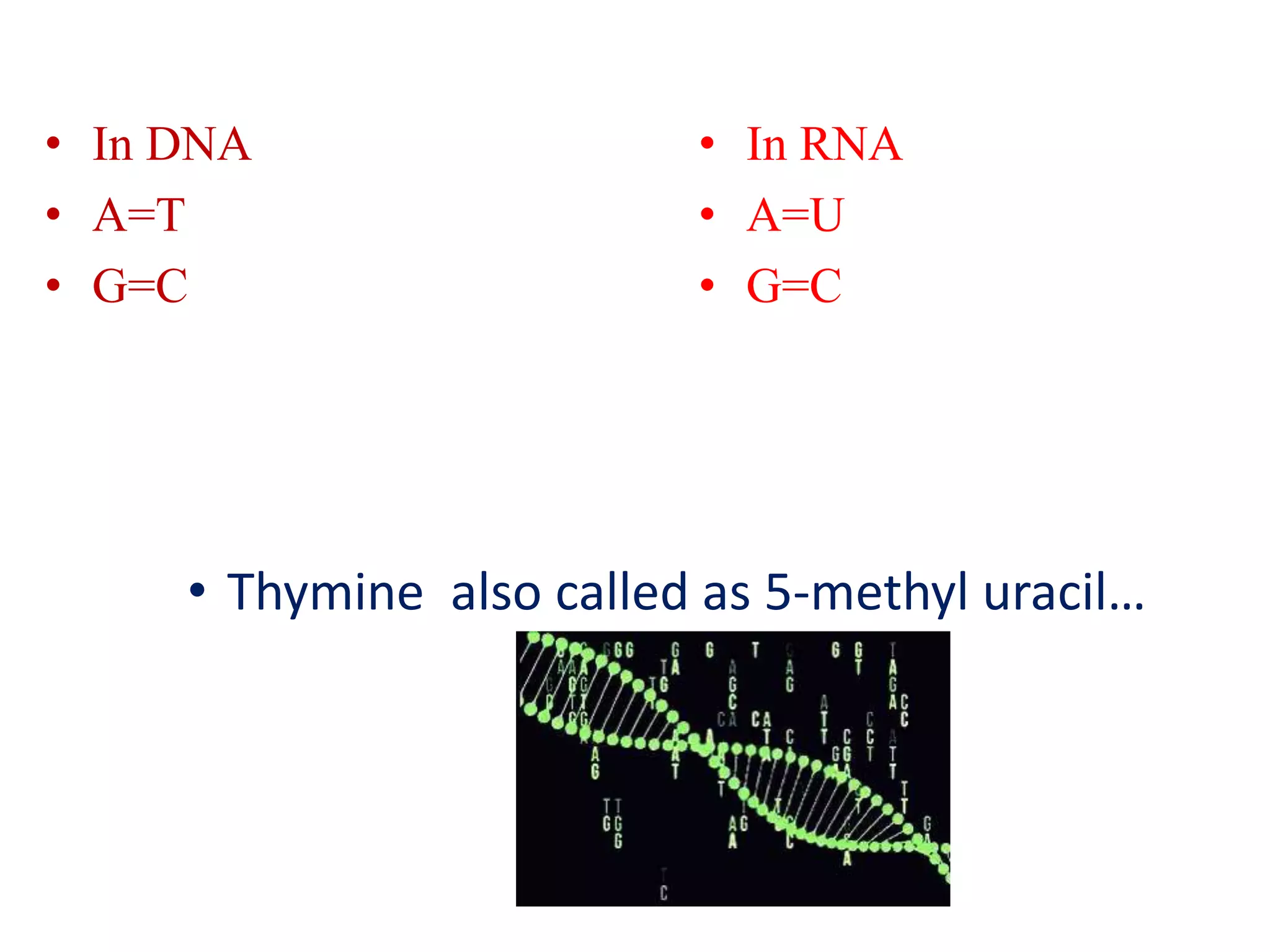
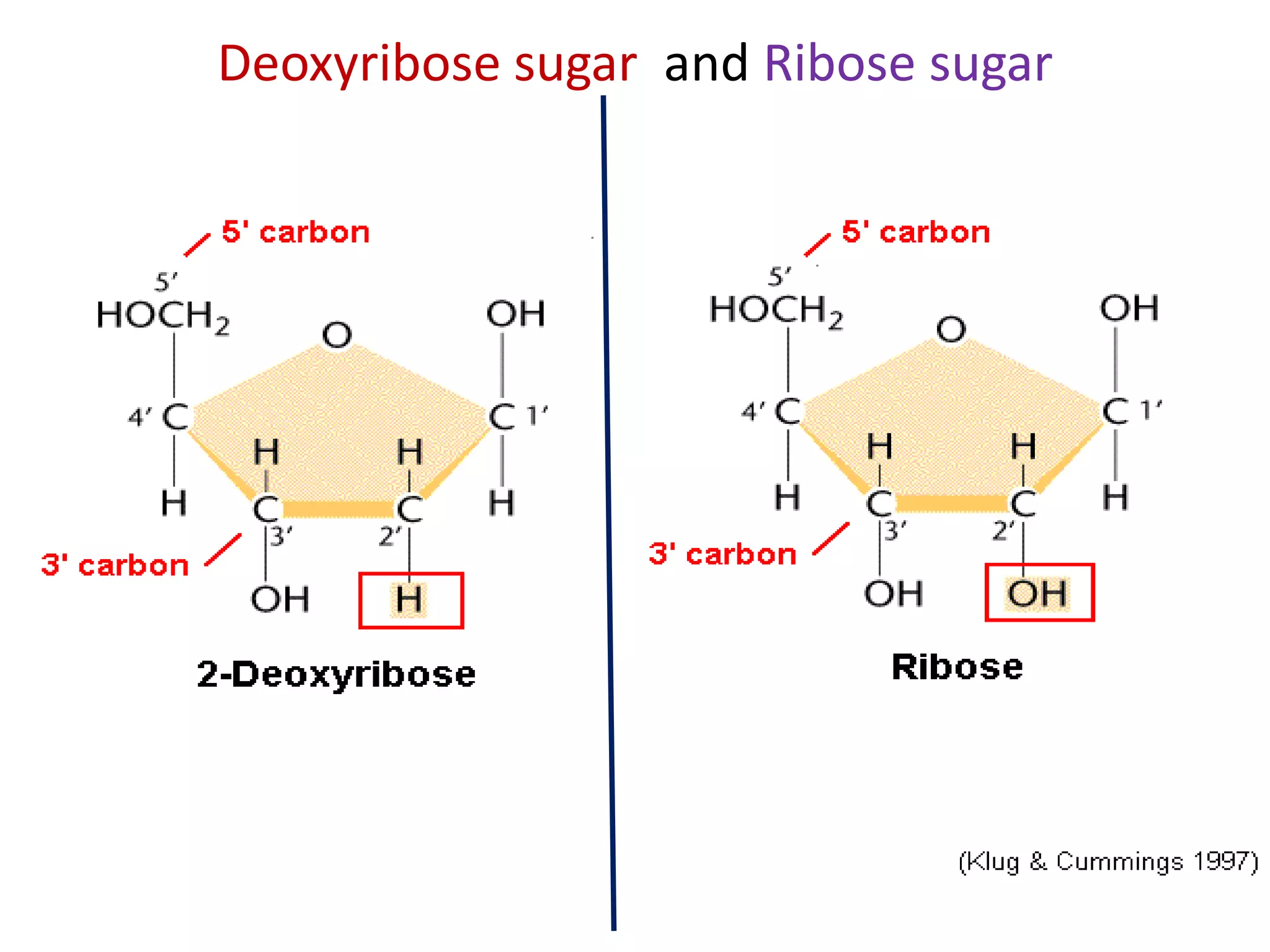
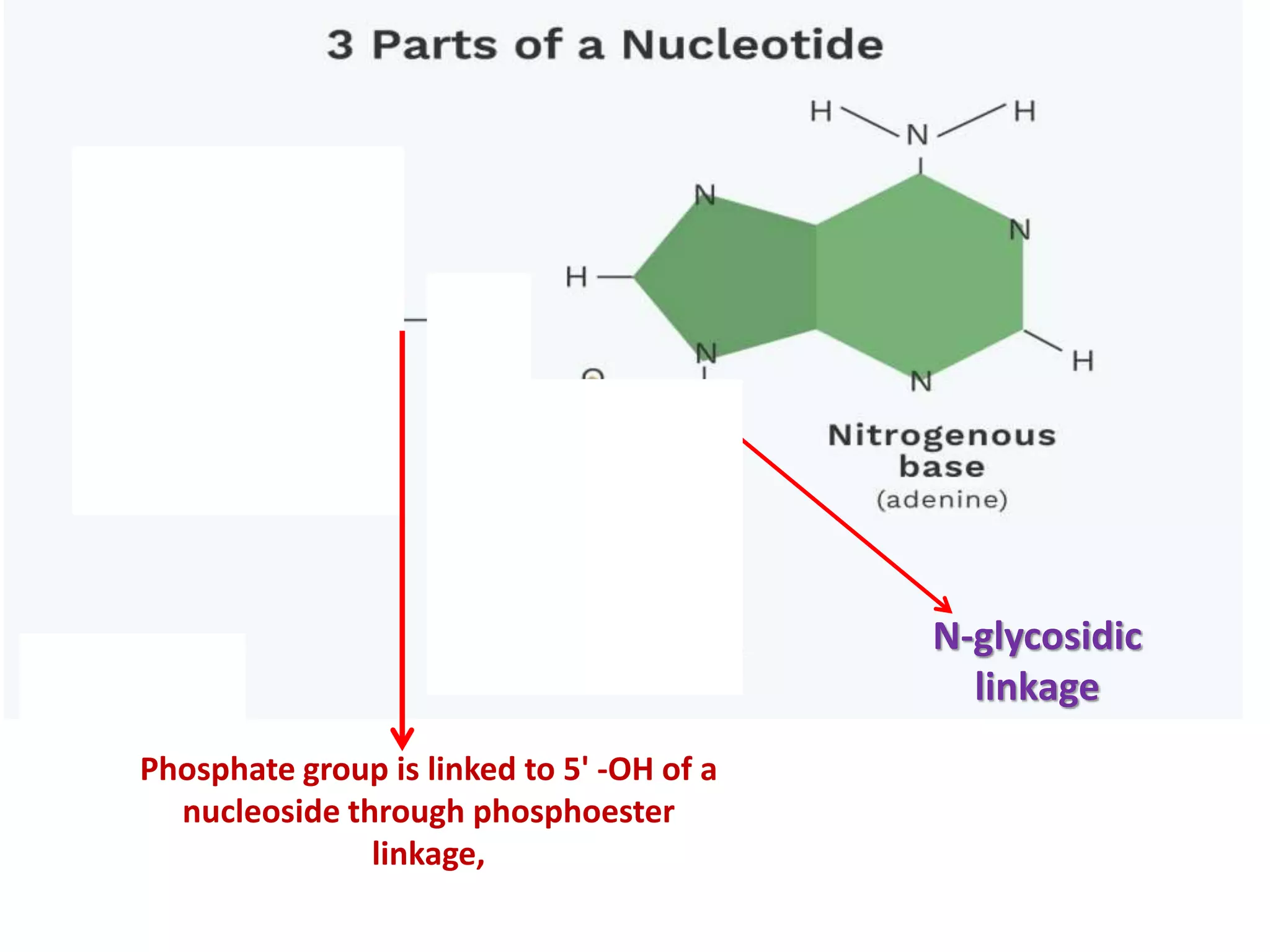
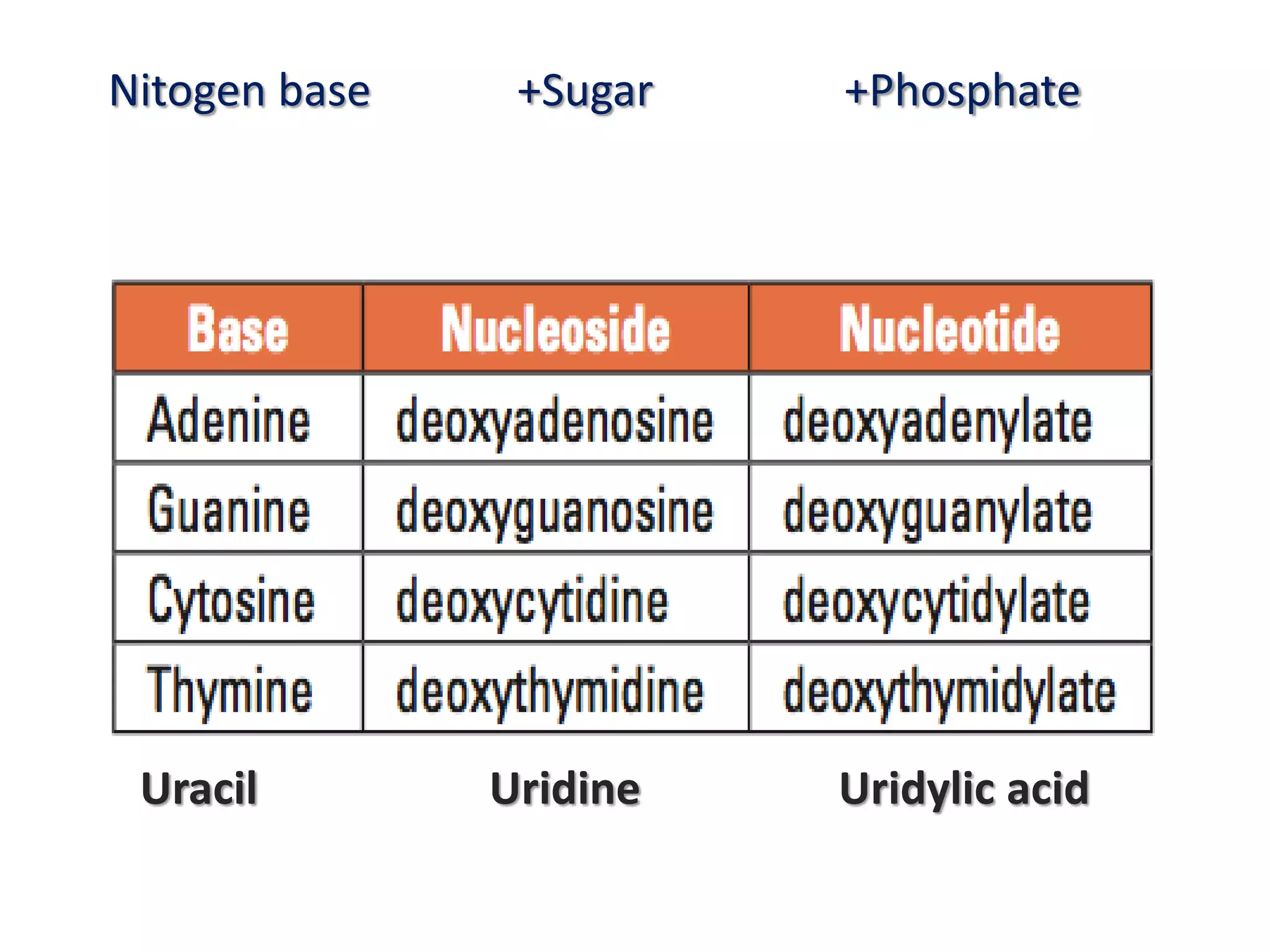
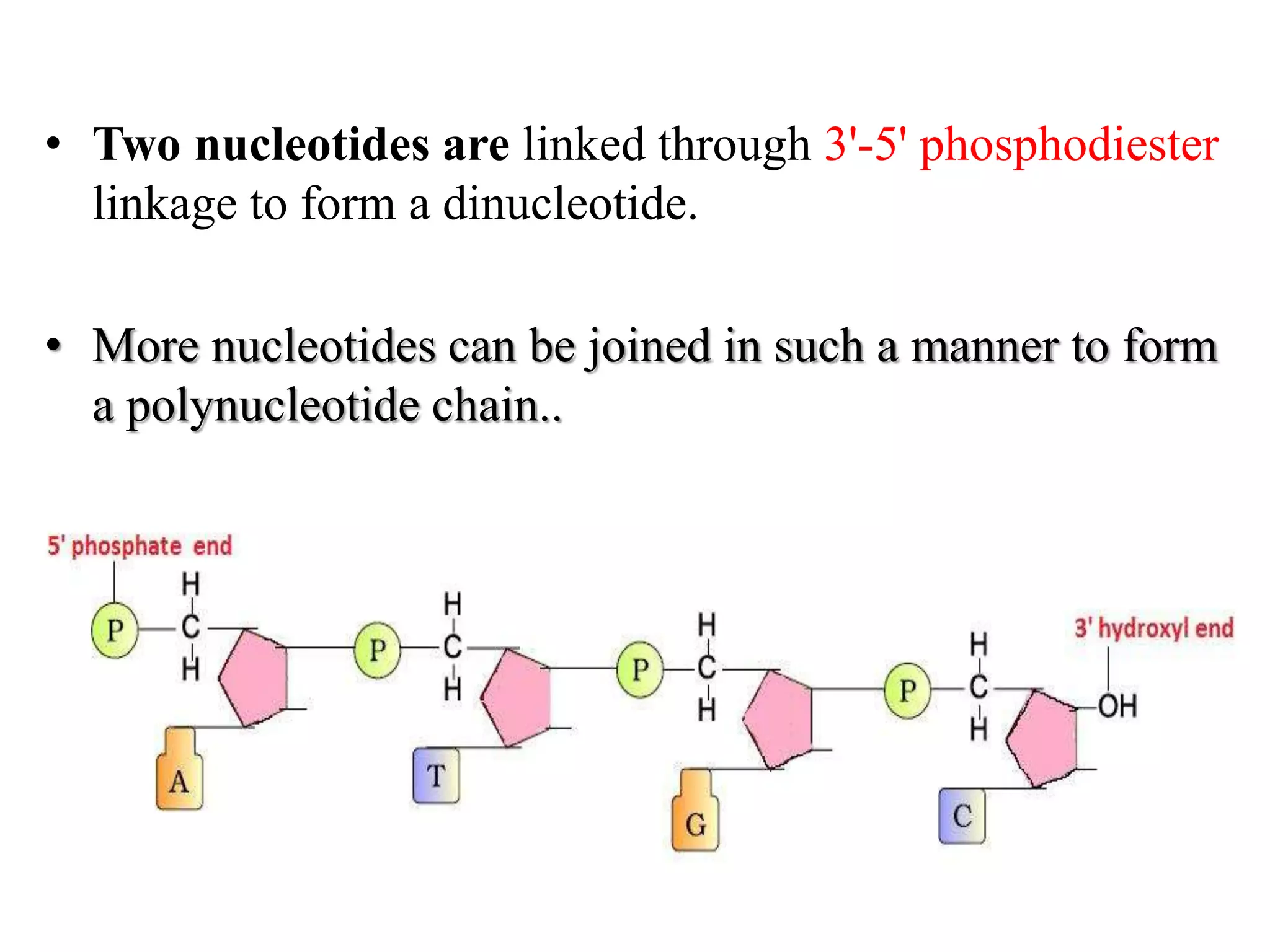
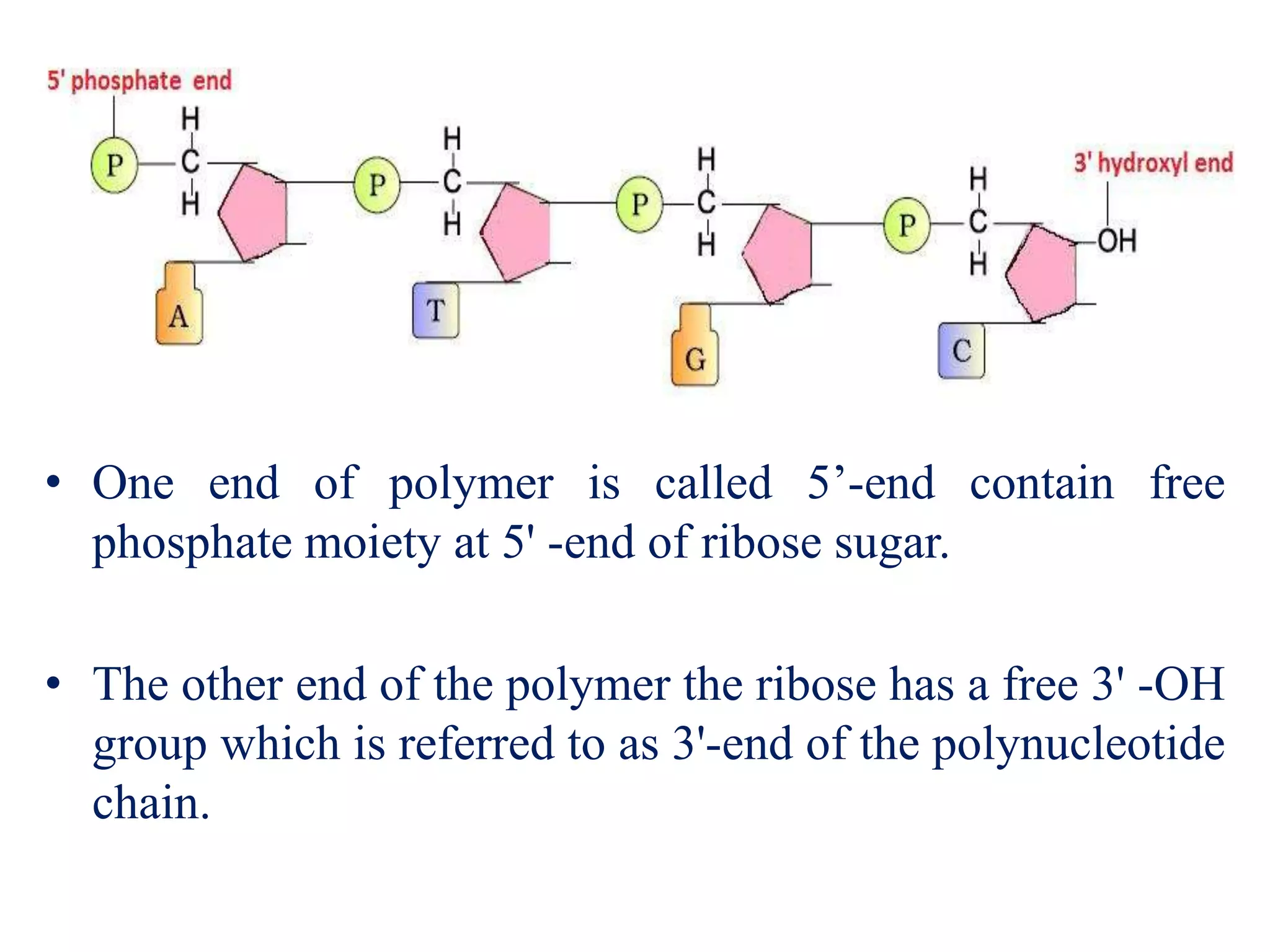
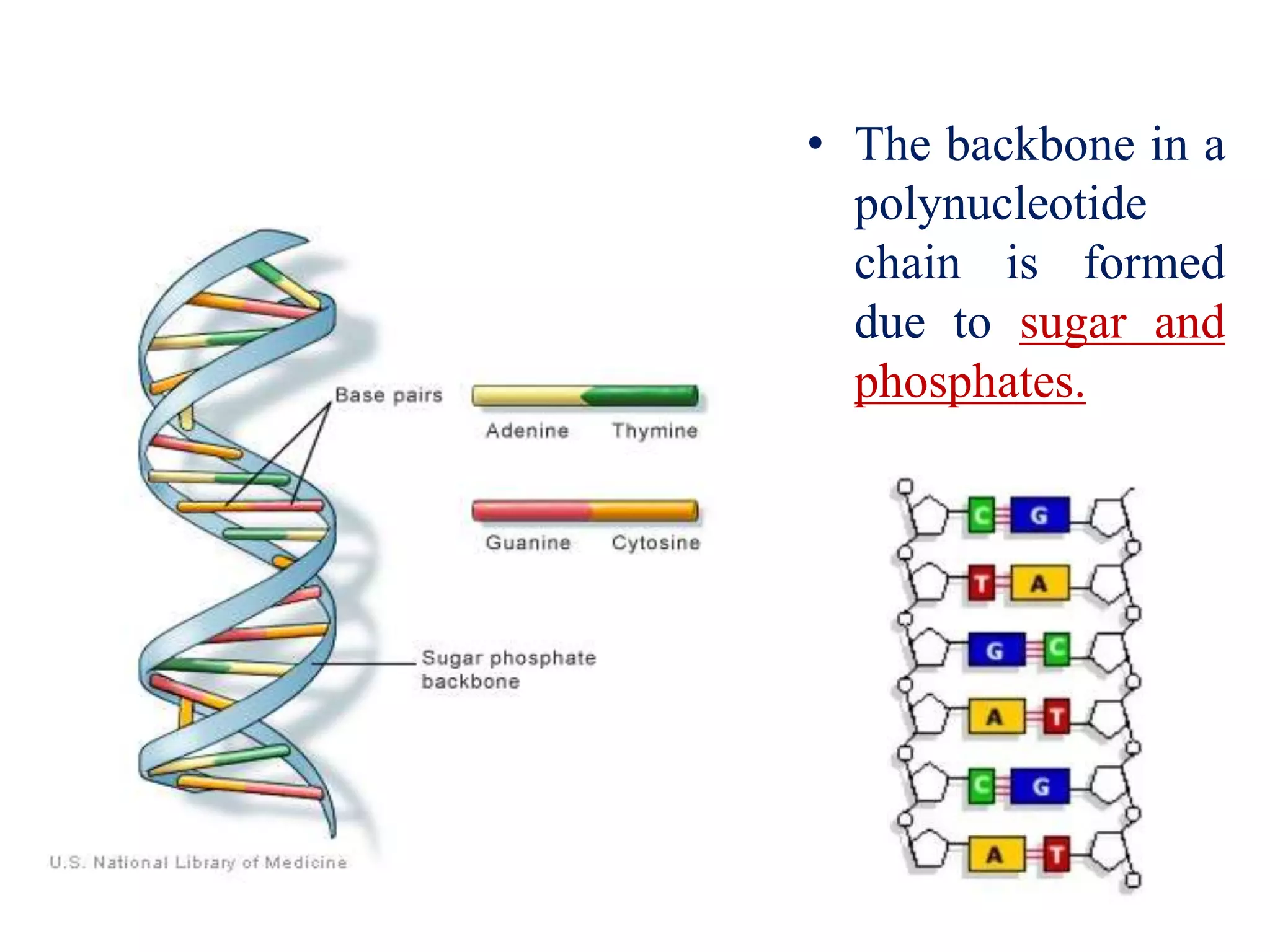
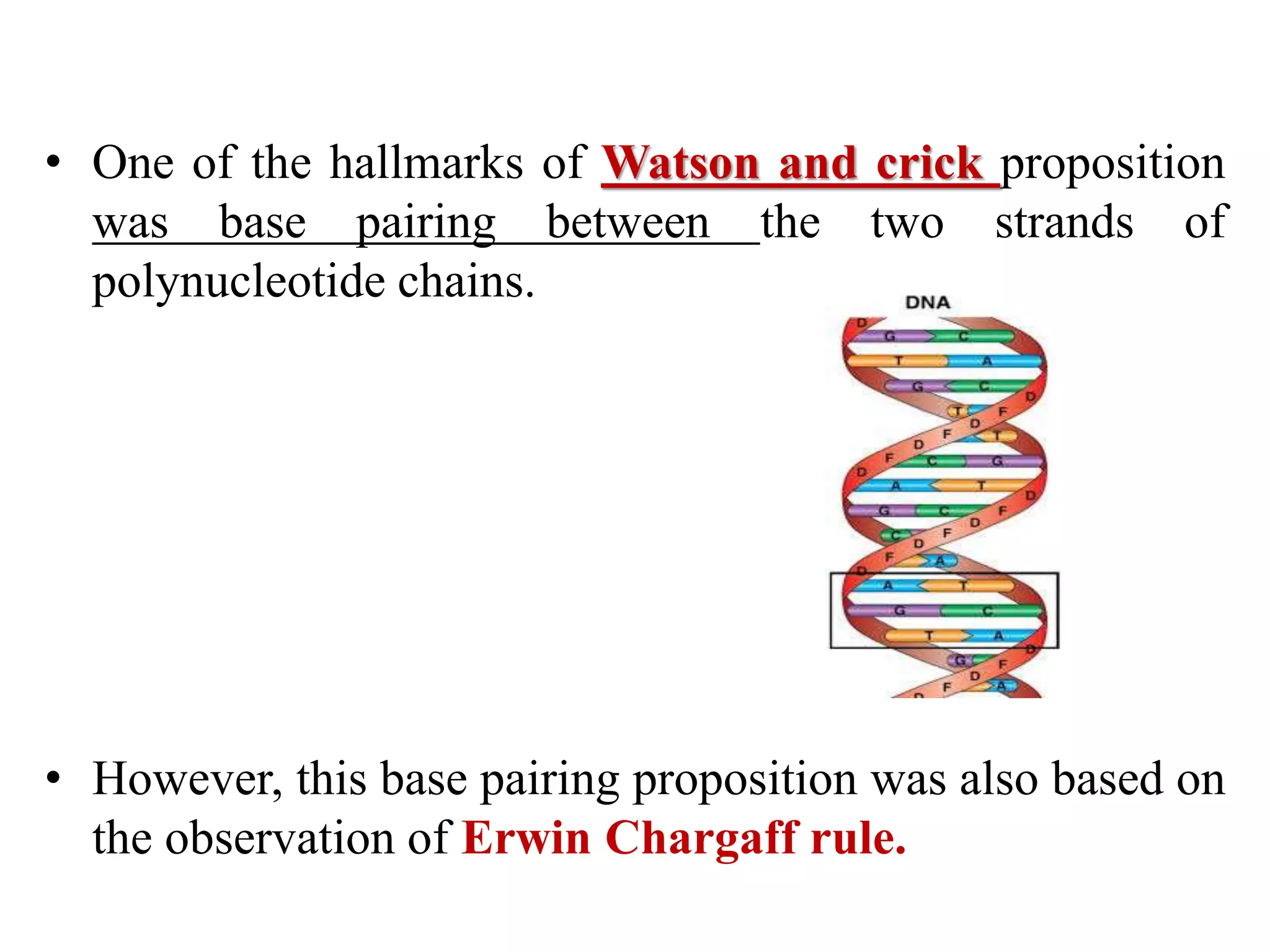
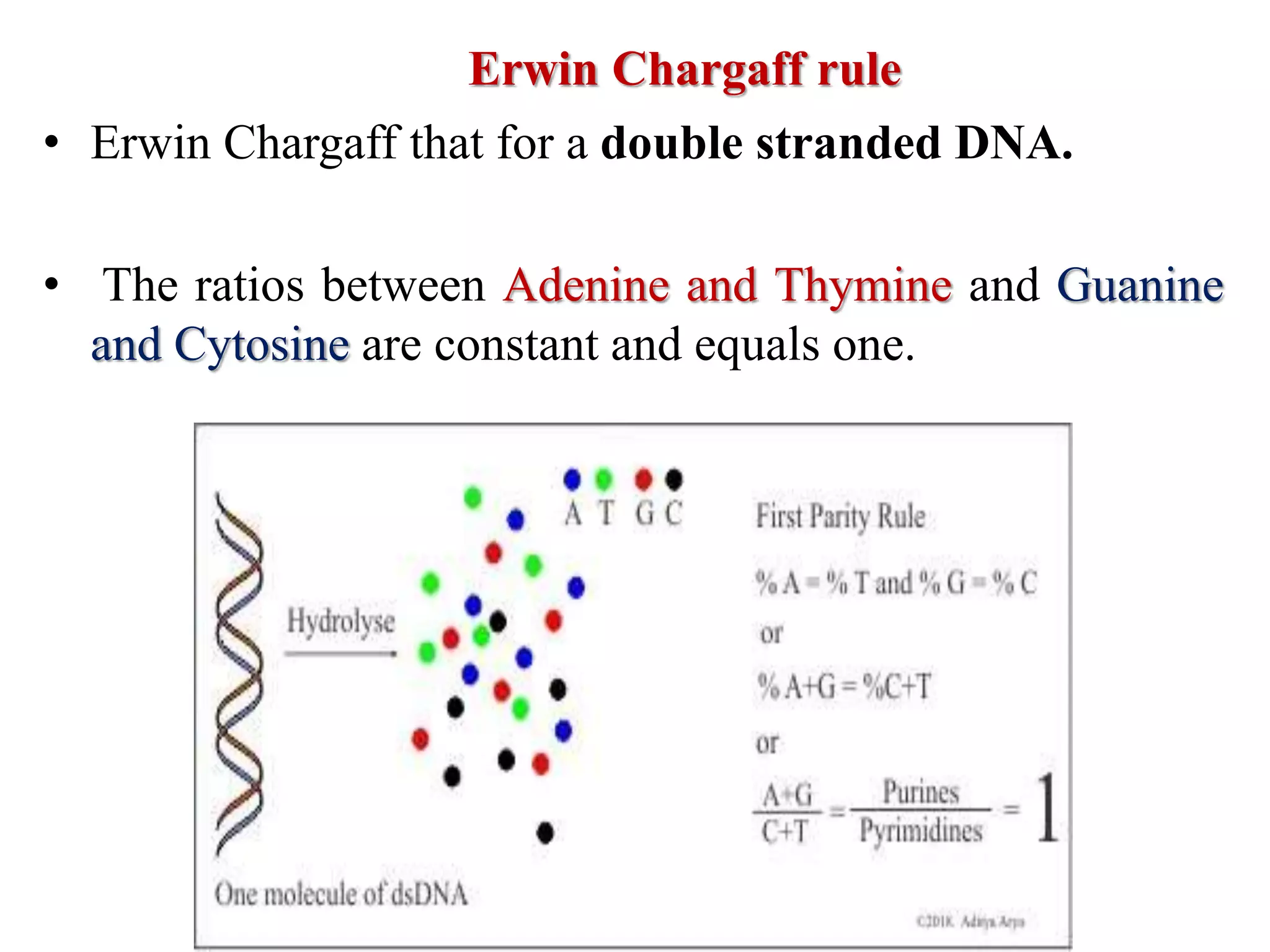
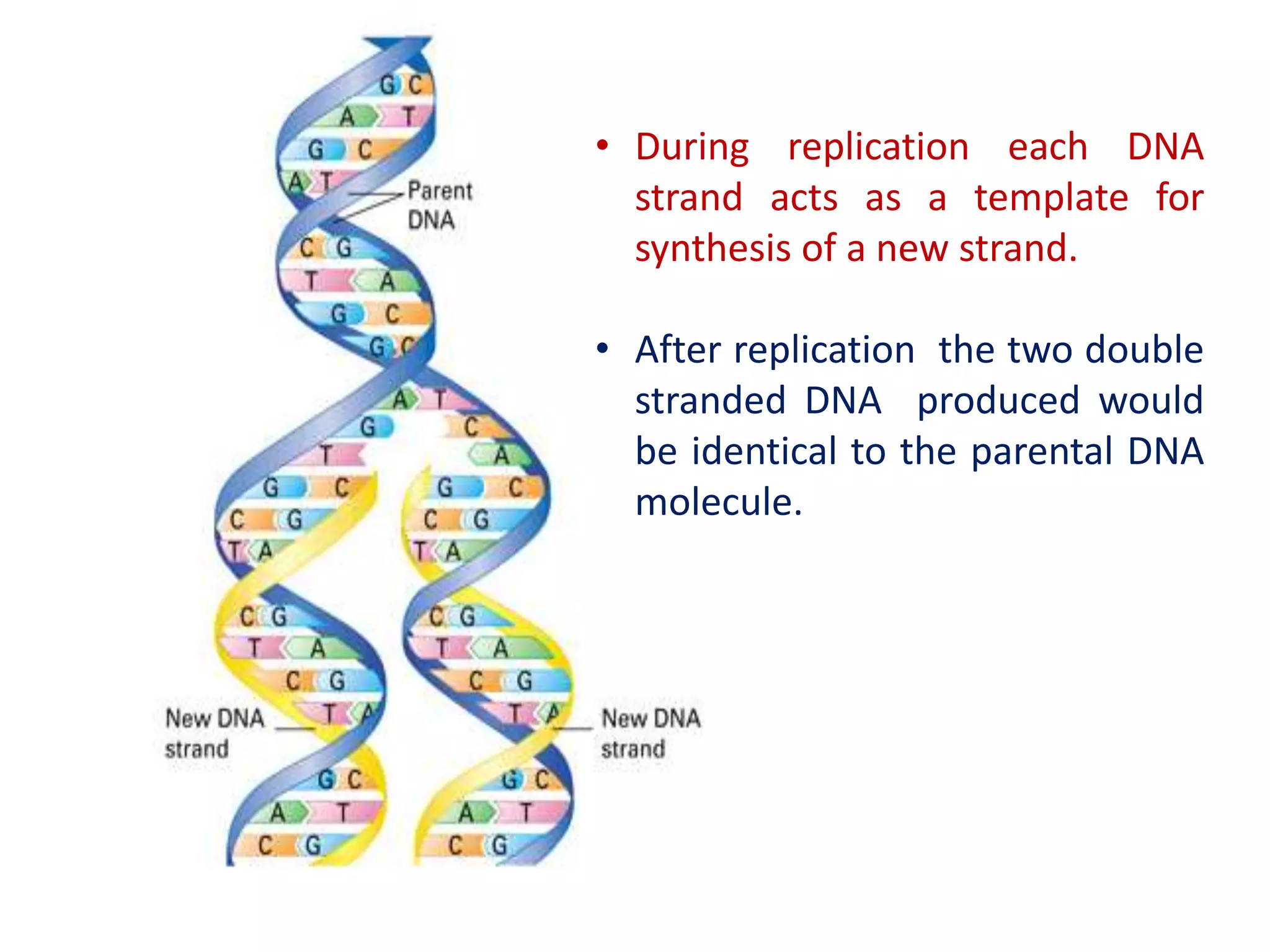
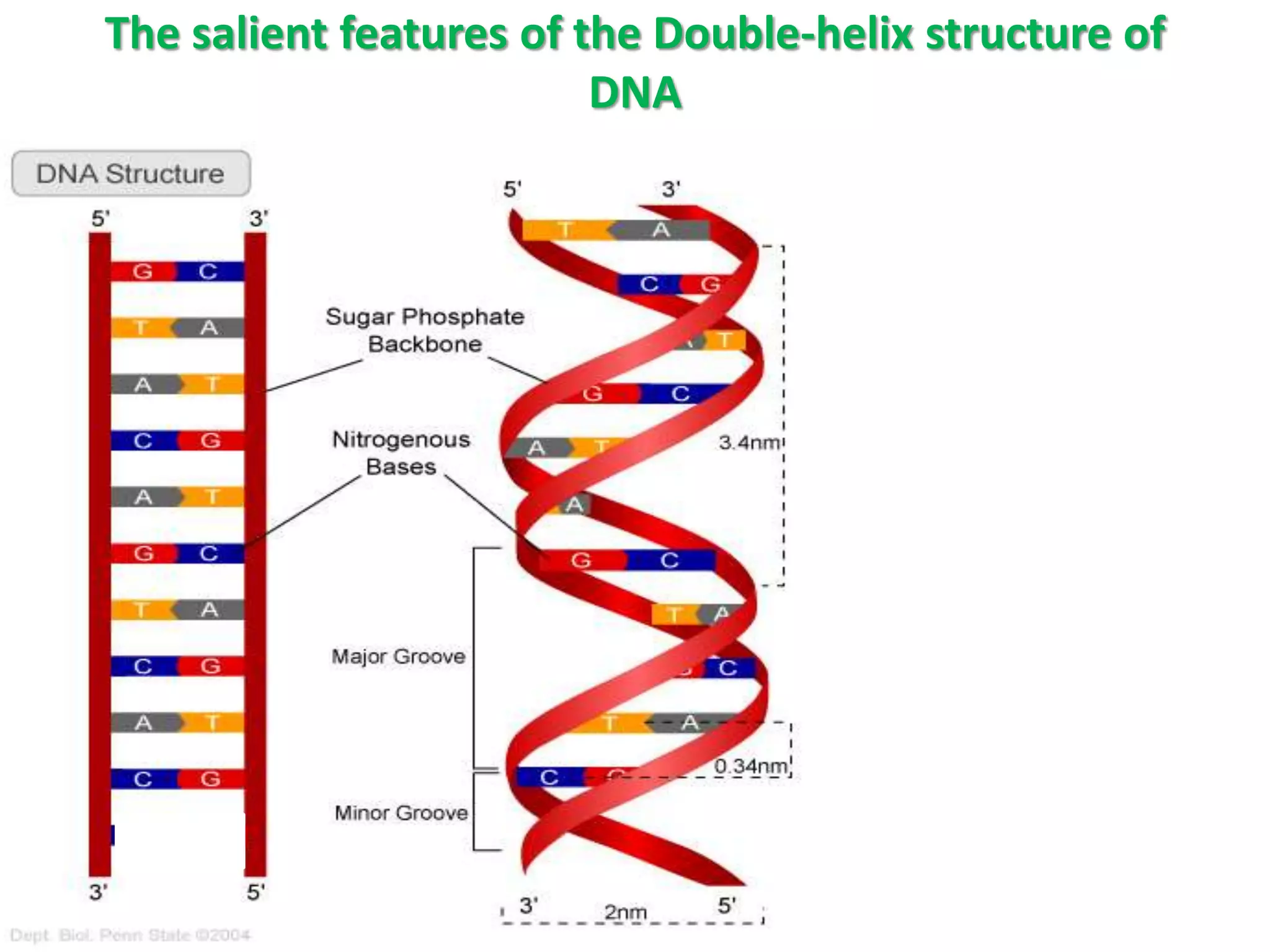
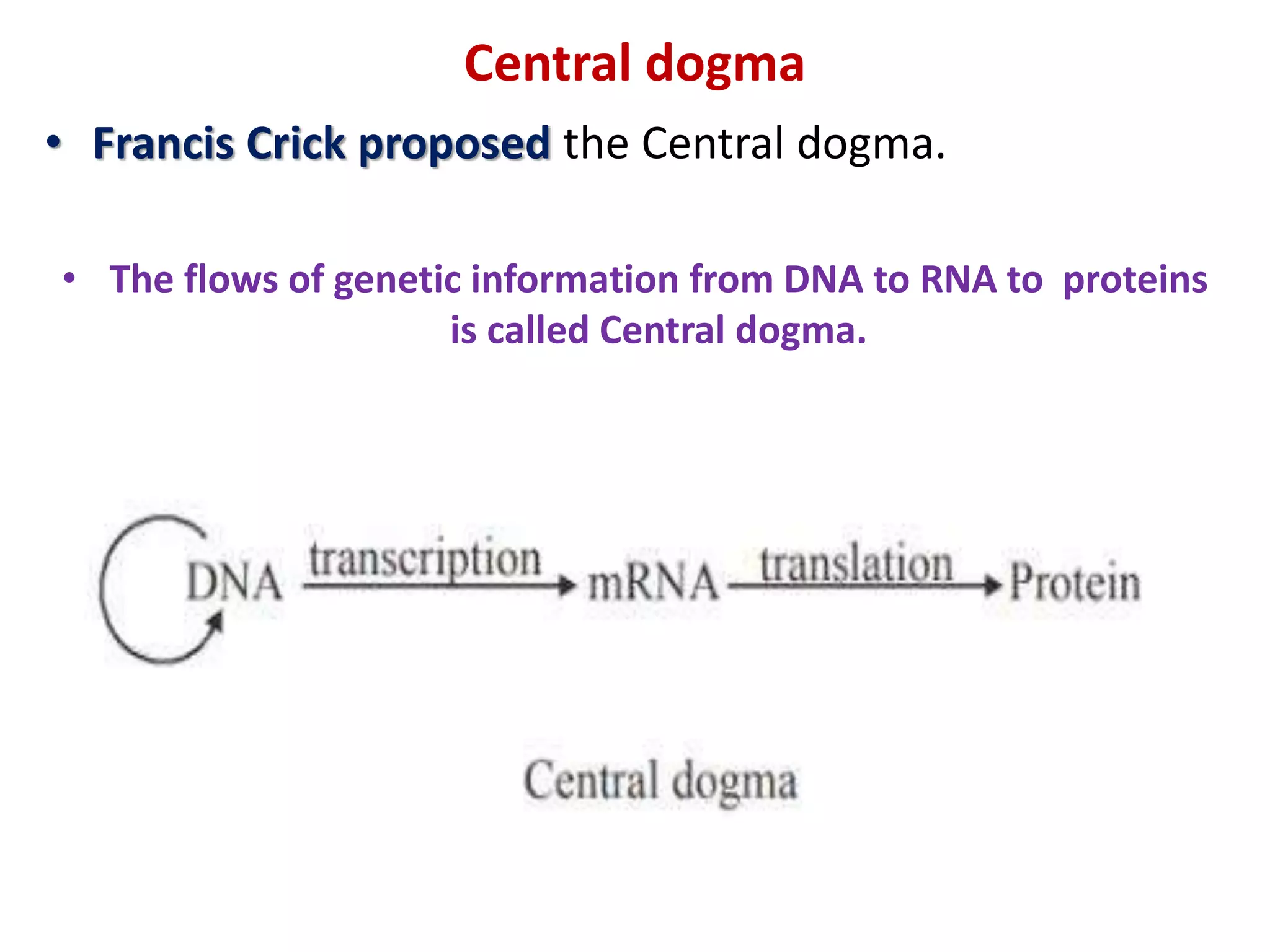
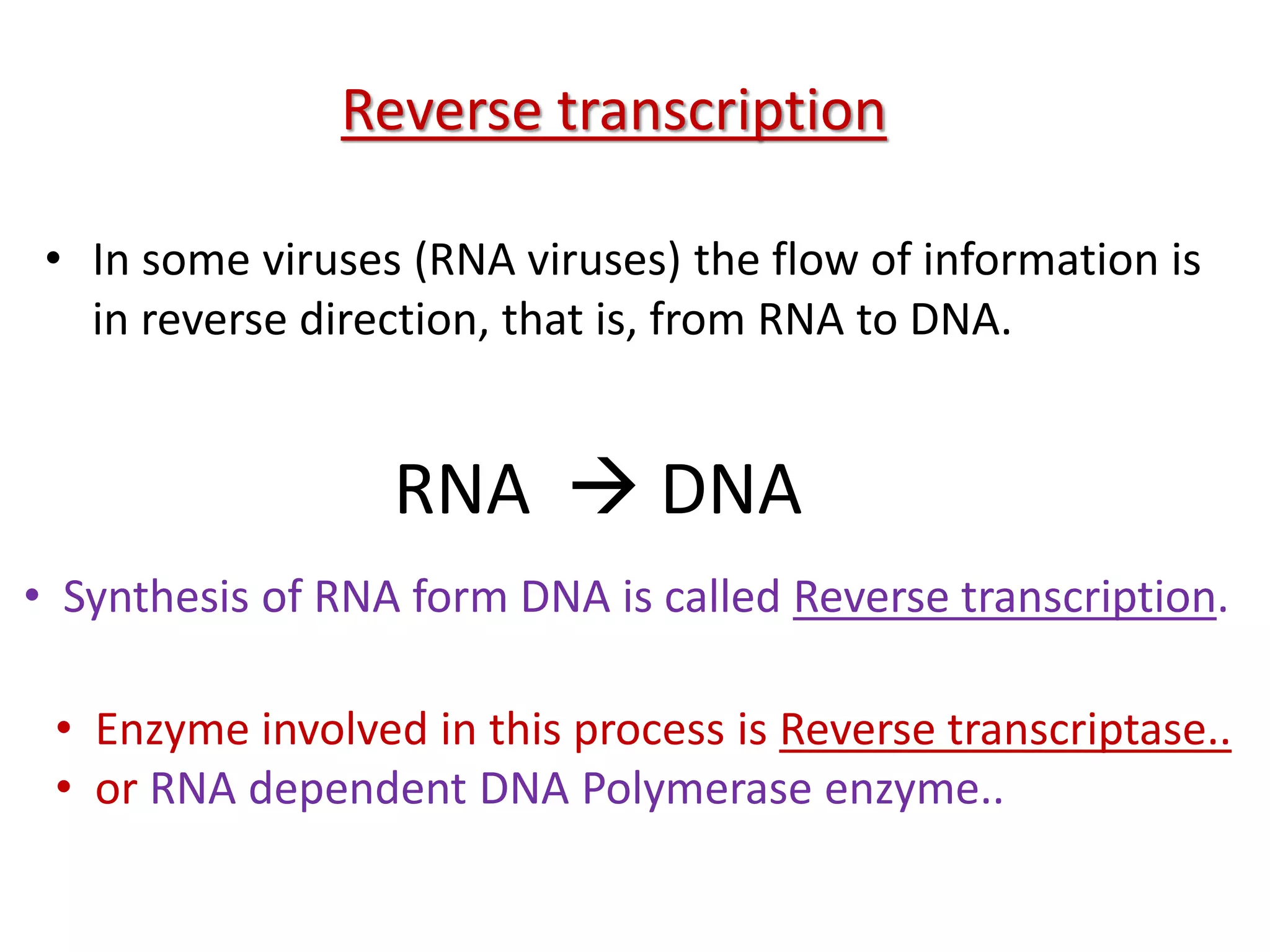
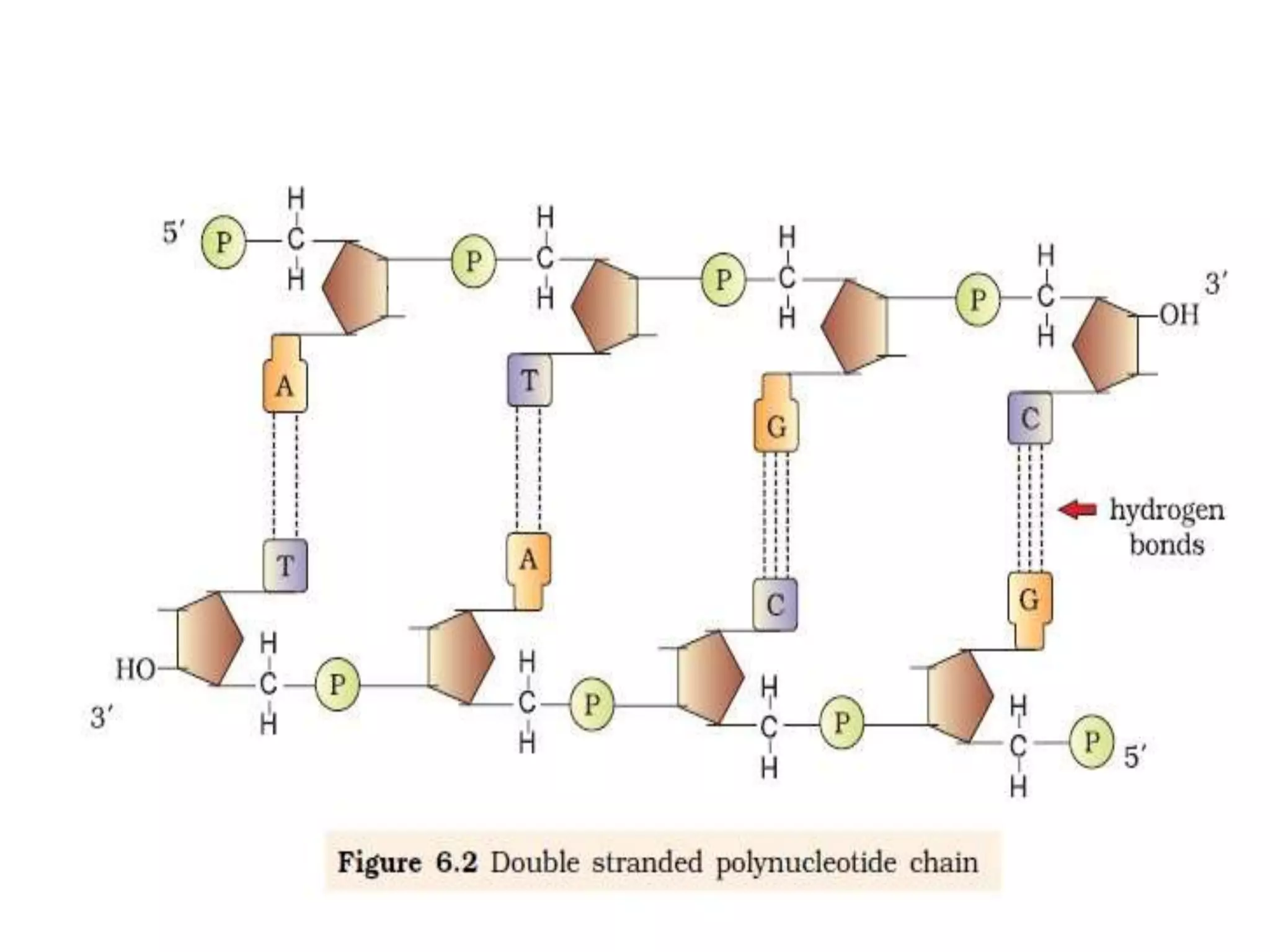
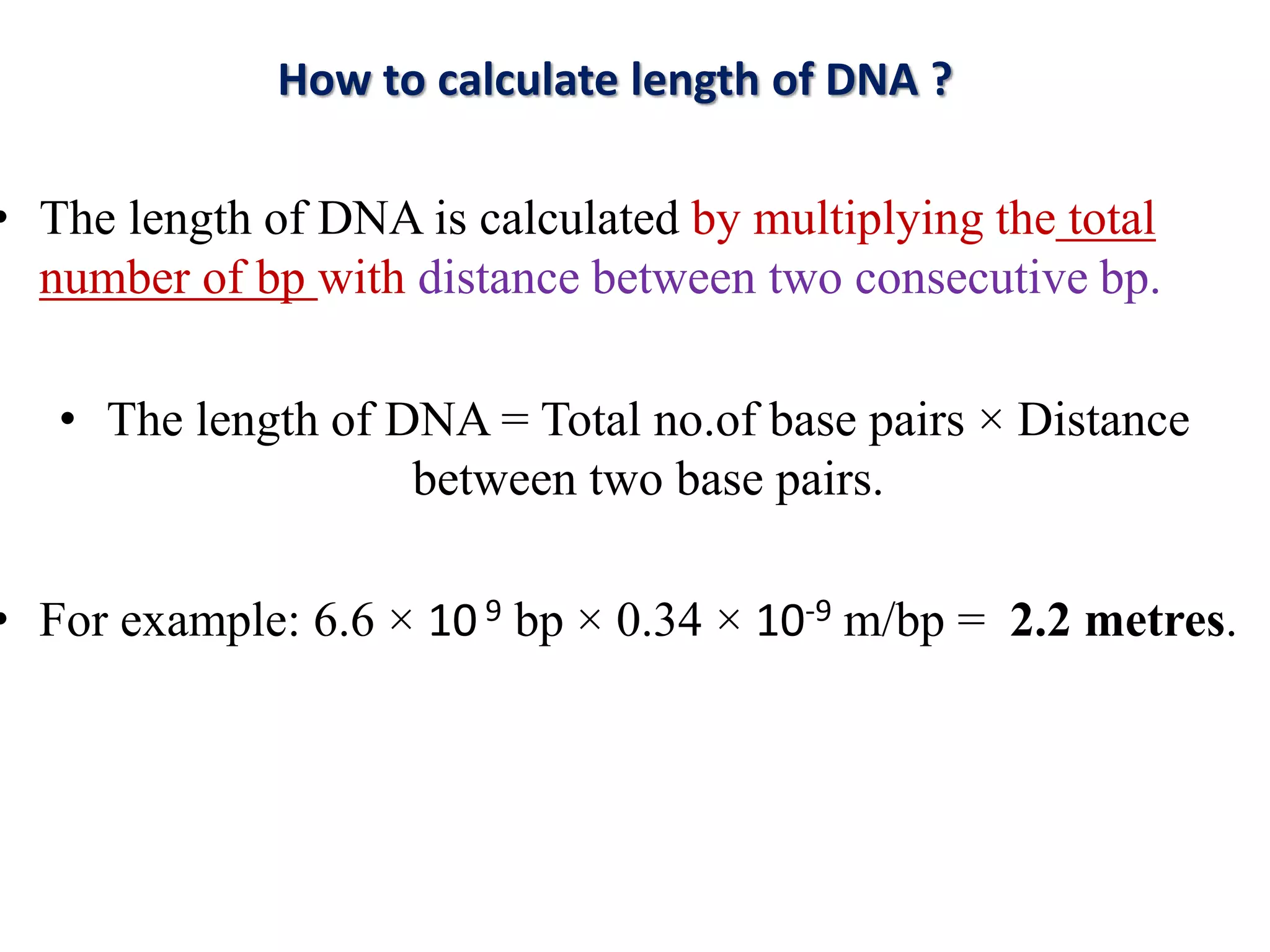
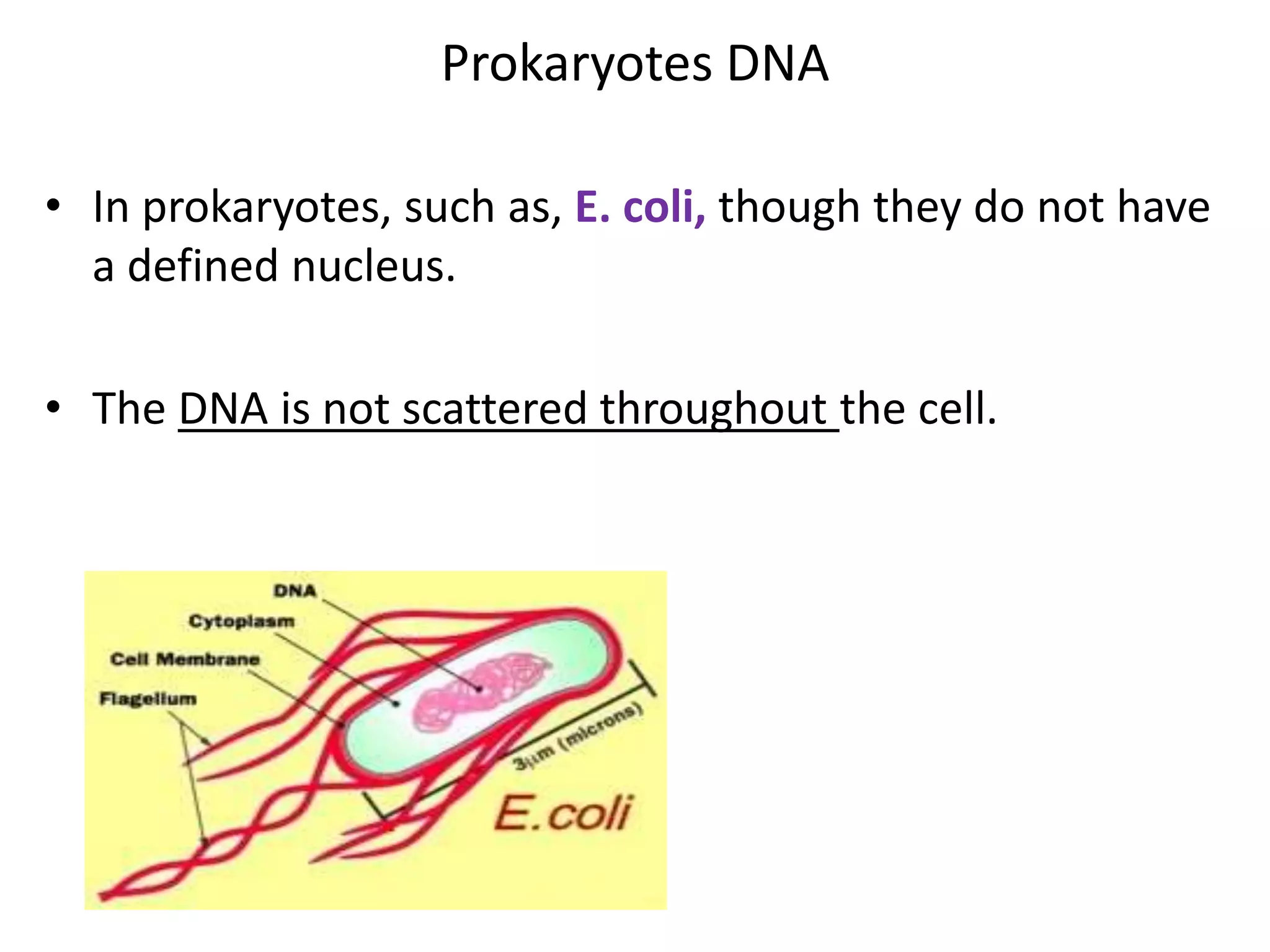
The document discusses several key topics regarding molecular genetics and DNA/RNA structure and function. It defines DNA and RNA as genetic materials, with DNA acting as the genetic material in most organisms and RNA serving additional roles. It describes nucleic acids as polymers made of nucleotides, and how DNA is a double-stranded helix composed of two polynucleotide chains held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary nucleotide bases. The document also discusses DNA replication, transcription, translation, and the central dogma proposed by Francis Crick regarding the flow of genetic information.