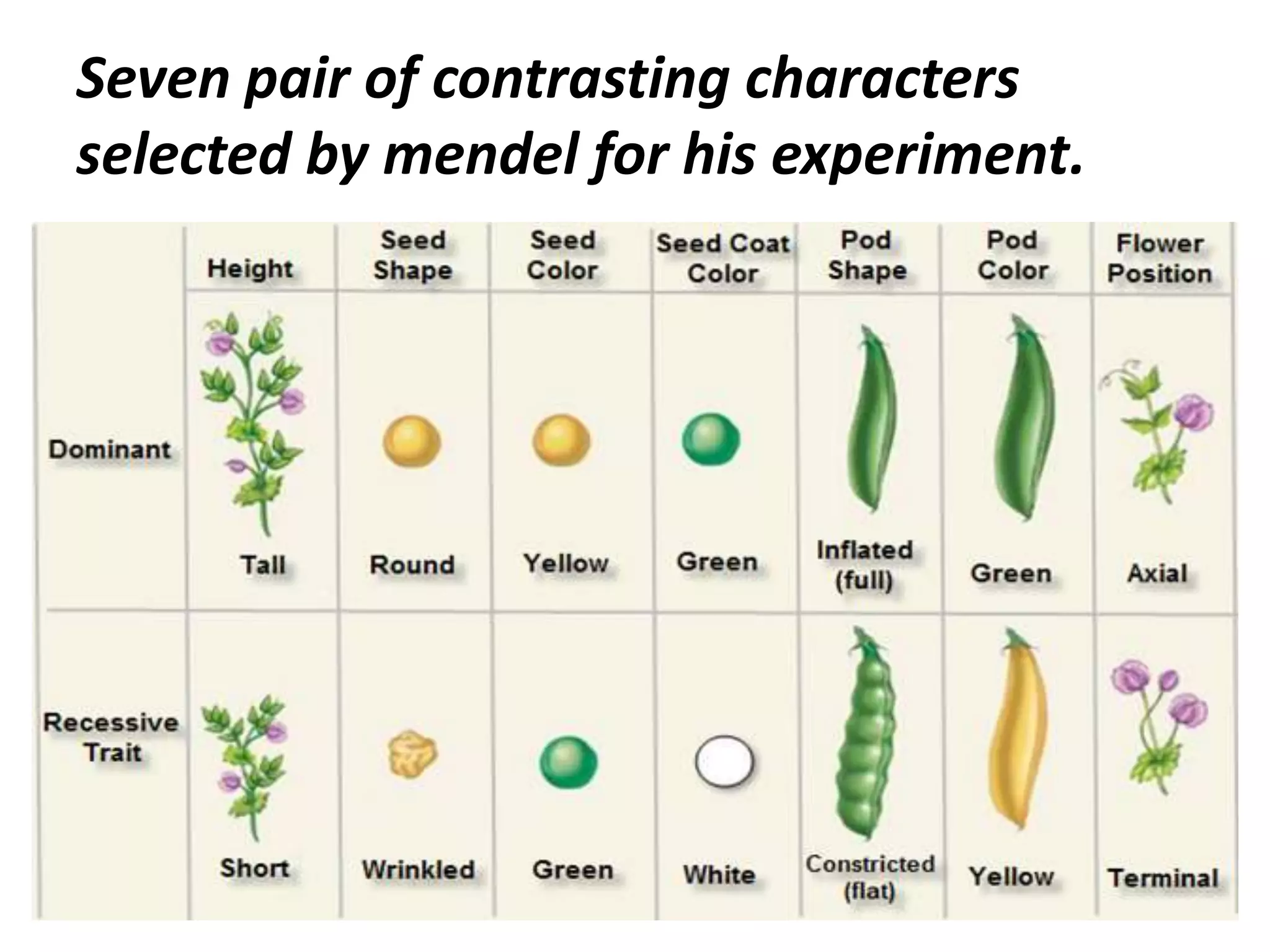
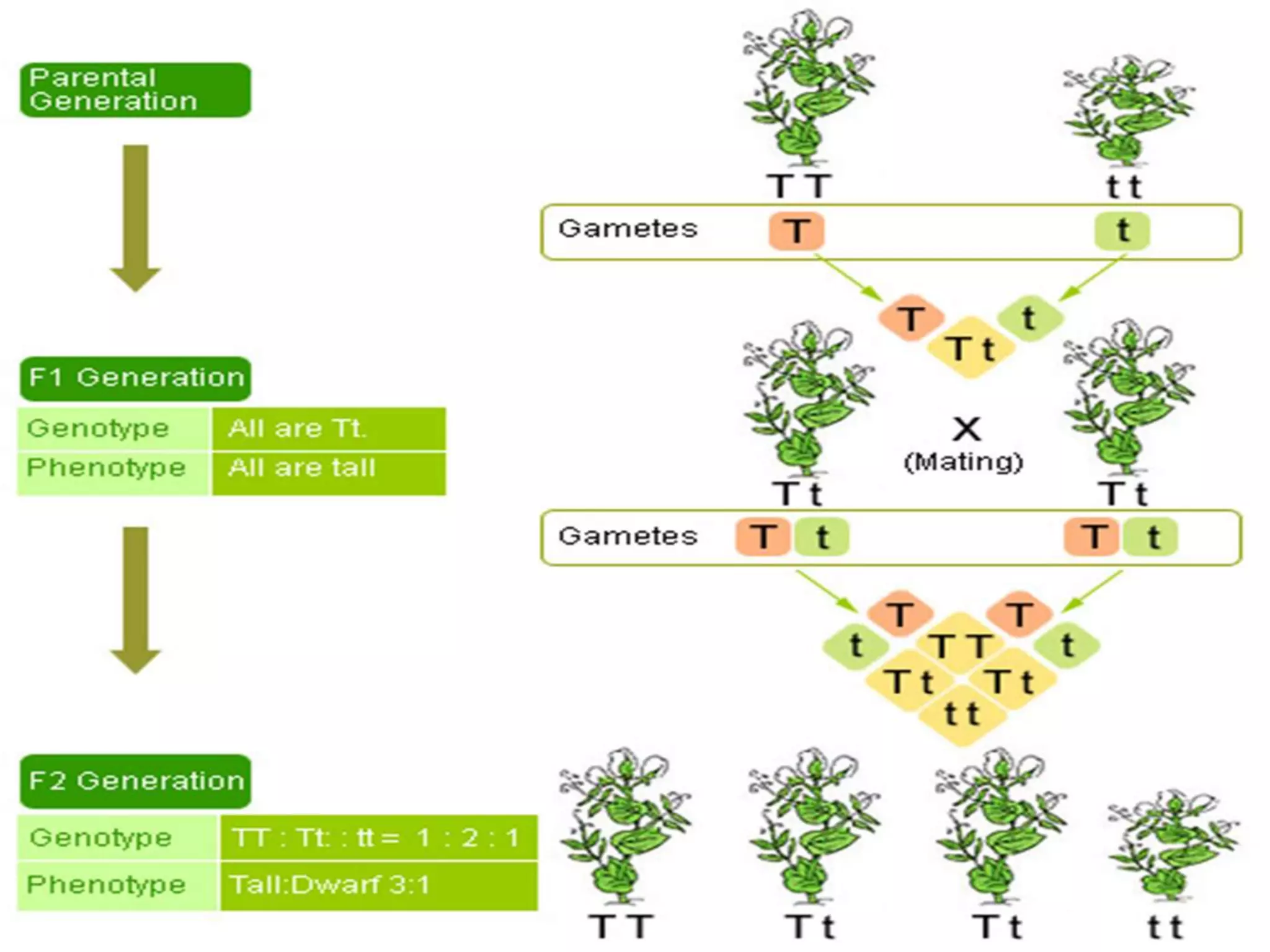
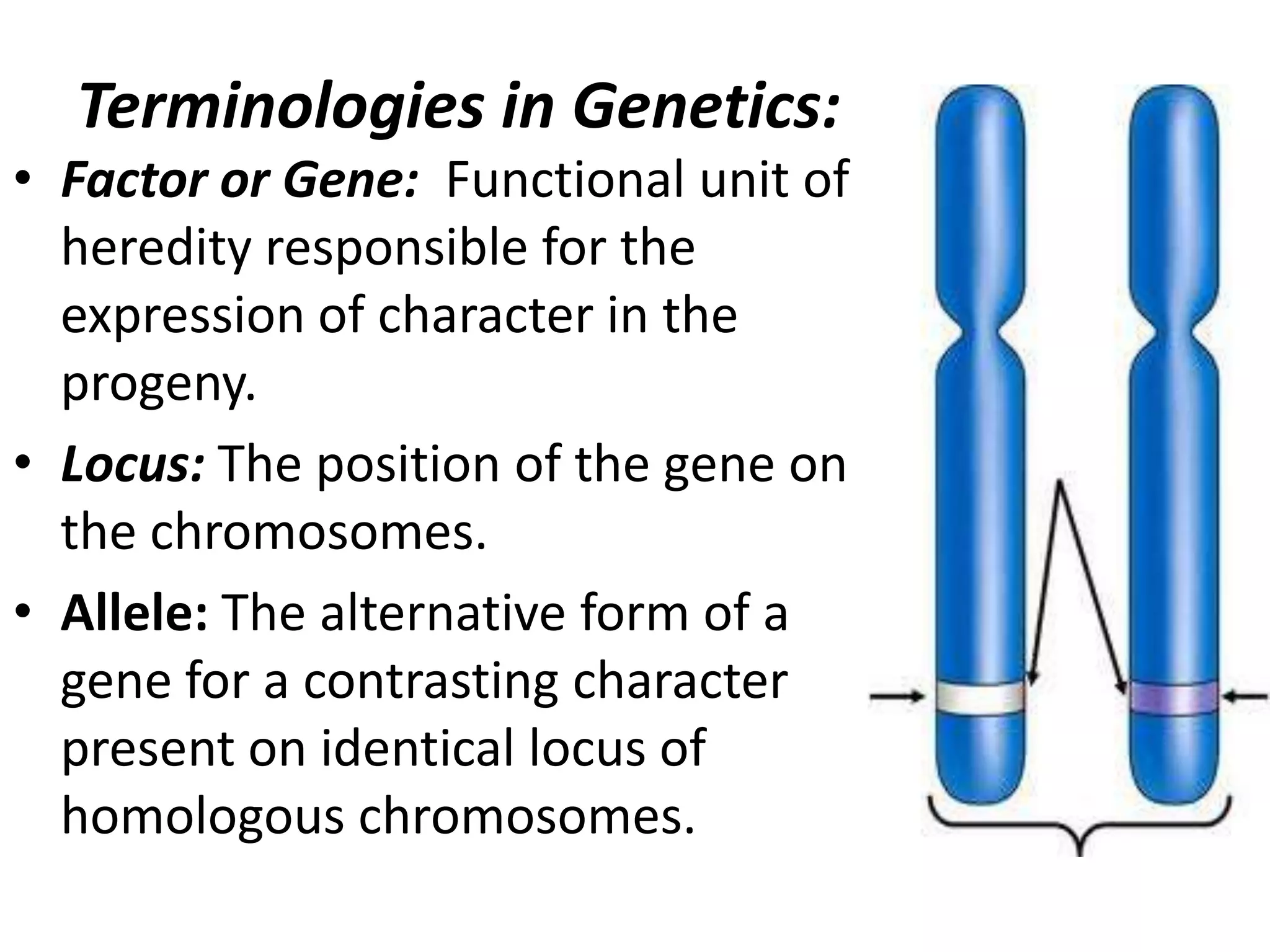
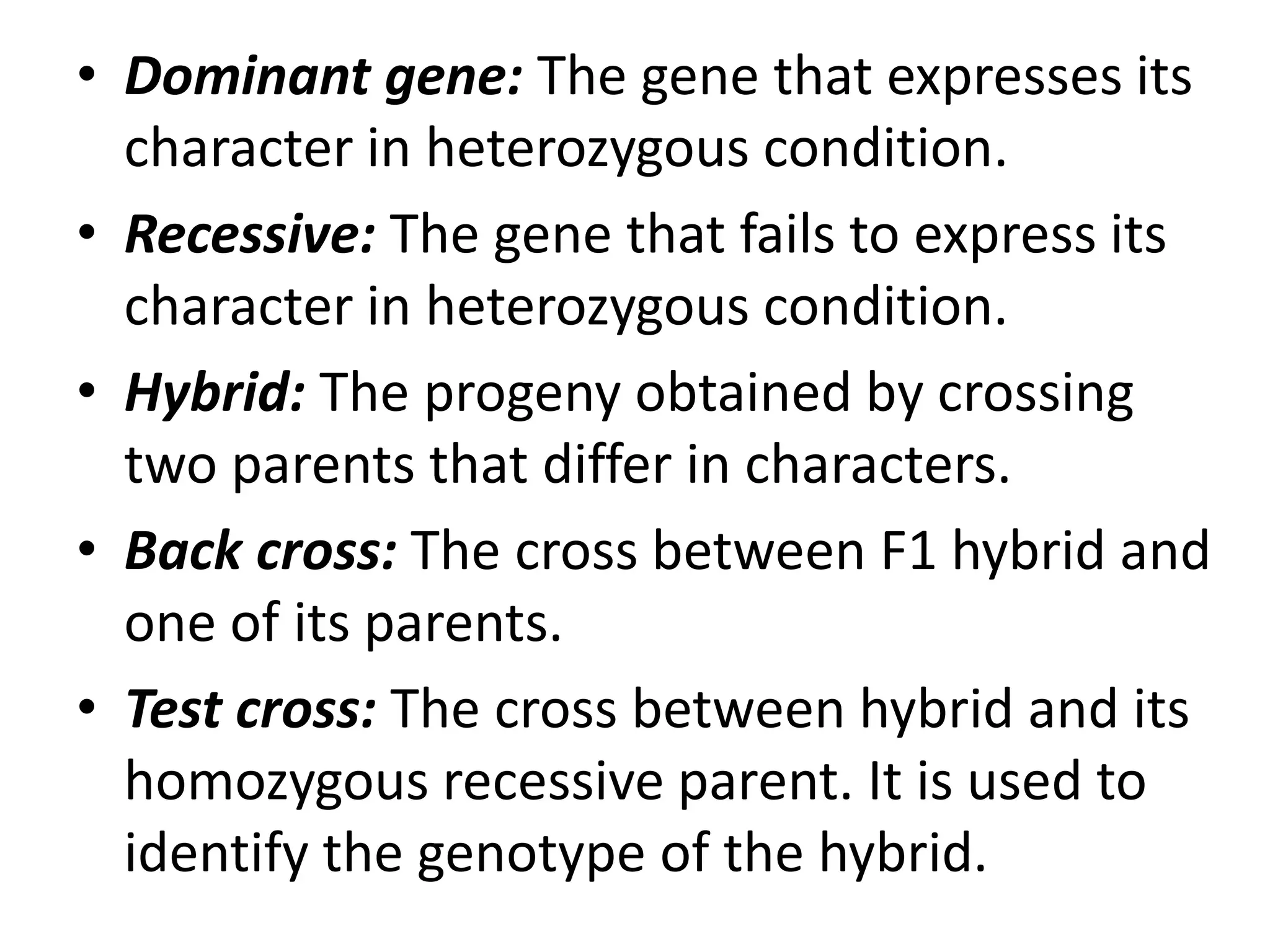
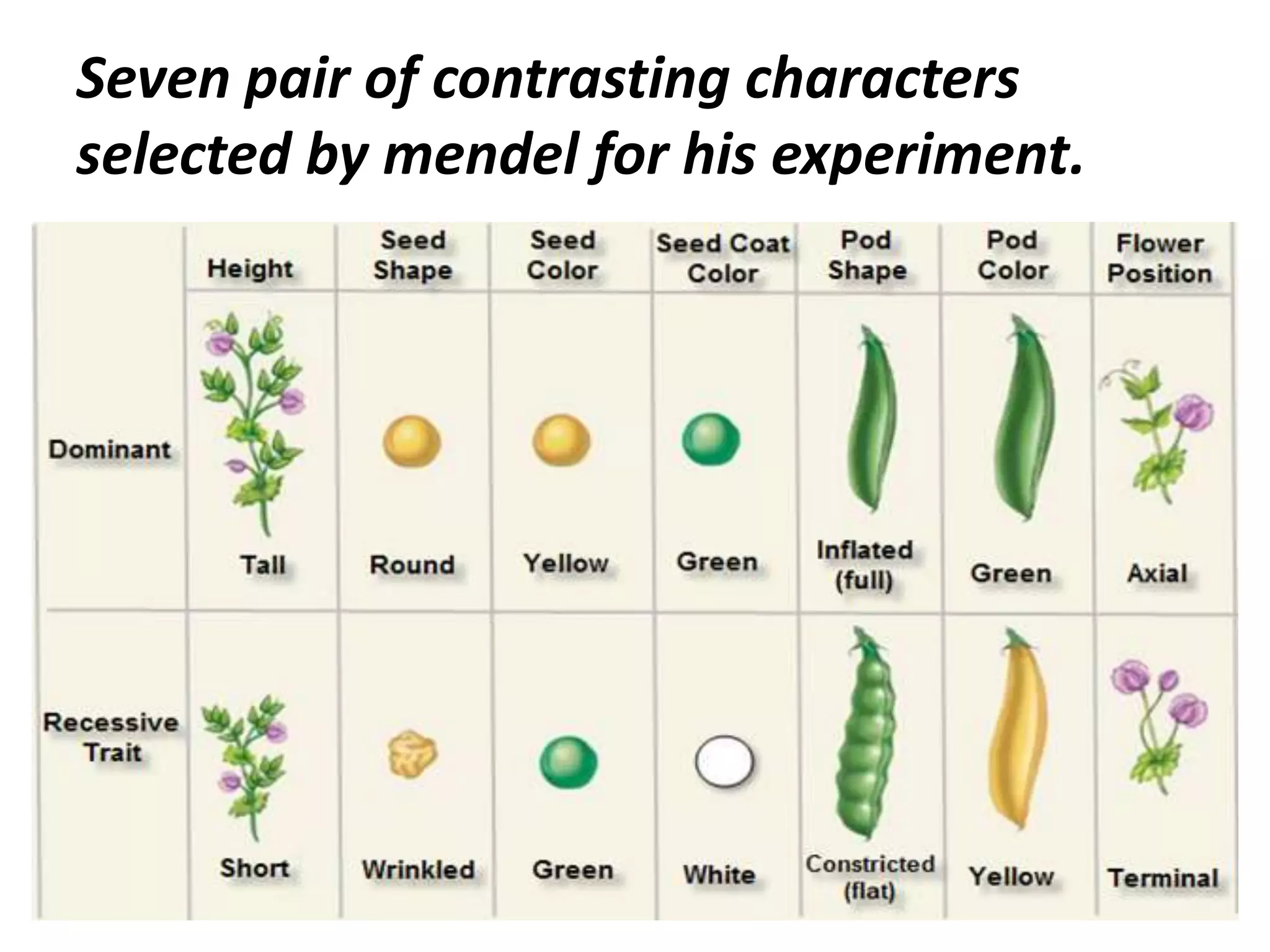
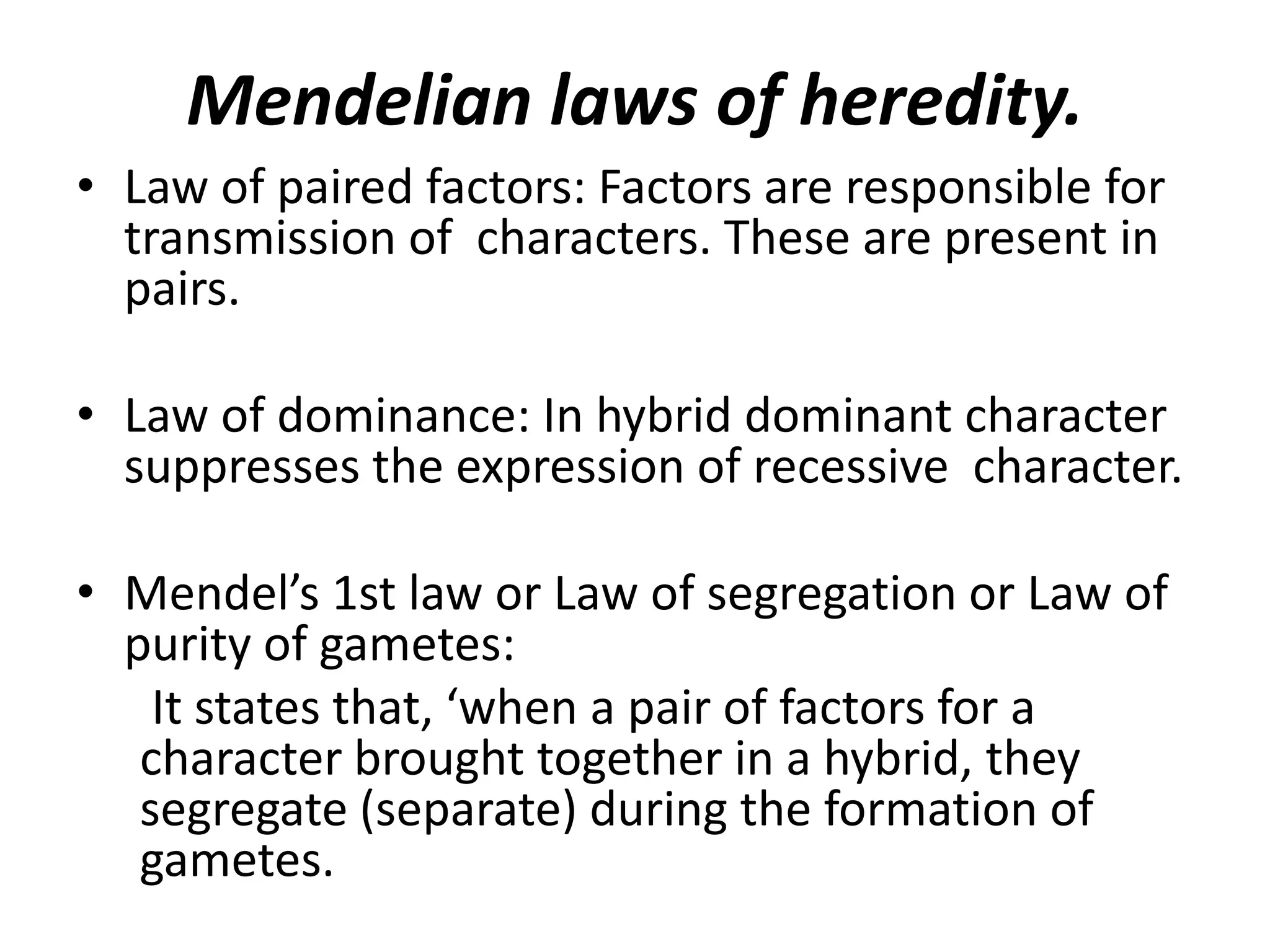
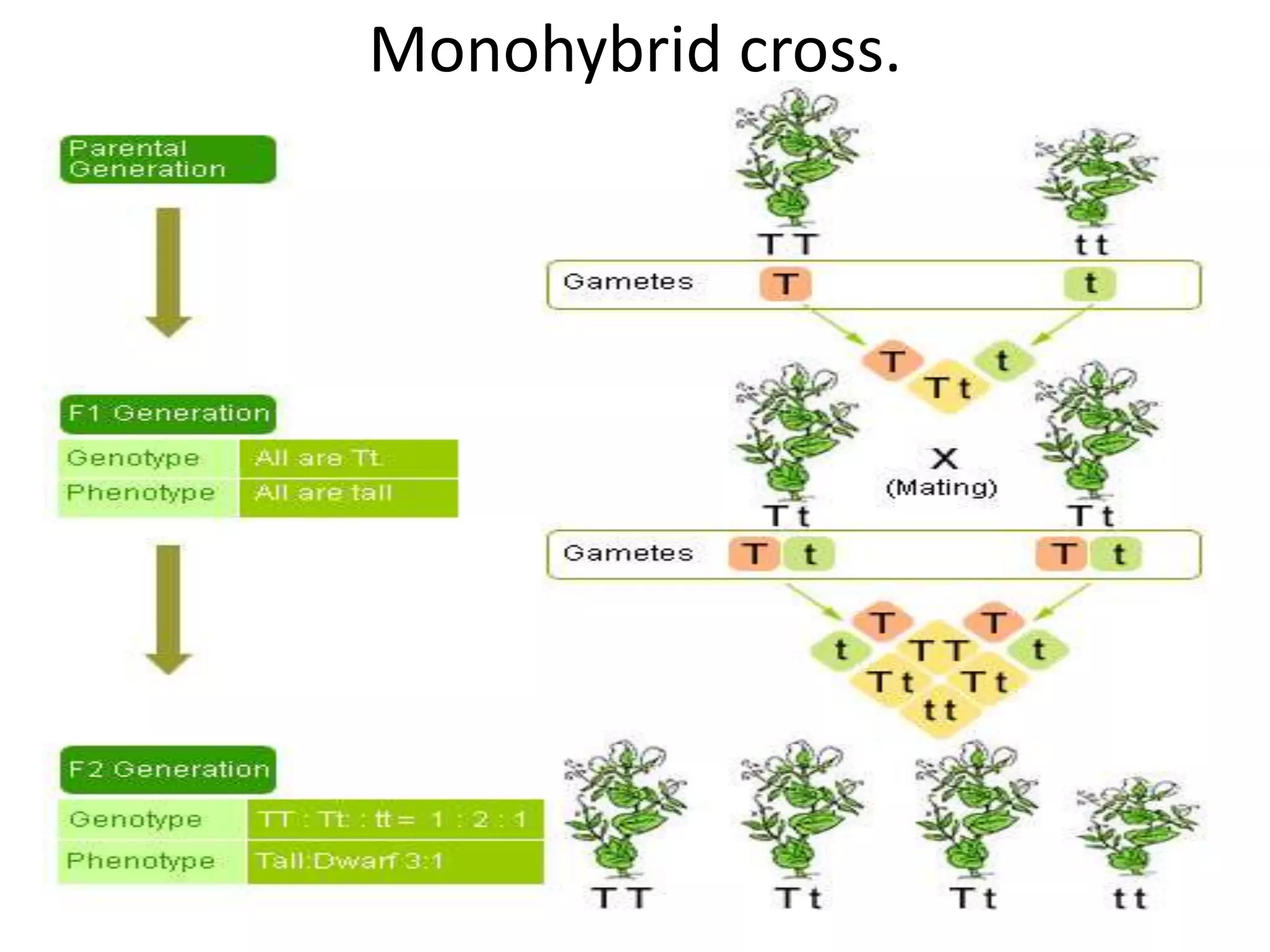
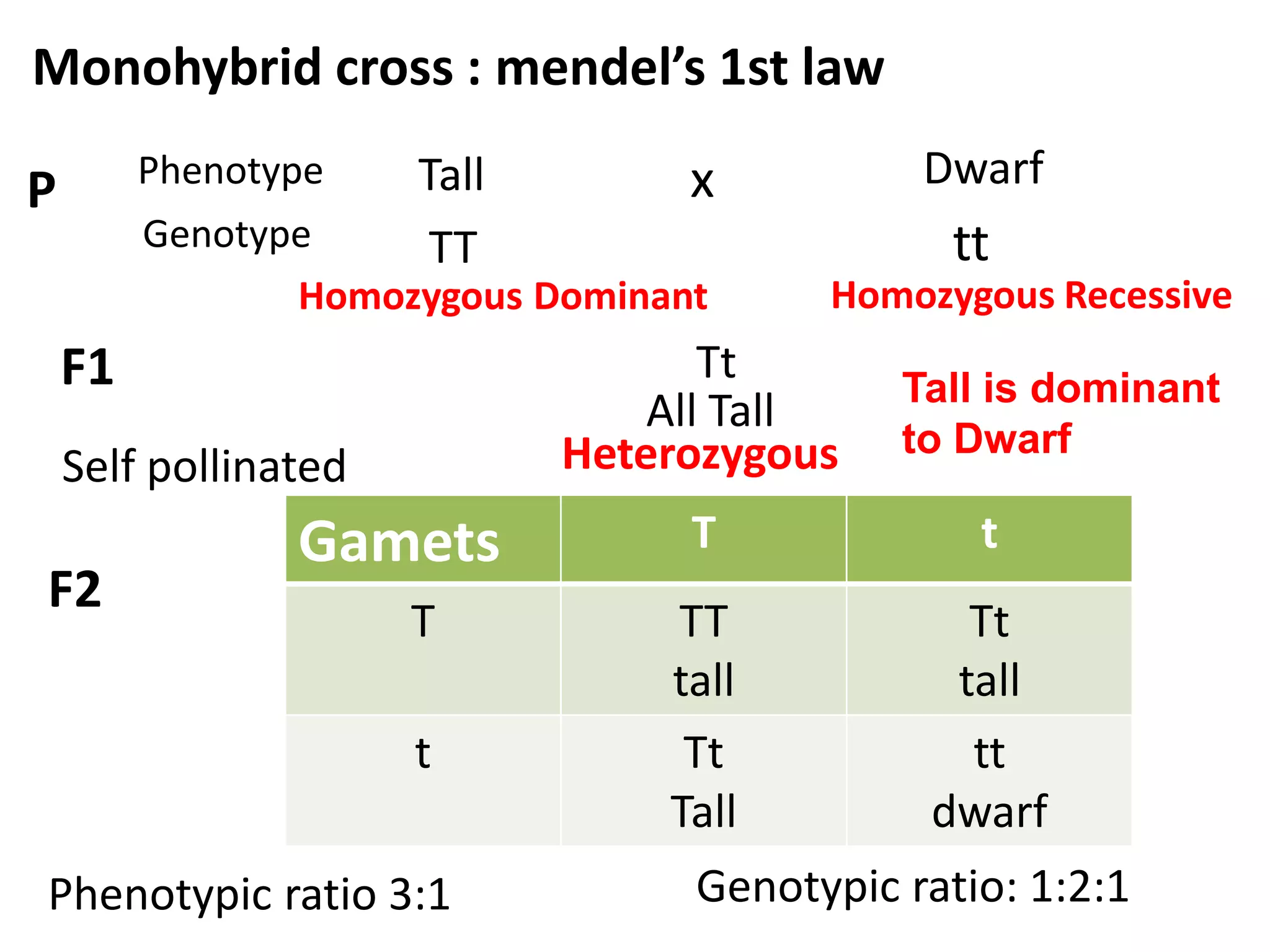
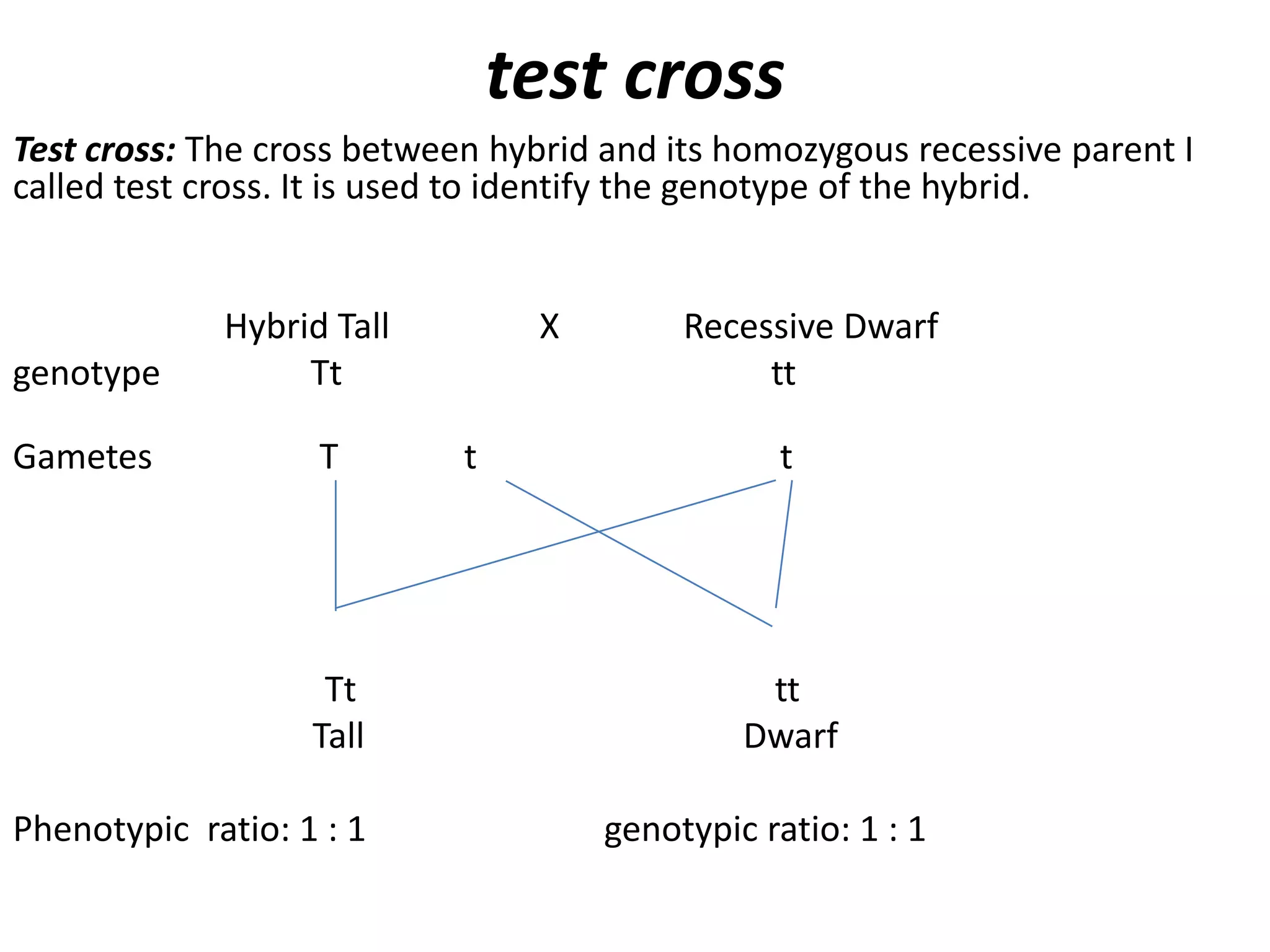
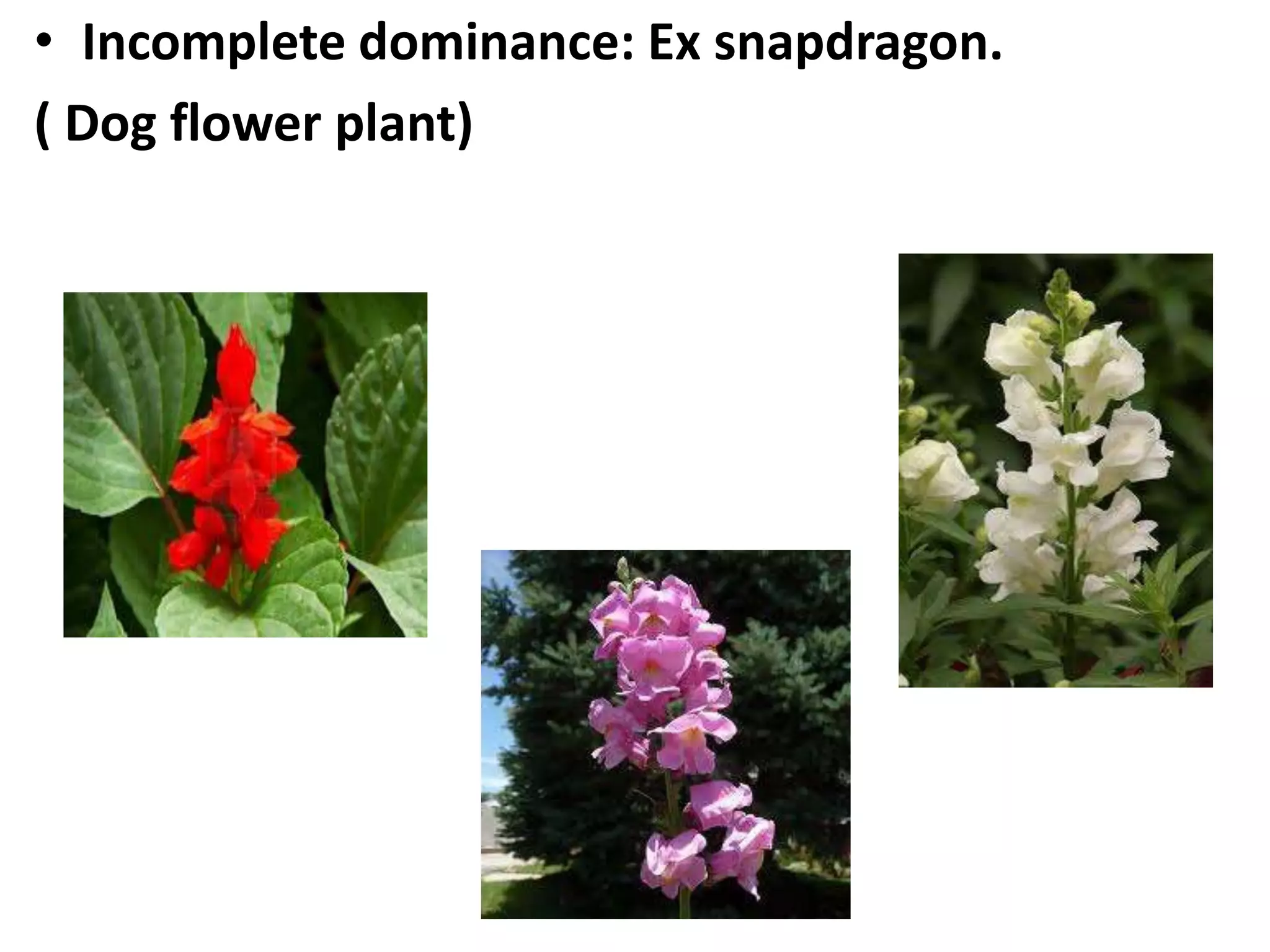
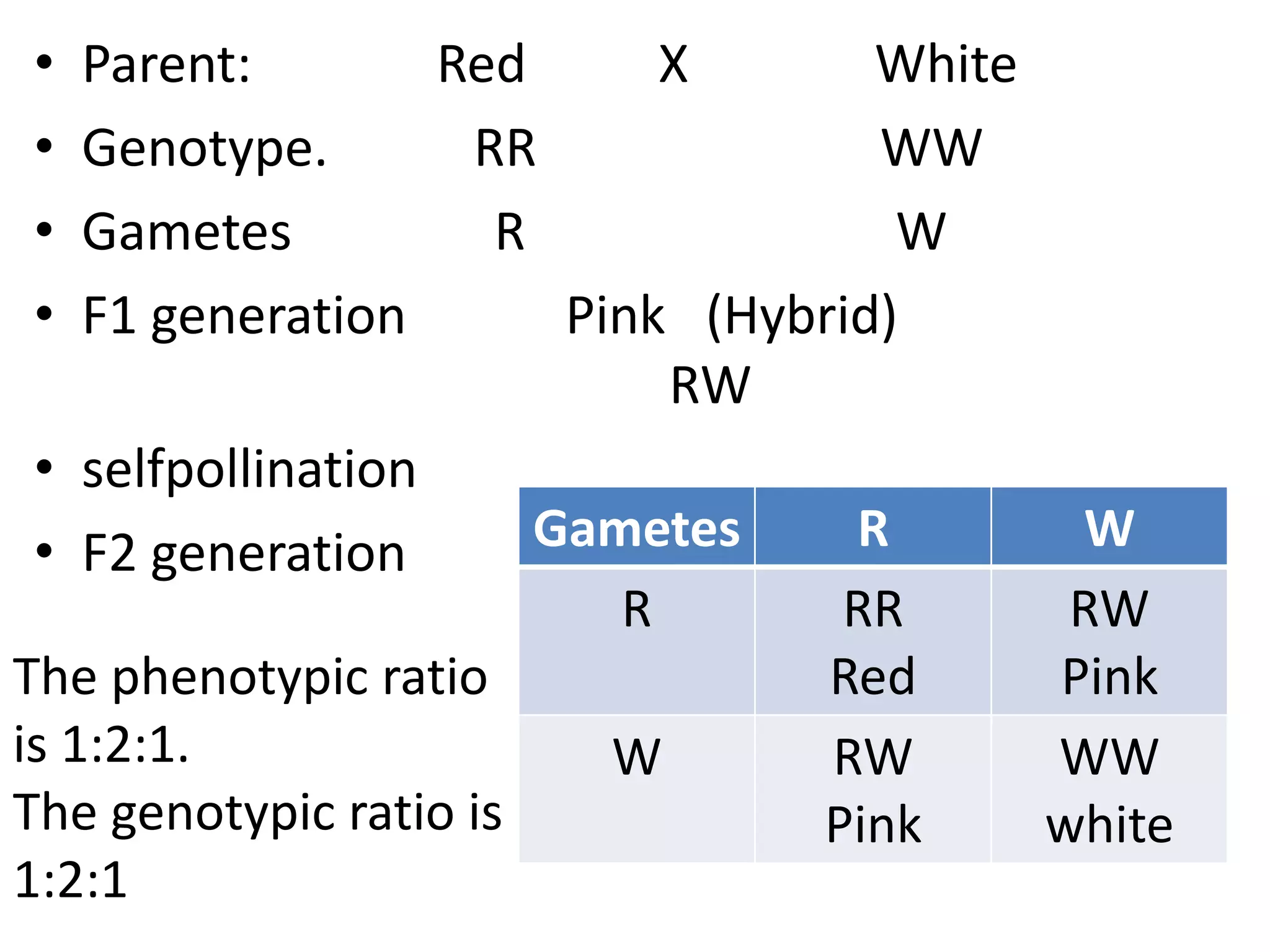
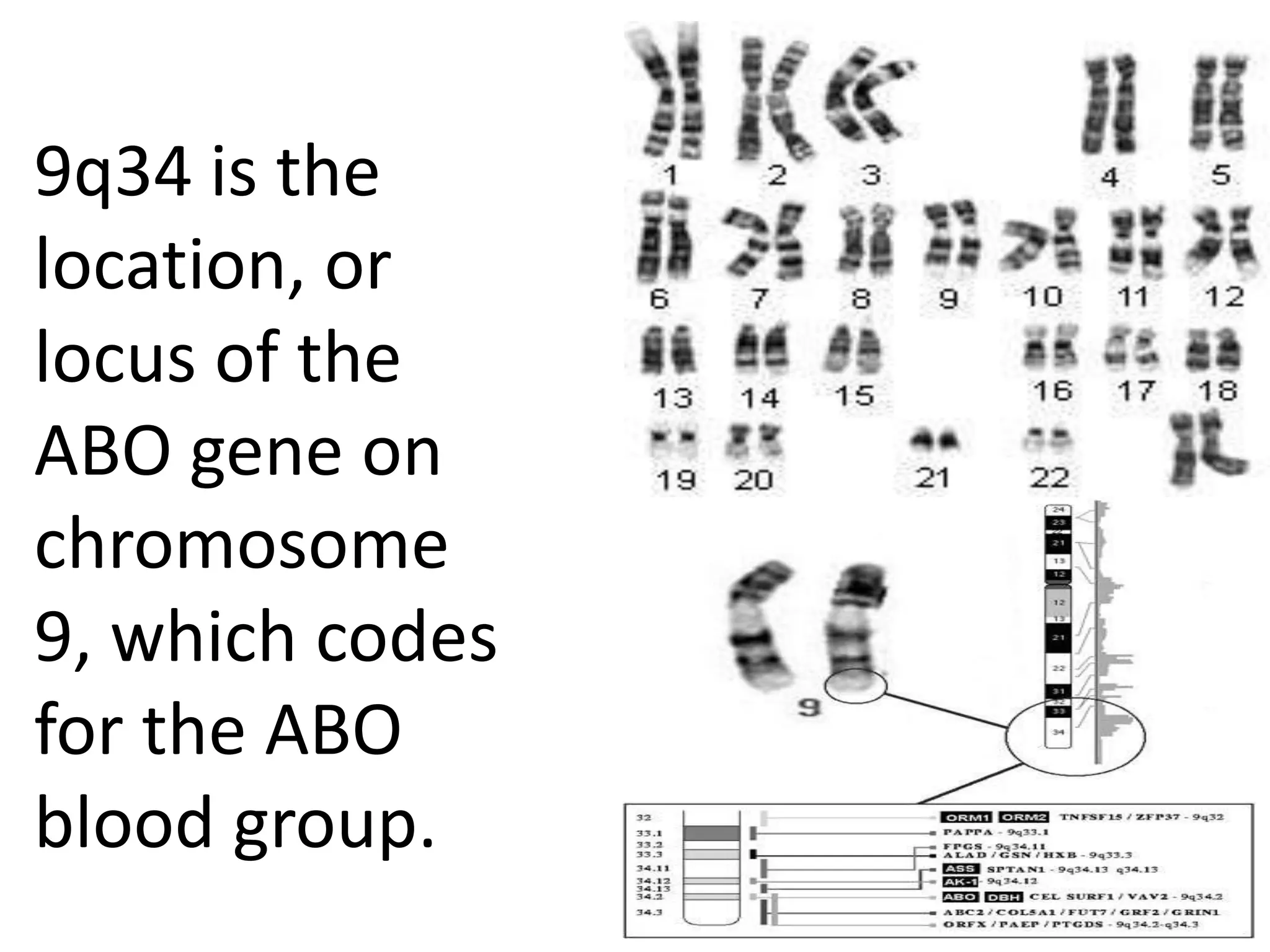
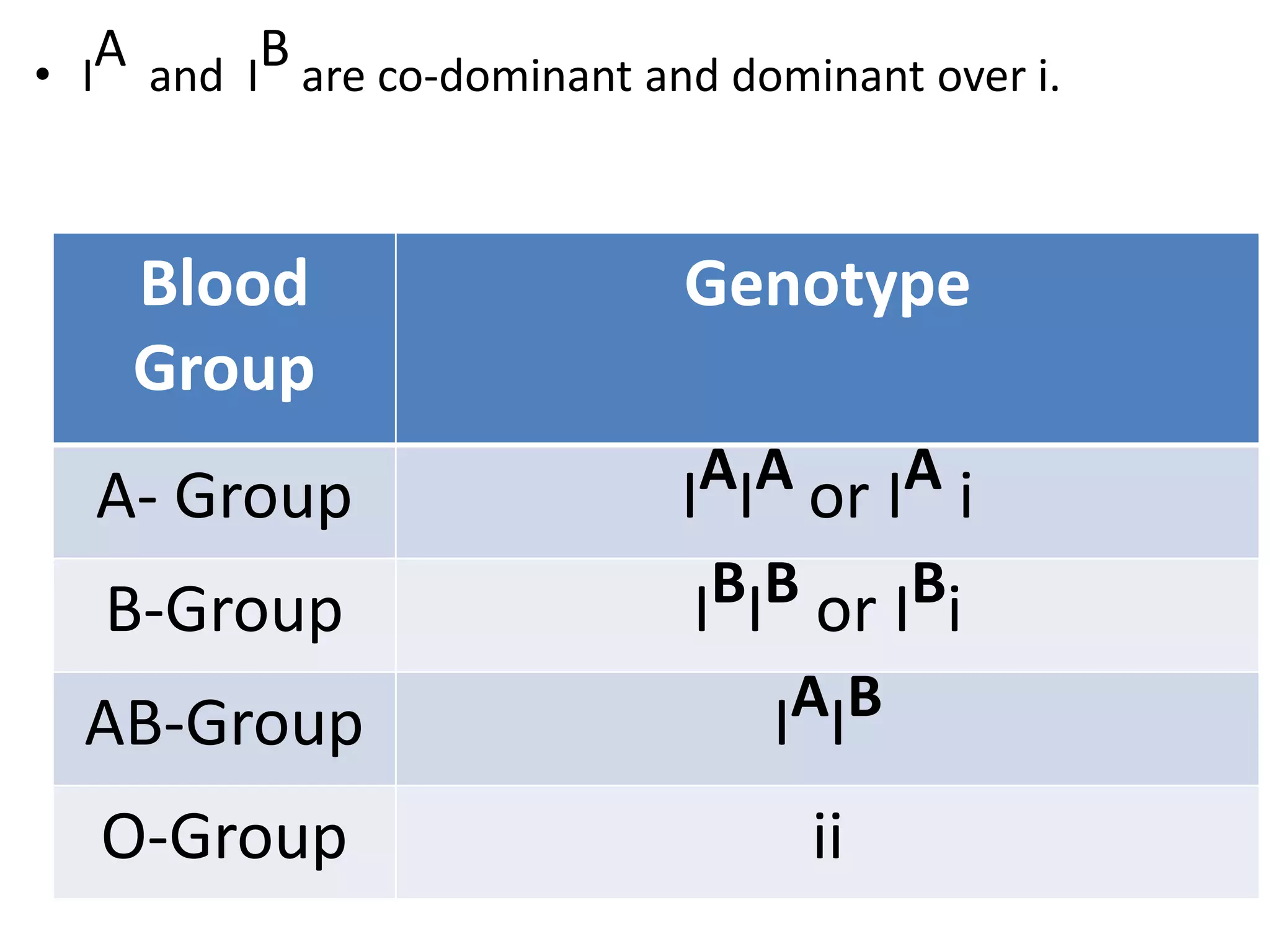
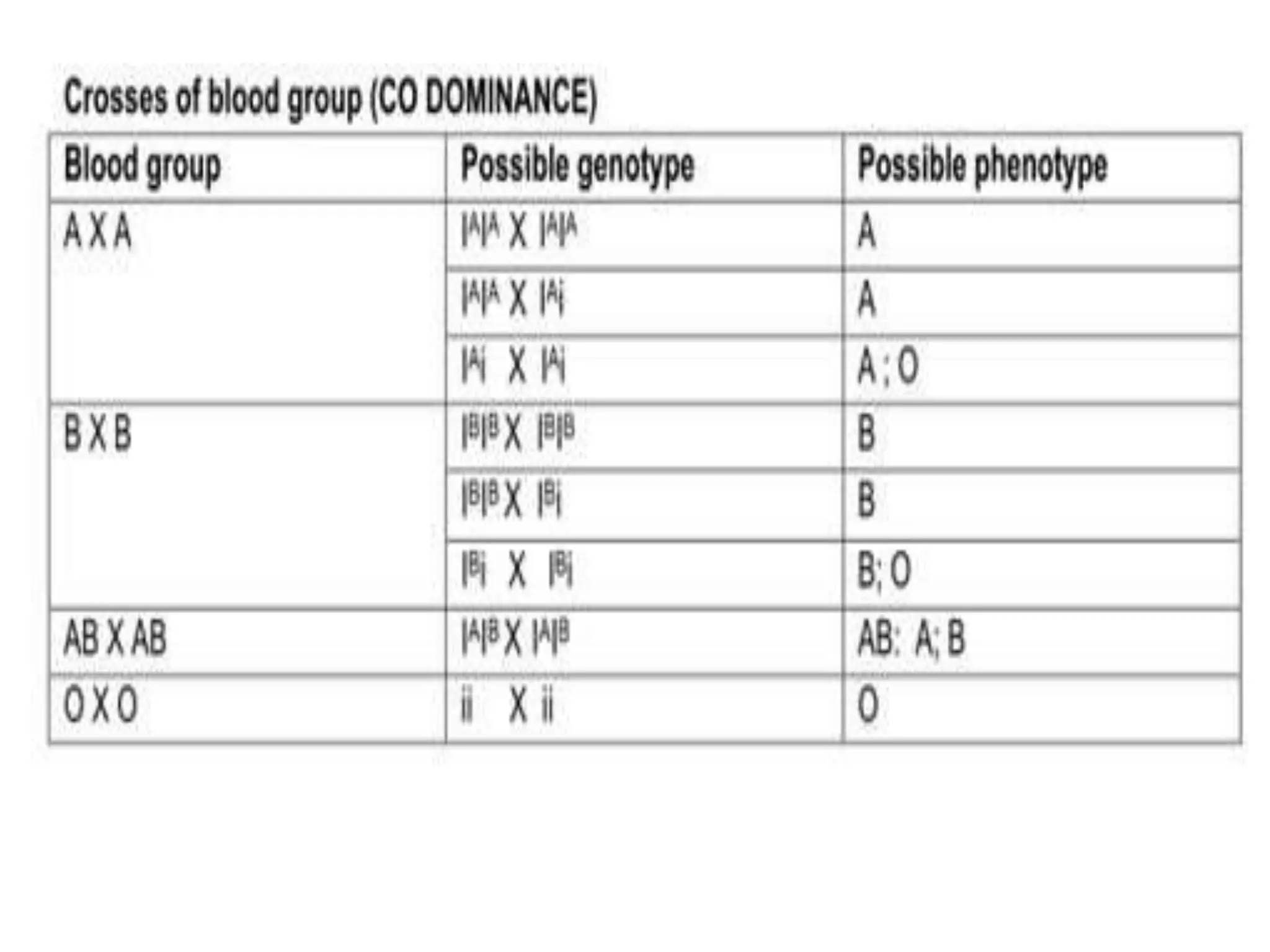
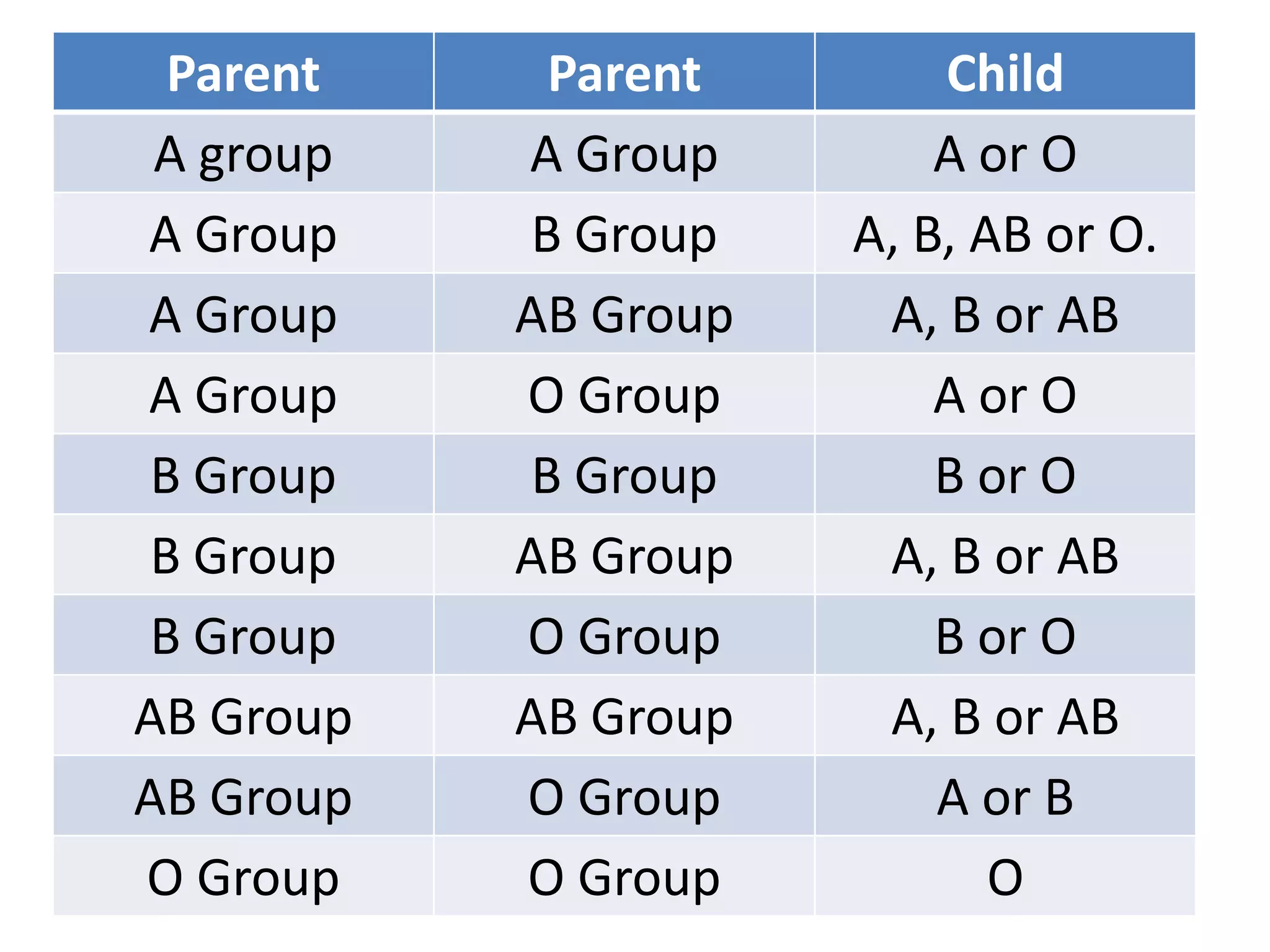
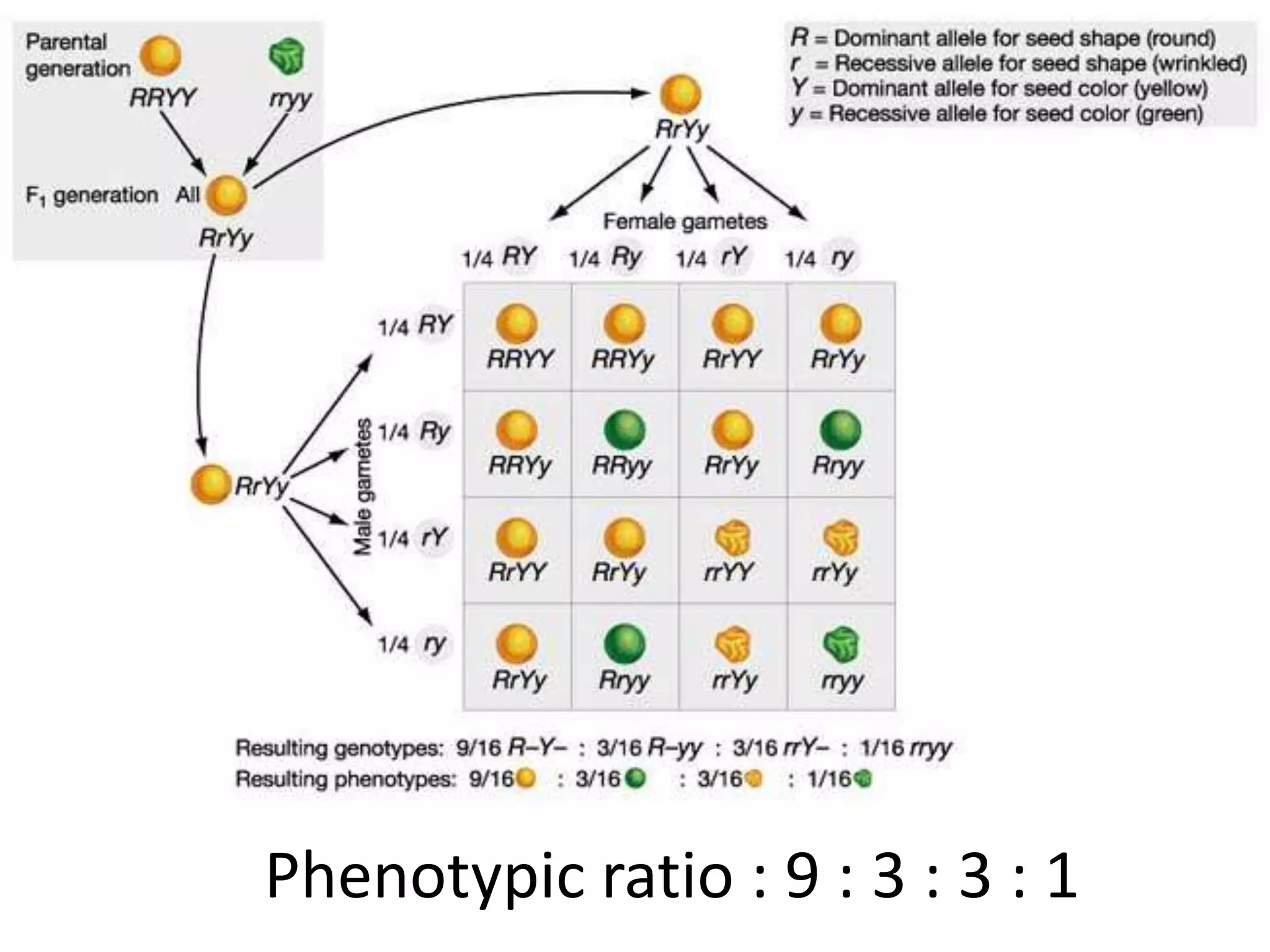
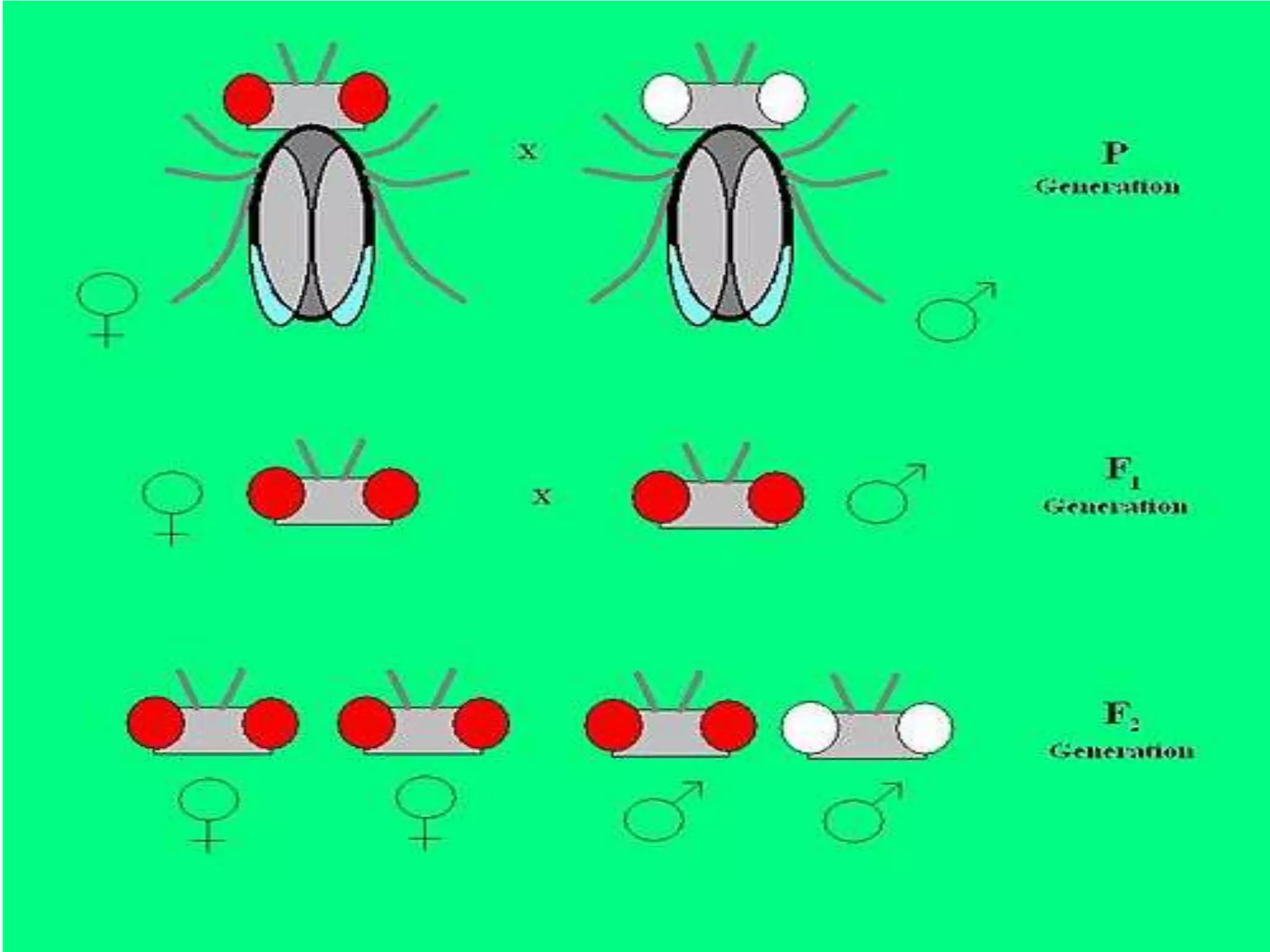
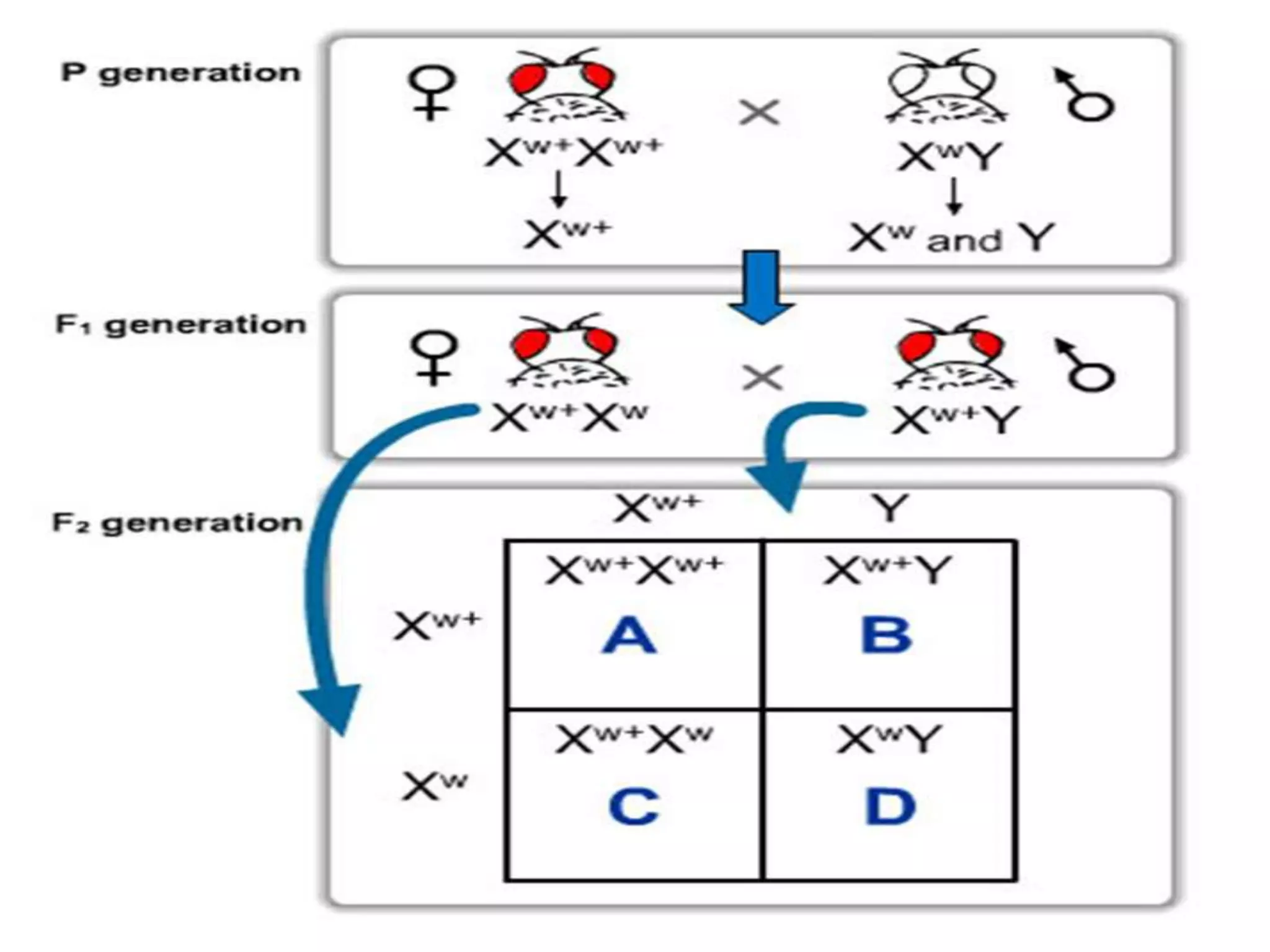
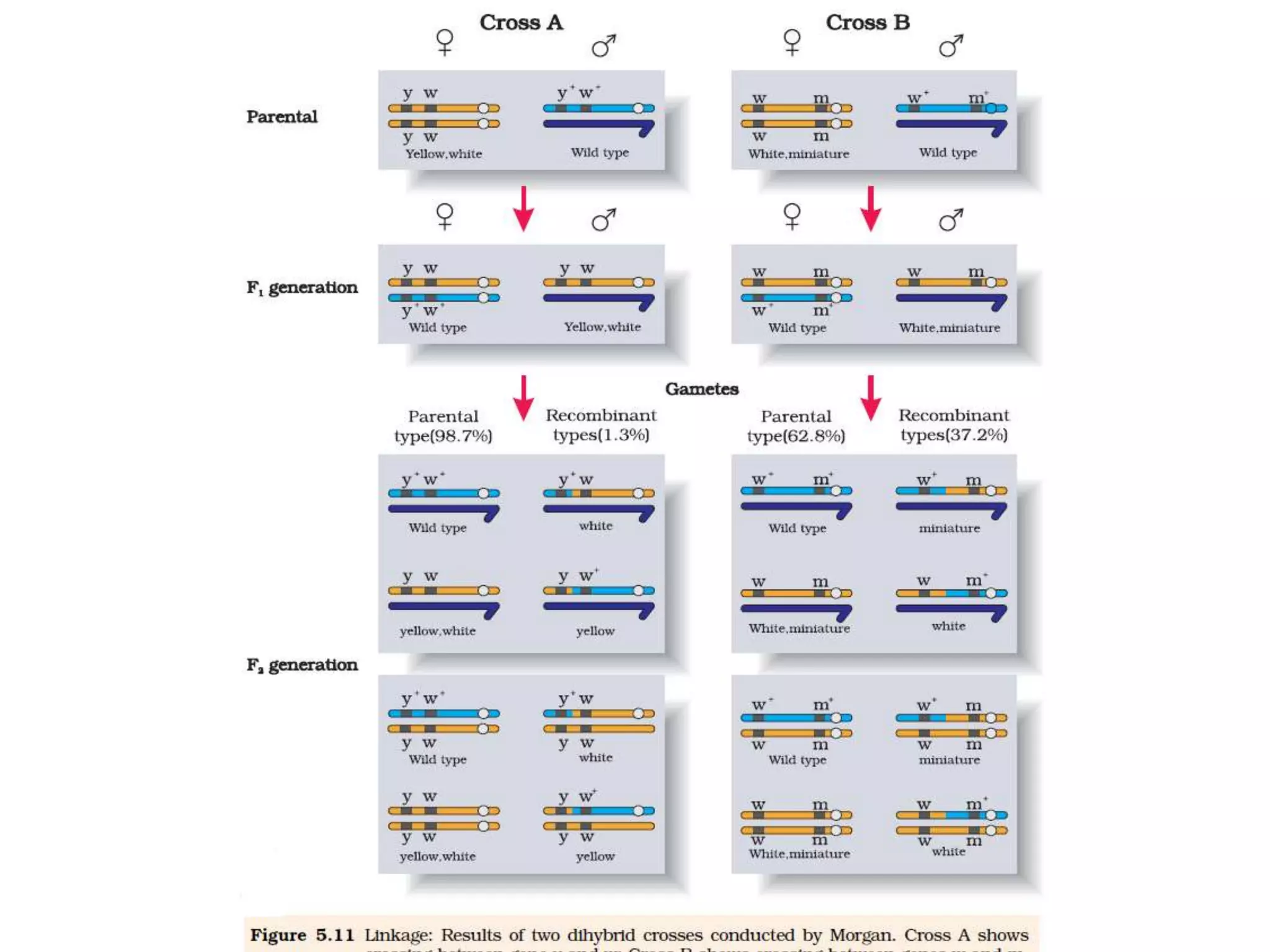
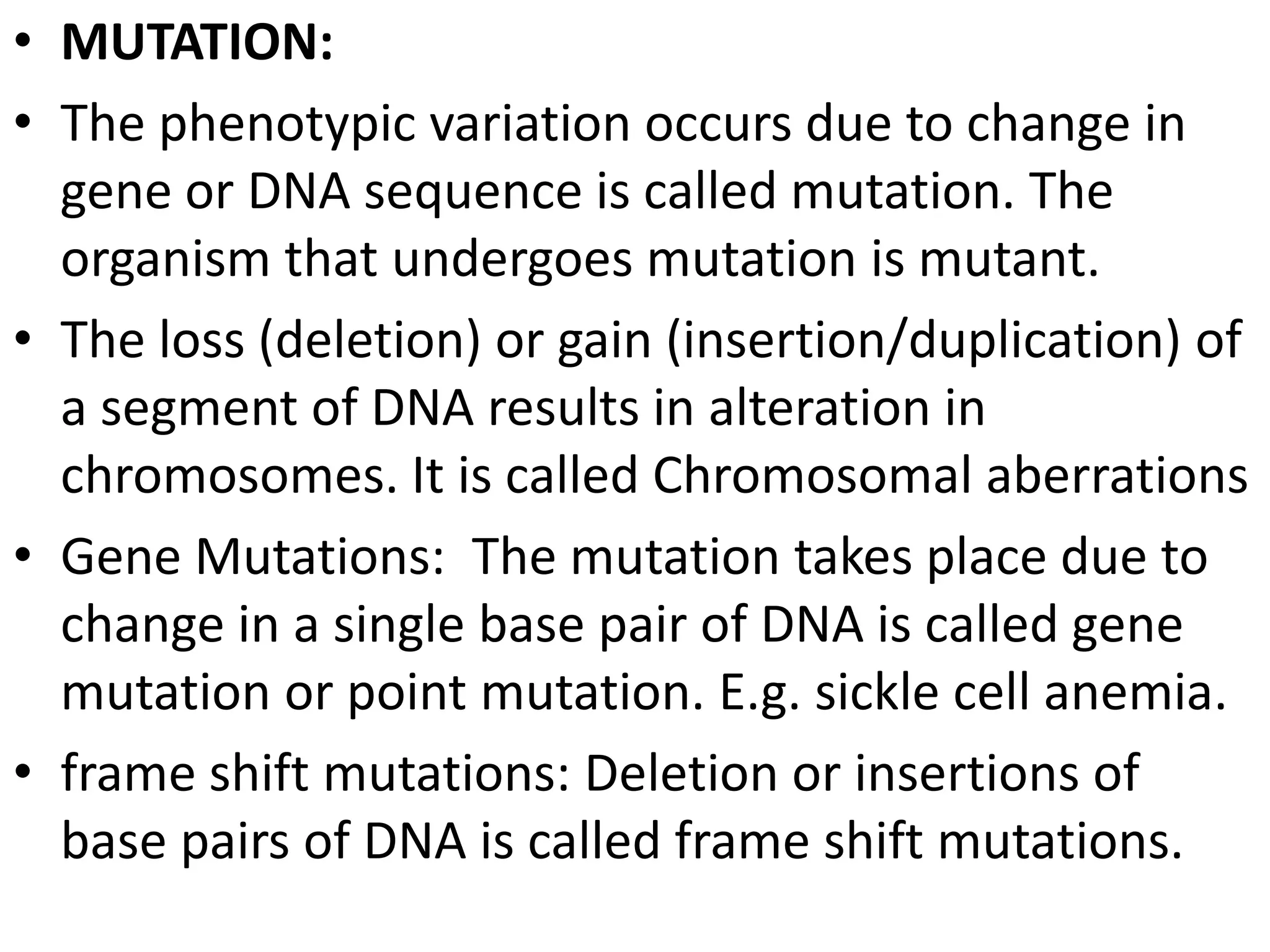
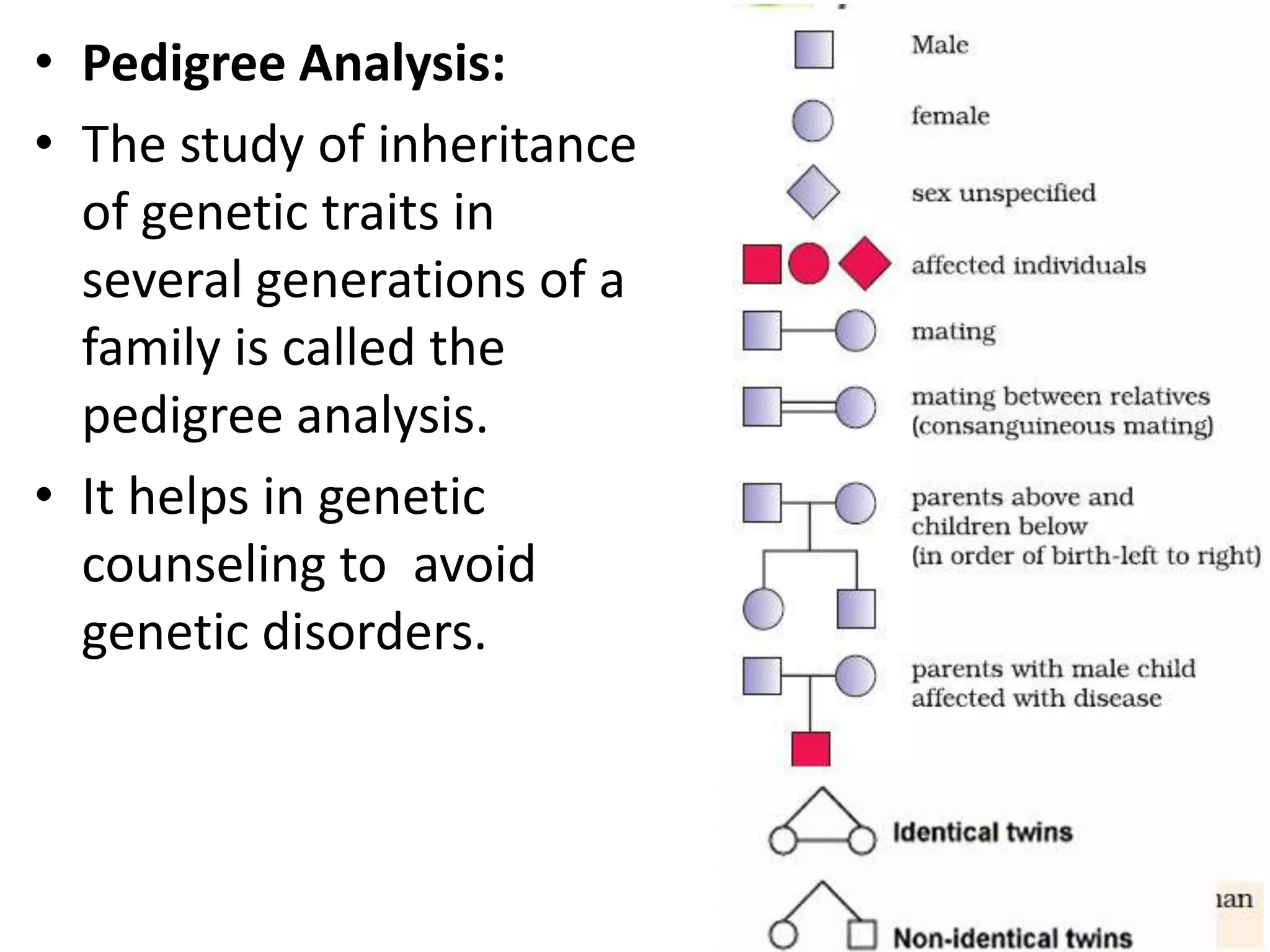
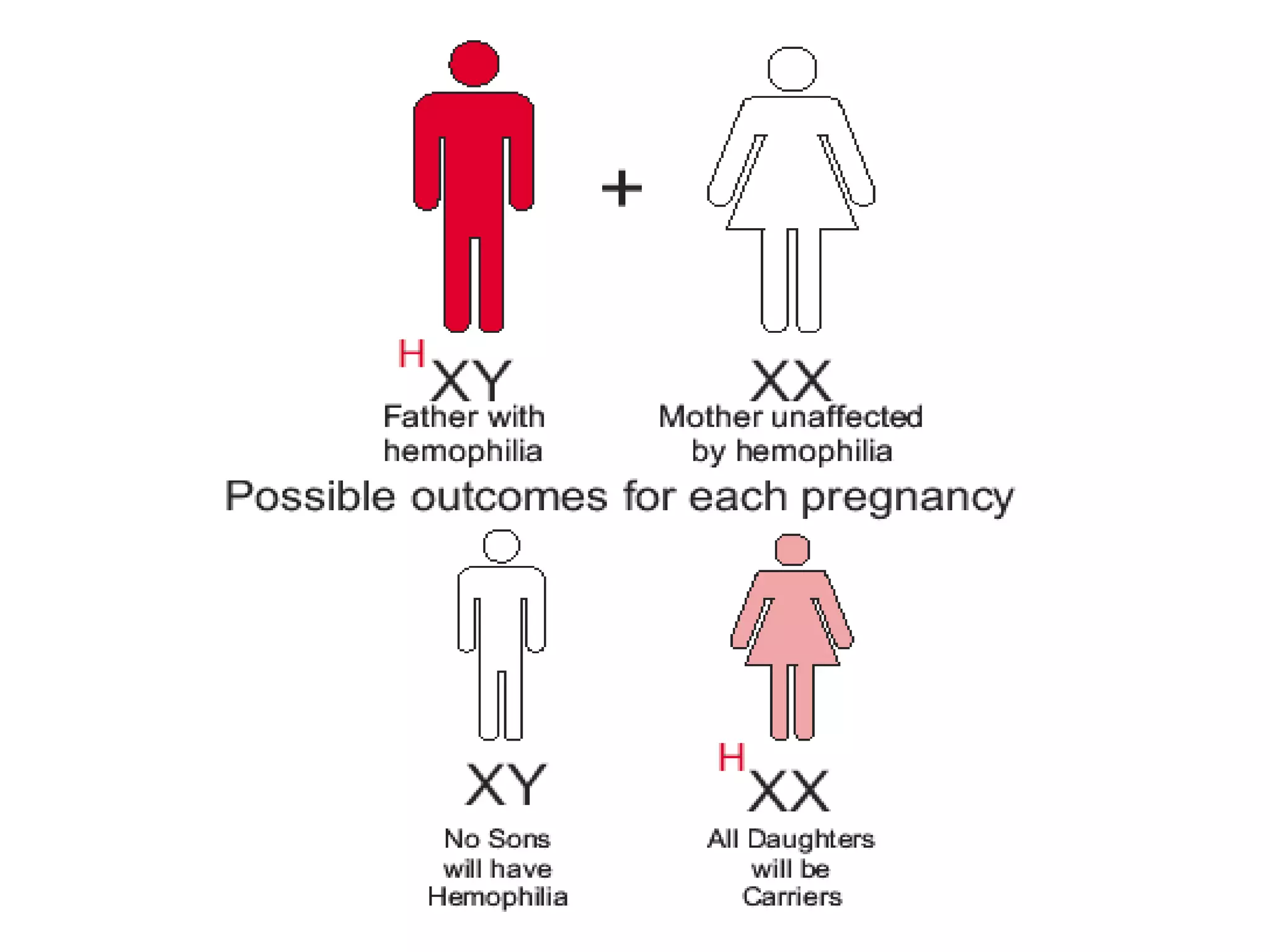
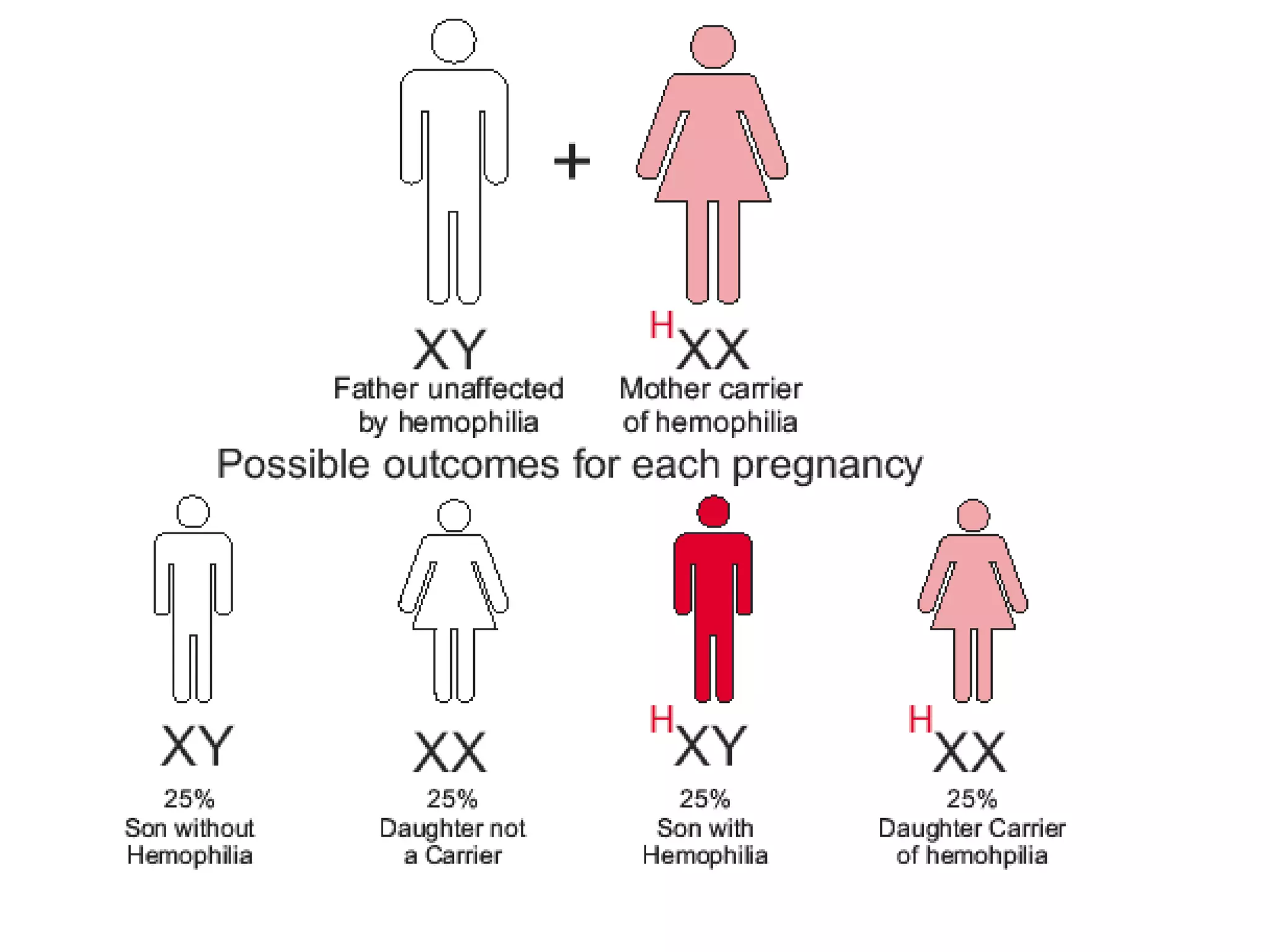
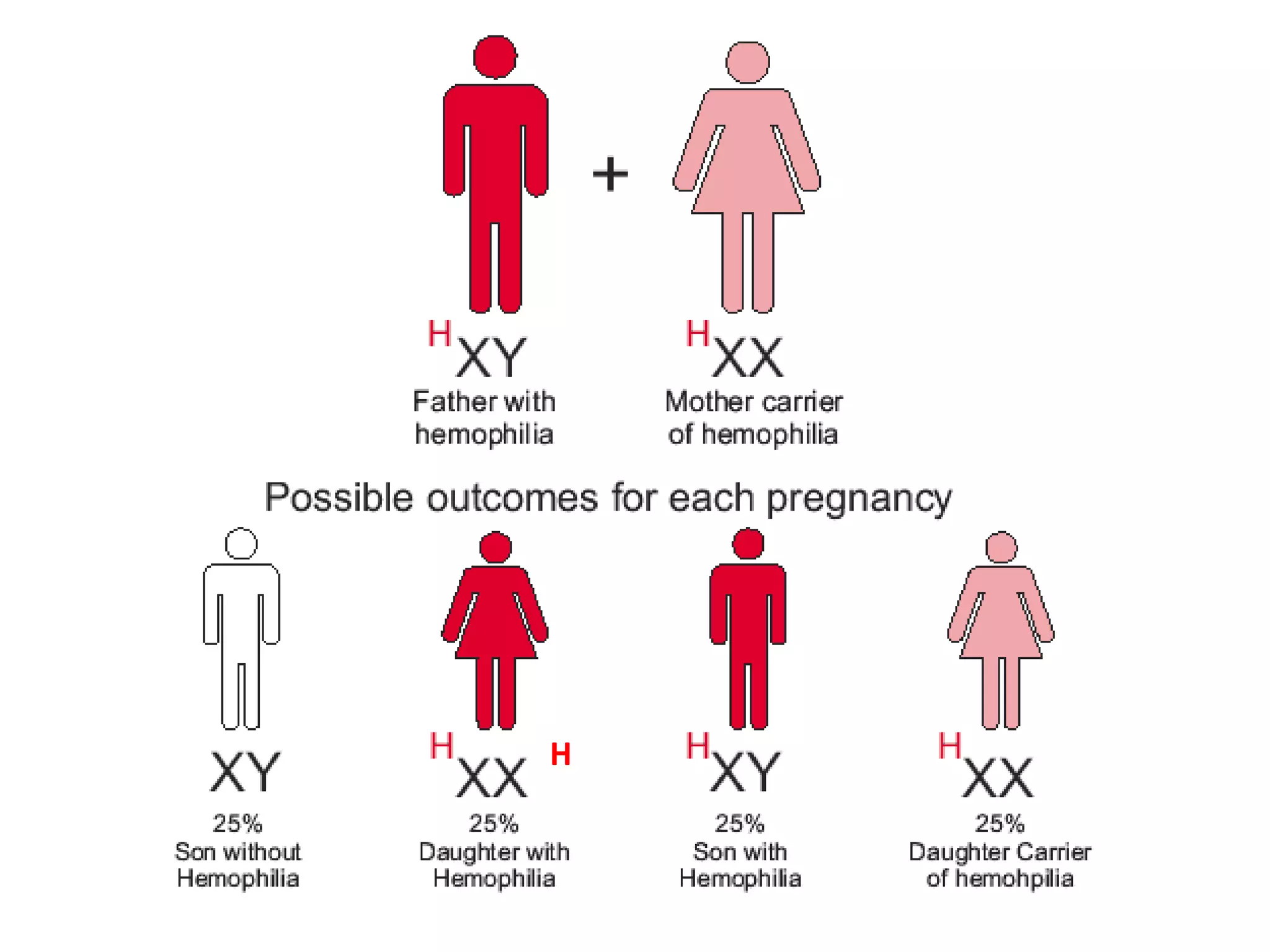
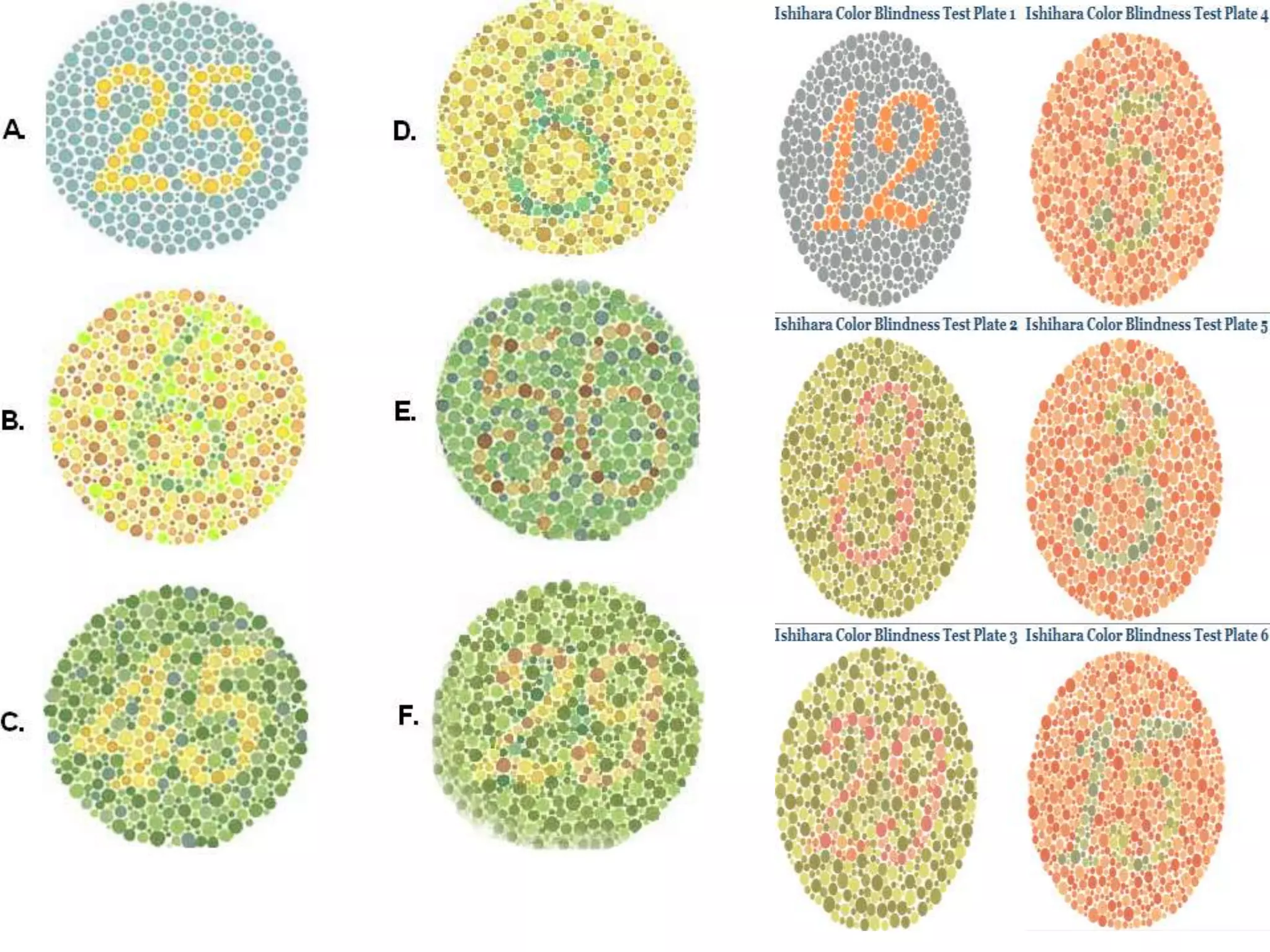
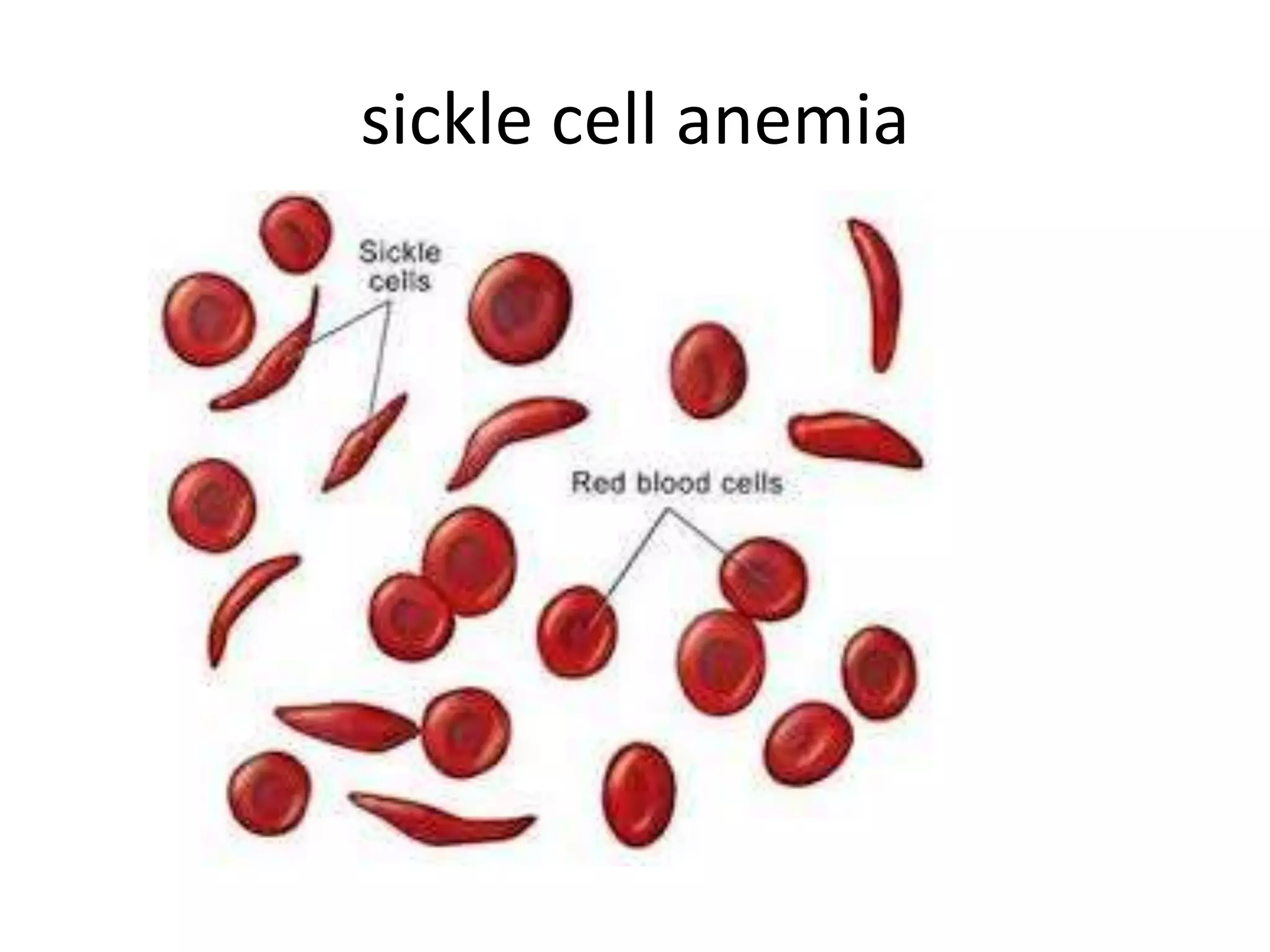
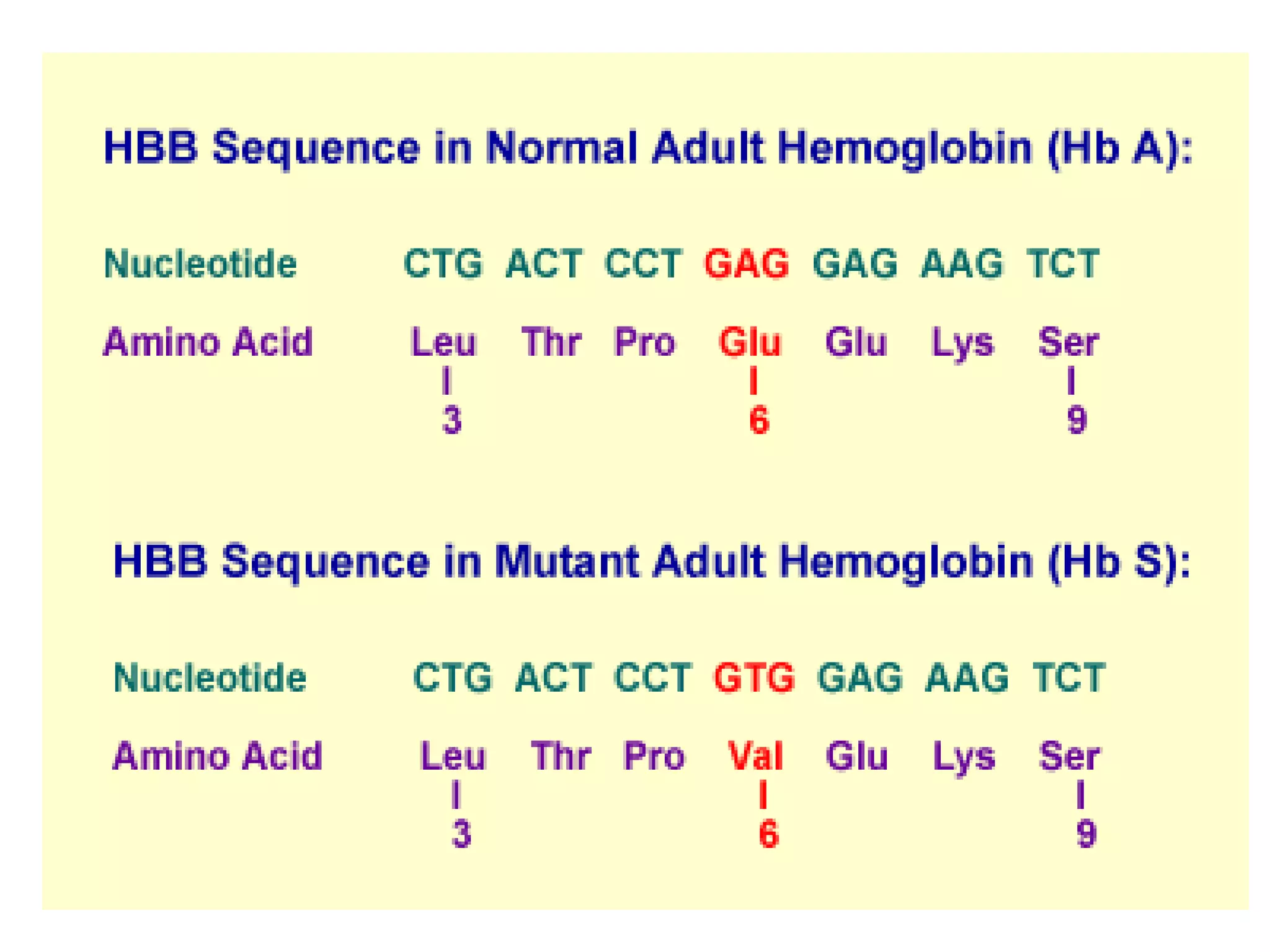
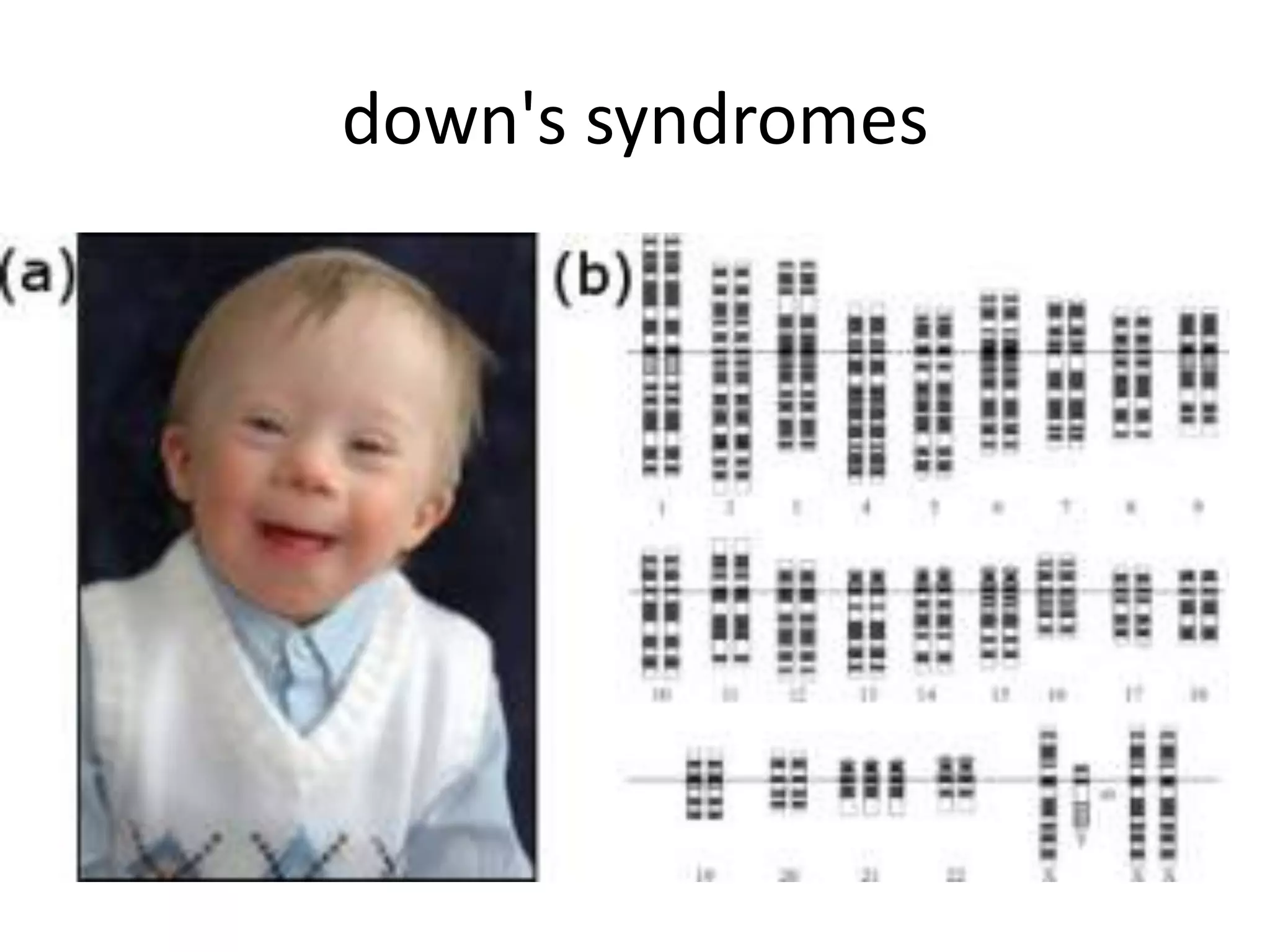
This document summarizes key aspects of Mendelian genetics. It begins by introducing Gregor Mendel, the Austrian monk considered the father of genetics, and his experiments breeding pea plants in the 1860s. Mendel discovered the laws of inheritance by tracking hereditary traits over generations. His work was later combined with the chromosomal theory of inheritance. The document then discusses various genetic concepts like dominant/recessive genes, monohybrid and dihybrid crosses, sex-linked inheritance, and genetic disorders. It provides examples like blood types, color blindness, and hemophilia to illustrate inheritance patterns.