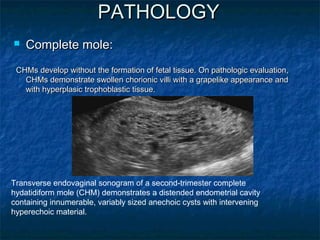
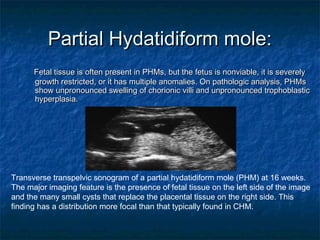
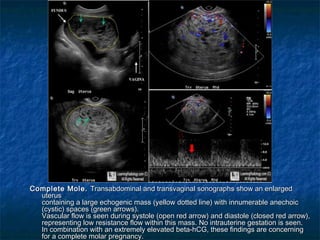
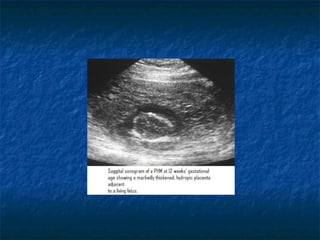
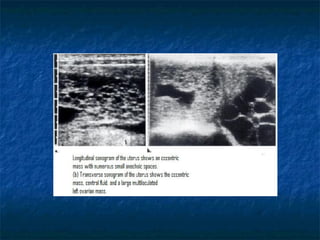
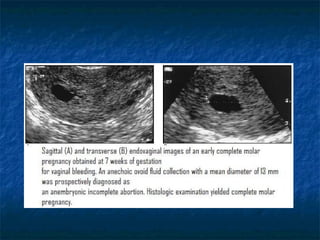
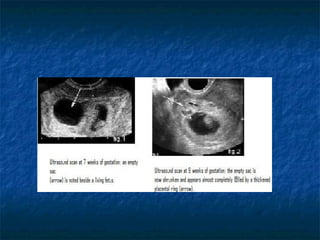
Molar pregnancy is a premalignant condition that occurs after abnormal fertilization and is characterized by swollen chorionic villi. There are two types: complete and partial hydatidiform moles. Complete moles have no fetal tissue and are diploid, while partial moles may contain nonviable fetal tissue and are usually triploid. Symptoms include vaginal bleeding, uterine enlargement, and hyperemesis gravidarum. Complications can include hemorrhage, sepsis, invasive mole, and choriocarcinoma. Diagnosis is made through hCG levels, ultrasound showing cystic spaces without fetal parts, and pathology. Treatment is suction curettage, with follow up hCG monitoring to