This document provides information about Caesarean section (C-section), including its definition, indications, types, and procedures. Some key points:
- A C-section is a surgical procedure to deliver babies through incisions in the abdominal and uterine walls after 28 weeks of pregnancy. Its use has steadily increased to around 25% currently due to various medical and safety factors.
- Indications can be maternal, fetal, or both and include conditions like cephalopelvic disproportion, breech presentation, fetal distress, and previous C-section.
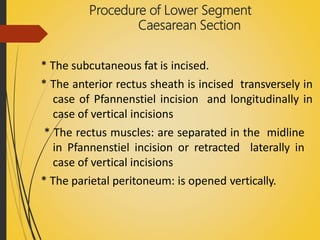
- The two main types are lower segment (transverse incision below the bladder) and upper segment (vertical incision through the upper uterus), with







![FETAL INDICATION
• Fetal distress and cord prolapse
• Breech presentation –[footling, knee presentation,
complicated breech]
• Malpresentation [ brow, transverse lie persistent
mentoposterior ]
• Sever IUGR
• Macrosomia
• Multiple pregnancy[first twin non -vertex and
monoamniotic twin]
• HIV complicating](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/caesareansectionothers-201130095713/85/Caesarean-section-others-8-320.jpg)