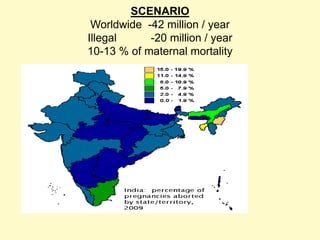
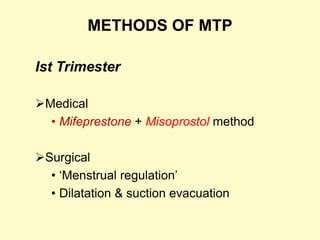
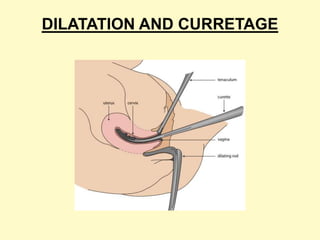
This document discusses medical termination of pregnancy (MTP) in India according to the MTP Act of 1971 and its 2002 amendment. It defines MTP as the deliberate termination of a pregnancy before fetal viability. The MTP Act legalized induced abortions in India and sets guidelines for gestational age limits, medical reasons, and certification of medical practitioners performing MTP. Common first and second trimester MTP methods include medical procedures using mifepristone and misoprostol or surgical dilation and curettage. Complications of MTP can include hemorrhage, perforation, incomplete evacuation, and sepsis.