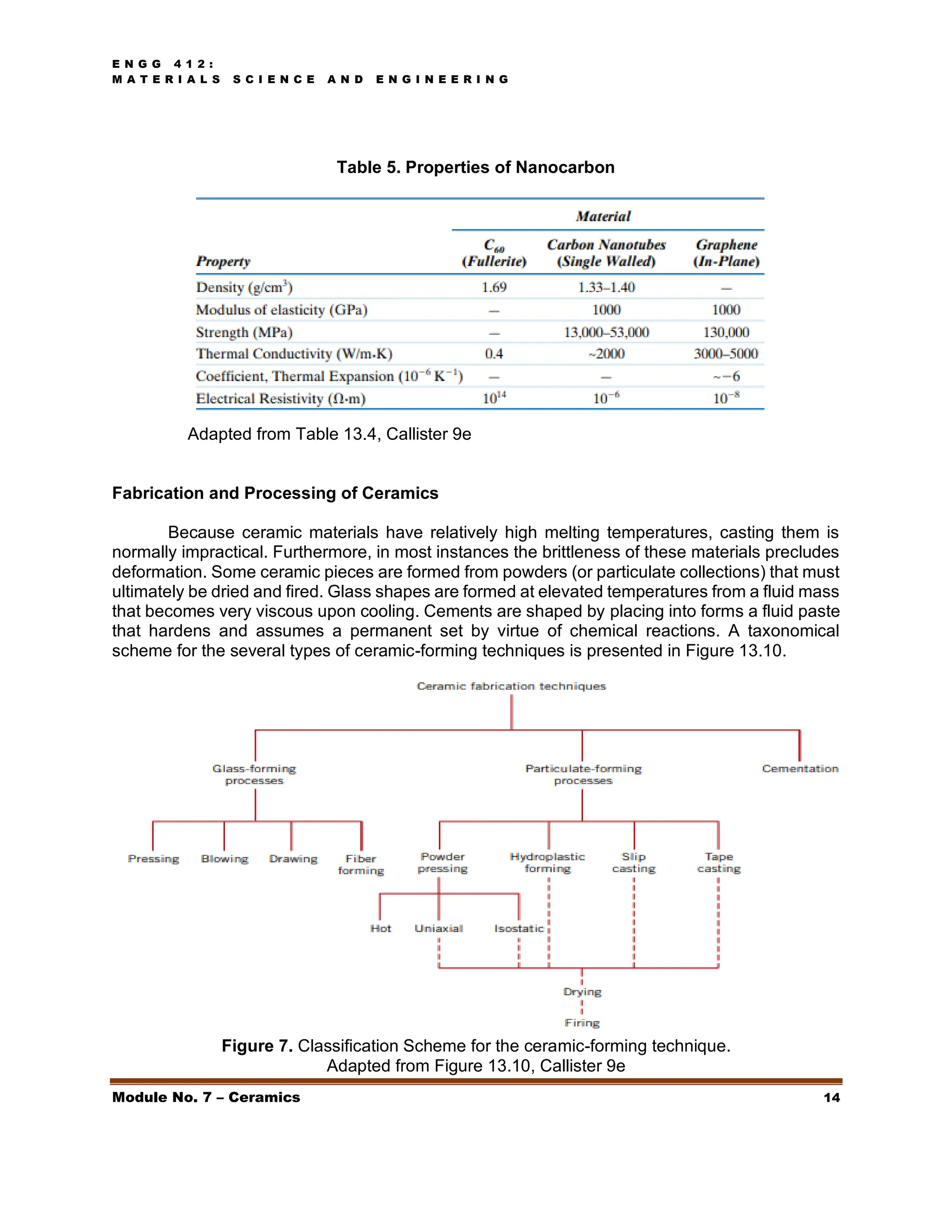
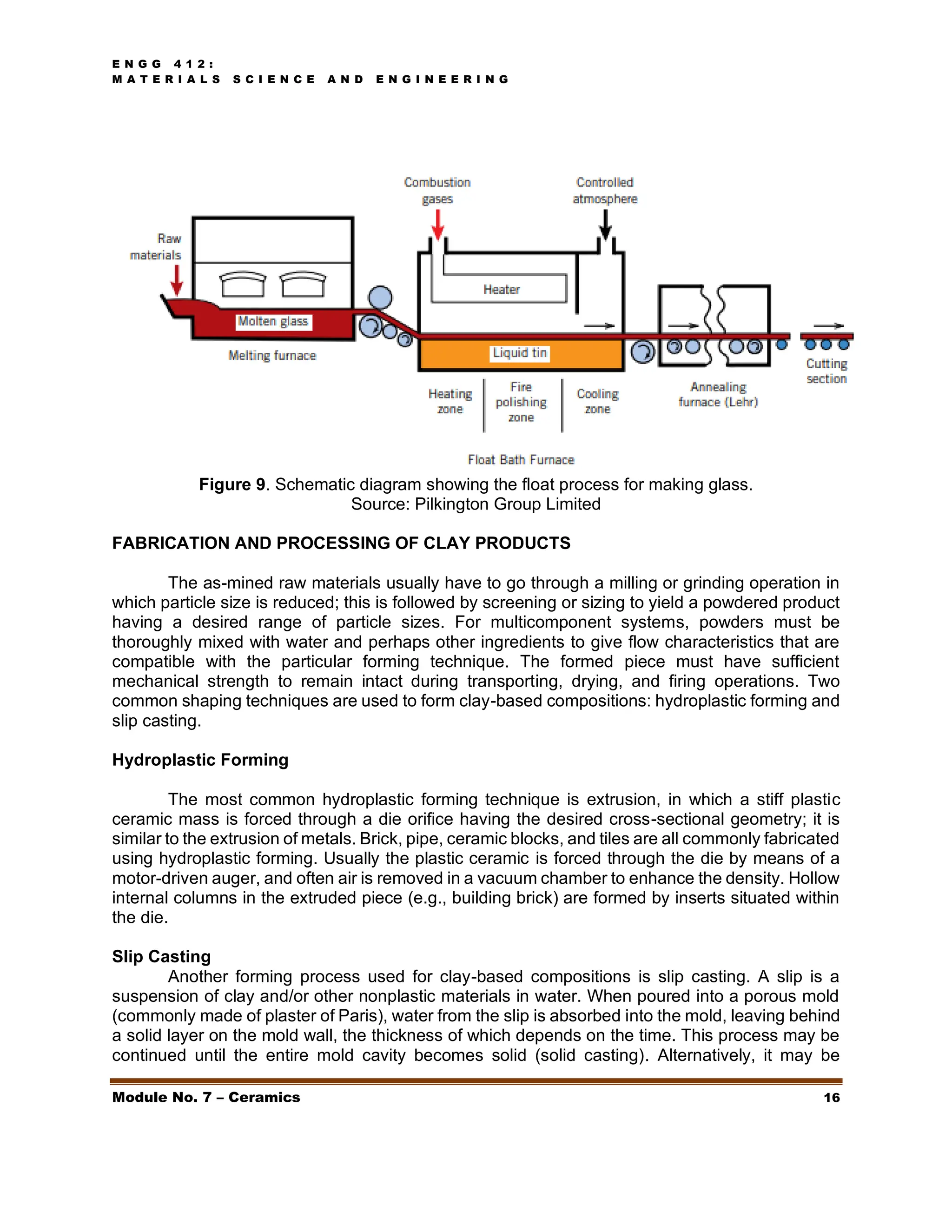
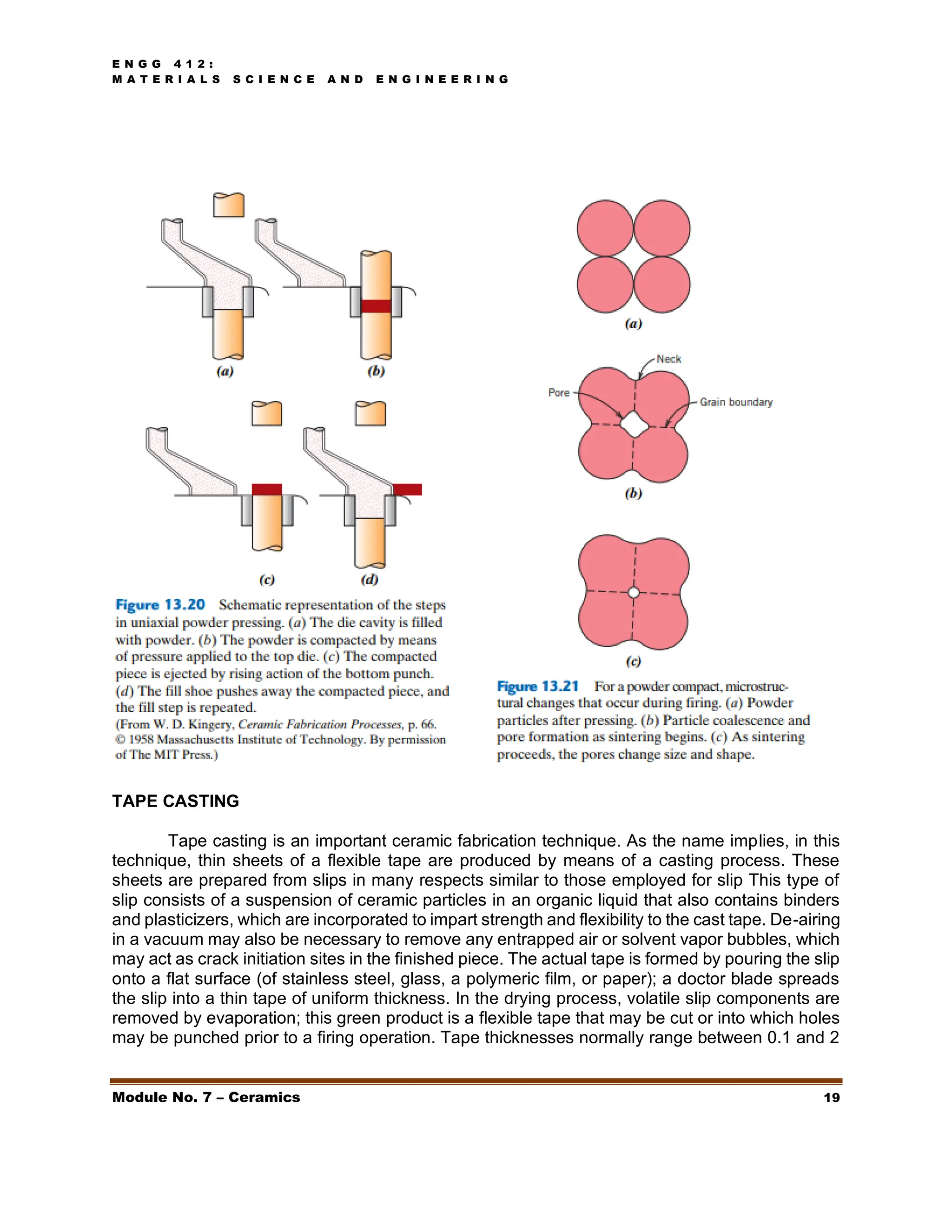
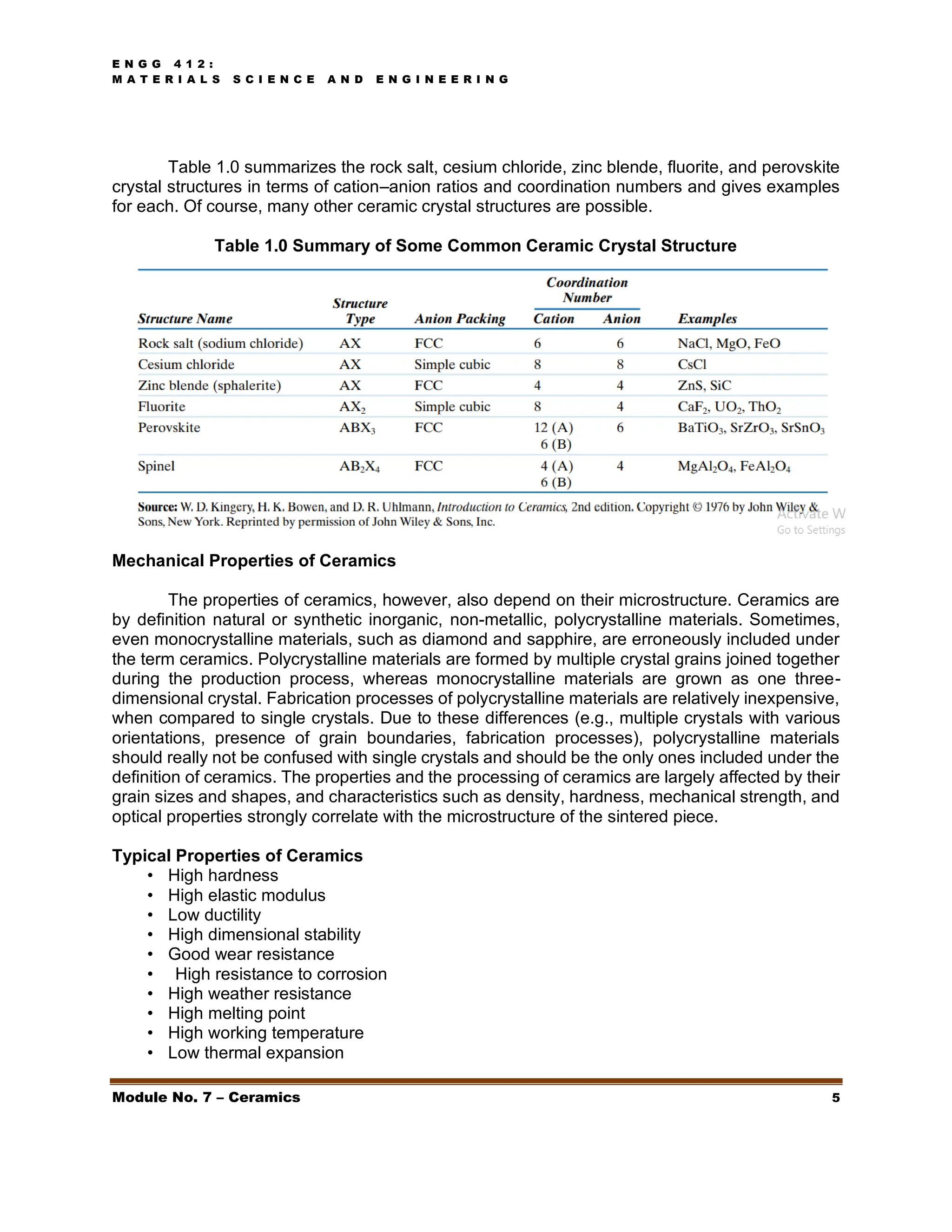
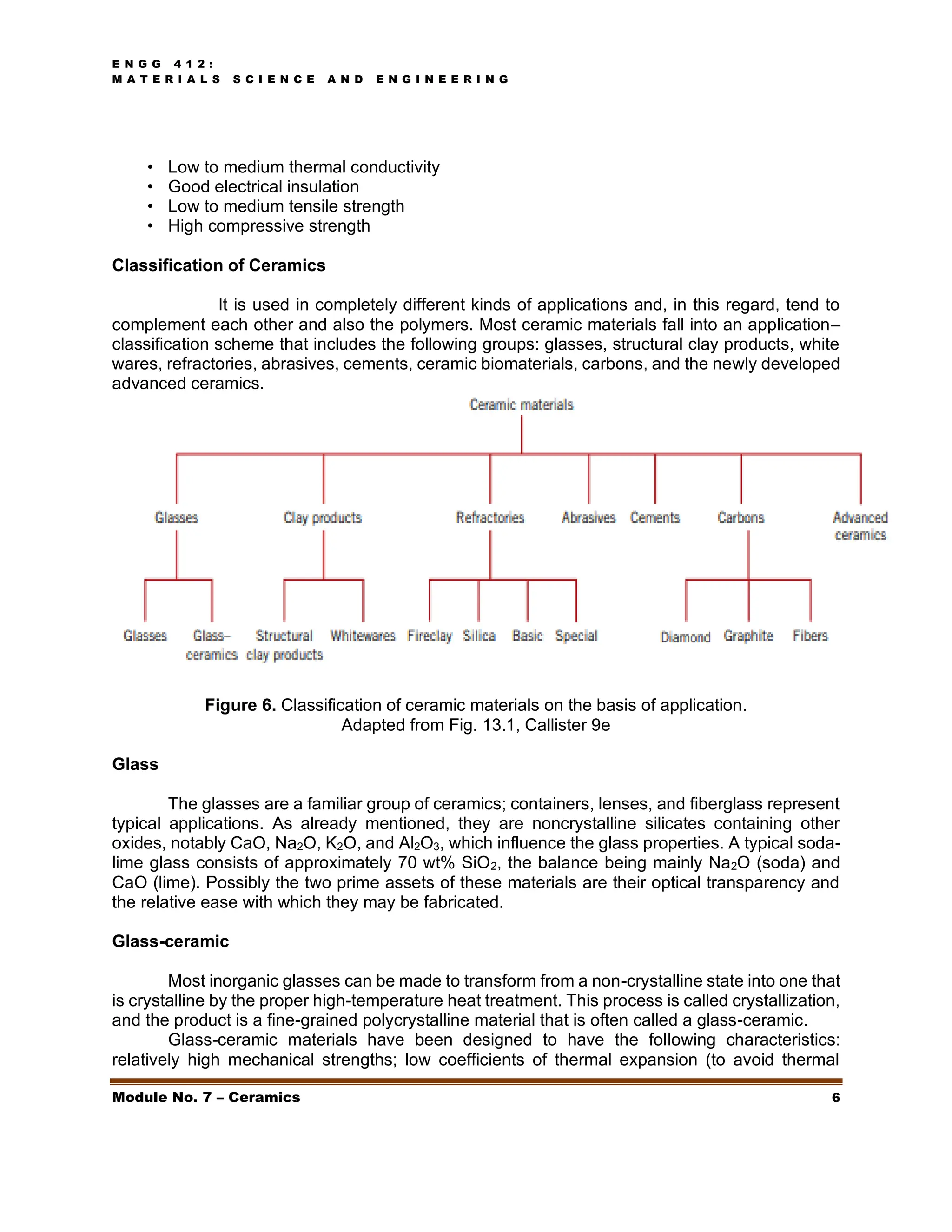
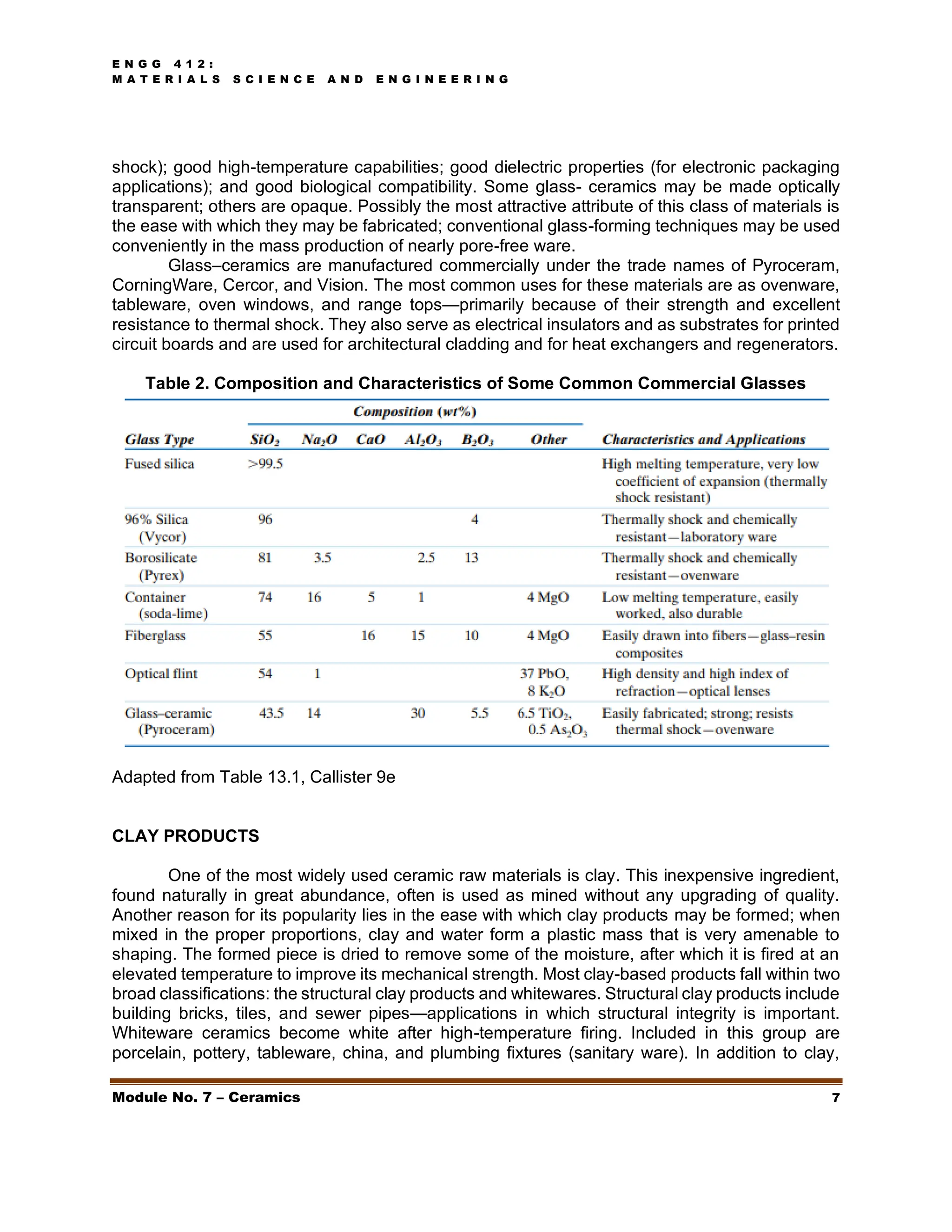
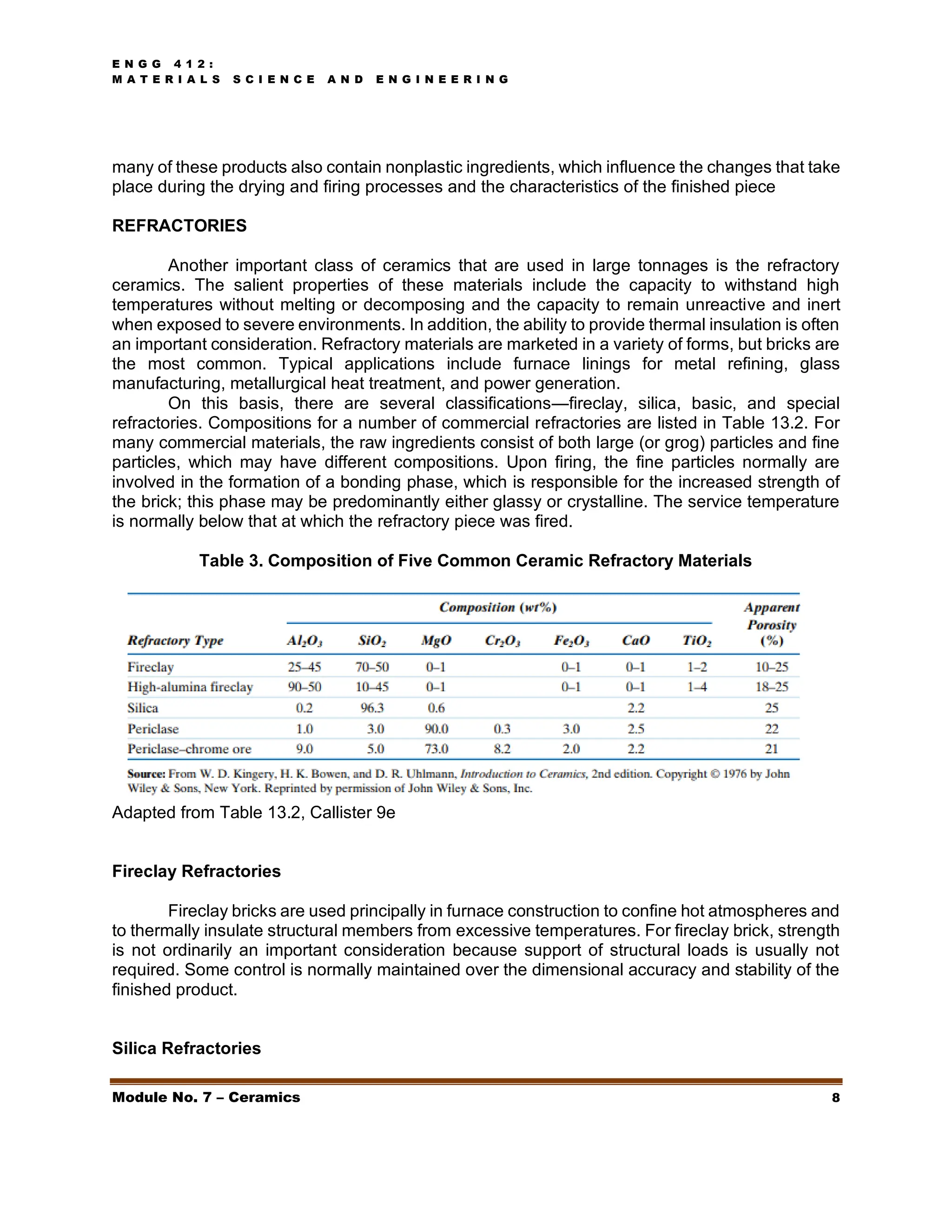
This document discusses ceramics, including their structures, properties, classifications, and applications. Ceramics are inorganic materials made by shaping and hardening compounds with heat. They are hard, corrosion-resistant, and brittle. Ceramics form ionic or covalent bonds and various crystal structures that give them useful properties but also brittleness. Major ceramic classes include glasses, clay products, refractories, advanced ceramics, and more. Each has distinct compositions and applications like containers, bricks, furnace linings.






![E N G G 4 1 2 :
M A T E R I A L S S C I E N C E A N D E N G I N E E R I N G
Module No. 7 – Ceramics 13
graphene) that is rolled into a tube. The term single-walled carbon nanotube (abbreviated
SWCNT) is used to denote this structure. Each nanotube is a single molecule composed of
millions of atoms; the length of this molecule is much greater (on the order of thousands of times
greater) than its diameter. Multiple-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) consisting of concentric
cylinders also exist.
Nanotubes are extremely strong and stiff and relatively ductile. For single-walled
nanotubes, measured tensile strengths range between 13 and 53 GPa (approximately an order
of magnitude greater than for carbon fibers—viz. 2 to 6 GPa); this is one of the strongest known
materials. Elastic modulus values are on the order of one terapascal [TPa (1 TPa =103
GPa)],
with fracture strains between about 5% and 20%. Furthermore, nanotubes have relatively low
densities.
Carbon nanotubes also have unique and structure-sensitive electrical characteristics.
Depending on the orientation of the hexagonal units in the graphene plane (i.e., tube wall) with
the tube axis, the nanotube may behave electrically as either a metal or a semiconductor. As a
metal, they have the potential for use as wiring for small-scale circuits. In the semiconducting
state they may be used for transistors and diodes. Furthermore, nanotubes are excellent electric
field emitters. As such, they can be used for flat-screen displays (e.g., television screens and
computer monitors).
Graphene
Graphene, the newest member of the nanocarbons, is a single-atomic-layer of graphite,
composed of hexagonally sp2 bonded carbon atoms (Figure 13.9). These bonds are extremely
strong, yet flexible, which allows the sheets to bend.
Two characteristics of graphene make it an exceptional material. First is the perfect order
found in its sheets—no atomic defects such as vacancies exist; also these sheets are extremely
pure—only carbon atoms are present. The second characteristic relates to the nature of the
unbonded electrons: at room temperature, they move much faster than conducting electrons in
ordinary metals and semiconducting materials.
In terms of its properties graphene could be labeled the ultimate material. It is the strongest
known material (~130 GPa), the best thermal conductor (~5000 W/mK), and has the lowest
electrical resistivity (10-8
Ωm)—that is, is the best electrical conductor. Furthermore, it is
transparent, chemically inert, and has a modulus of elasticity comparable to the other
nanocarbons (~1 TPa).
Given this set of properties, the technological potential for graphene is enormous, and it
is expected to revolutionize many industries to include electronics, energy, transportation,
medicine/biotechnology, and aeronautics. However, before this revolution can begin to be
realized, economical and reliable methods for the mass production of graphene must be devised.
The following is a short list of some of these potential applications for graphene: electronics—
touch-screens, conductive ink for electronic printing, transparent conductors, transistors, heat
sinks; energy—polymer solar cells, catalysts in fuel cells, battery electrodes, supercapacitors;
medicine/biotechnology—artificial muscle, enzyme and DNA biosensors, photoimaging;
aeronautics—chemical sensors (for explosives) and nanocomposites for aircraft structural
components.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module-7-240402160306-c5155b0d/75/Module-7-Ceramics-Structures-and-properties-of-ceramics-13-2048.jpg)