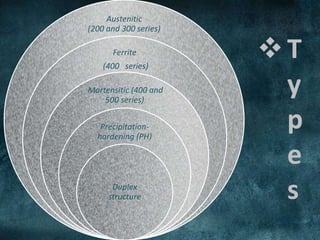
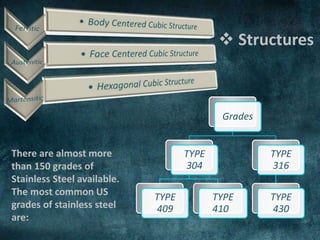
The document discusses stainless steel, highlighting its history, composition, types, and various properties such as corrosion resistance, strength, and ductility. It outlines common grades of stainless steel and their mechanical, chemical, and physical properties, along with applications in industries like medical, automotive, and construction. Advantages include hygiene and aesthetic appeal, while disadvantages mention challenges in welding and high costs.