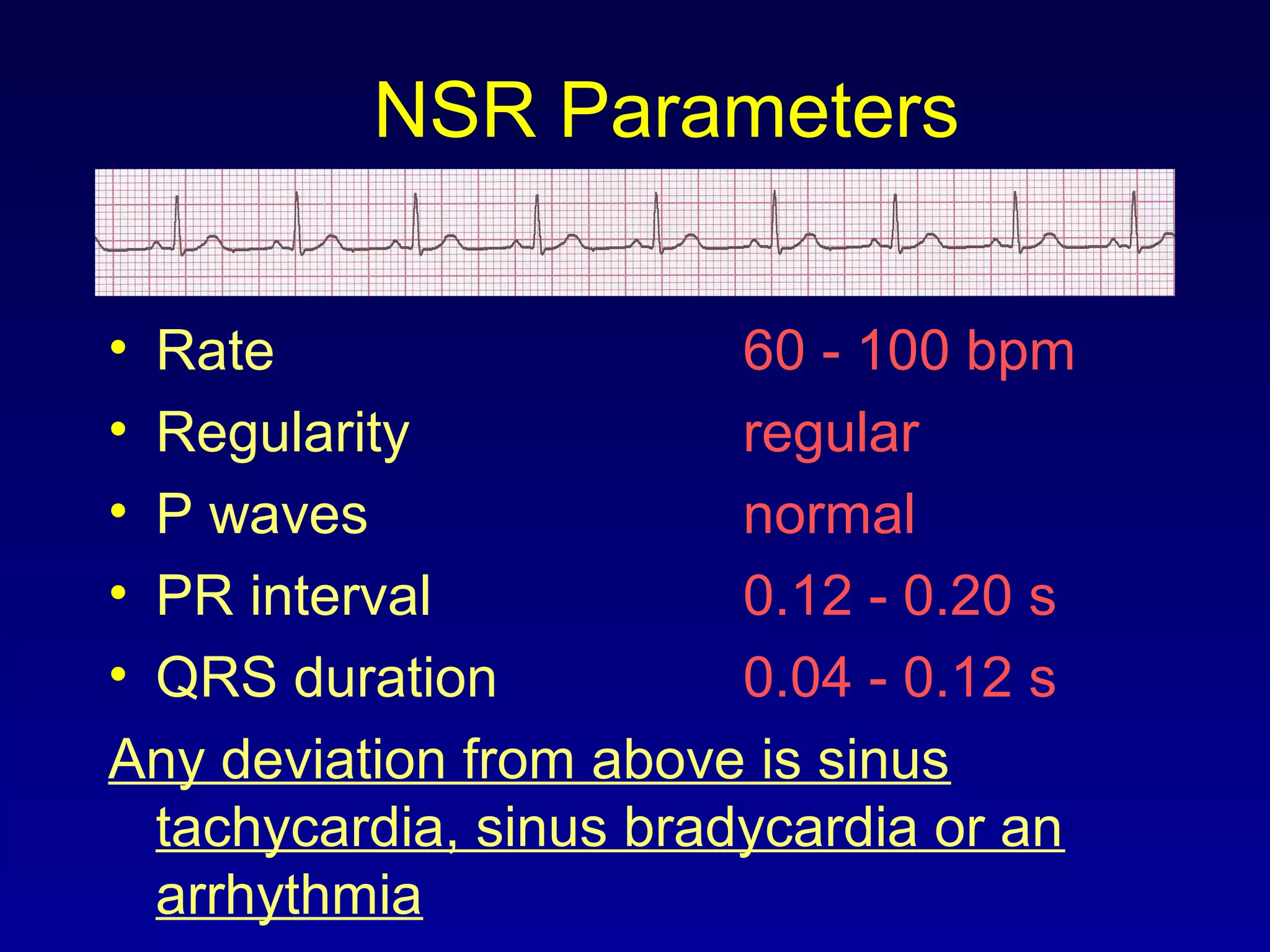
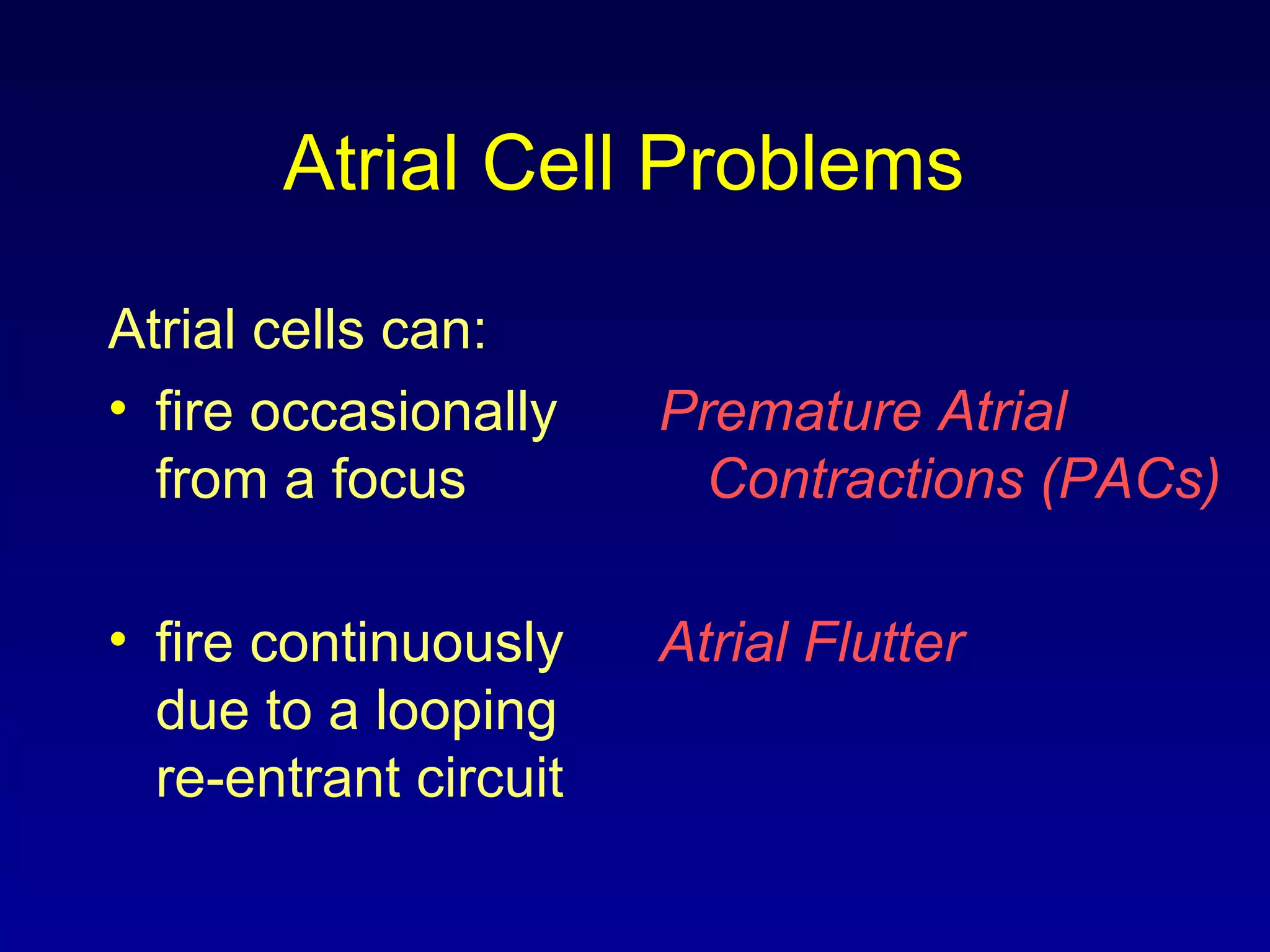
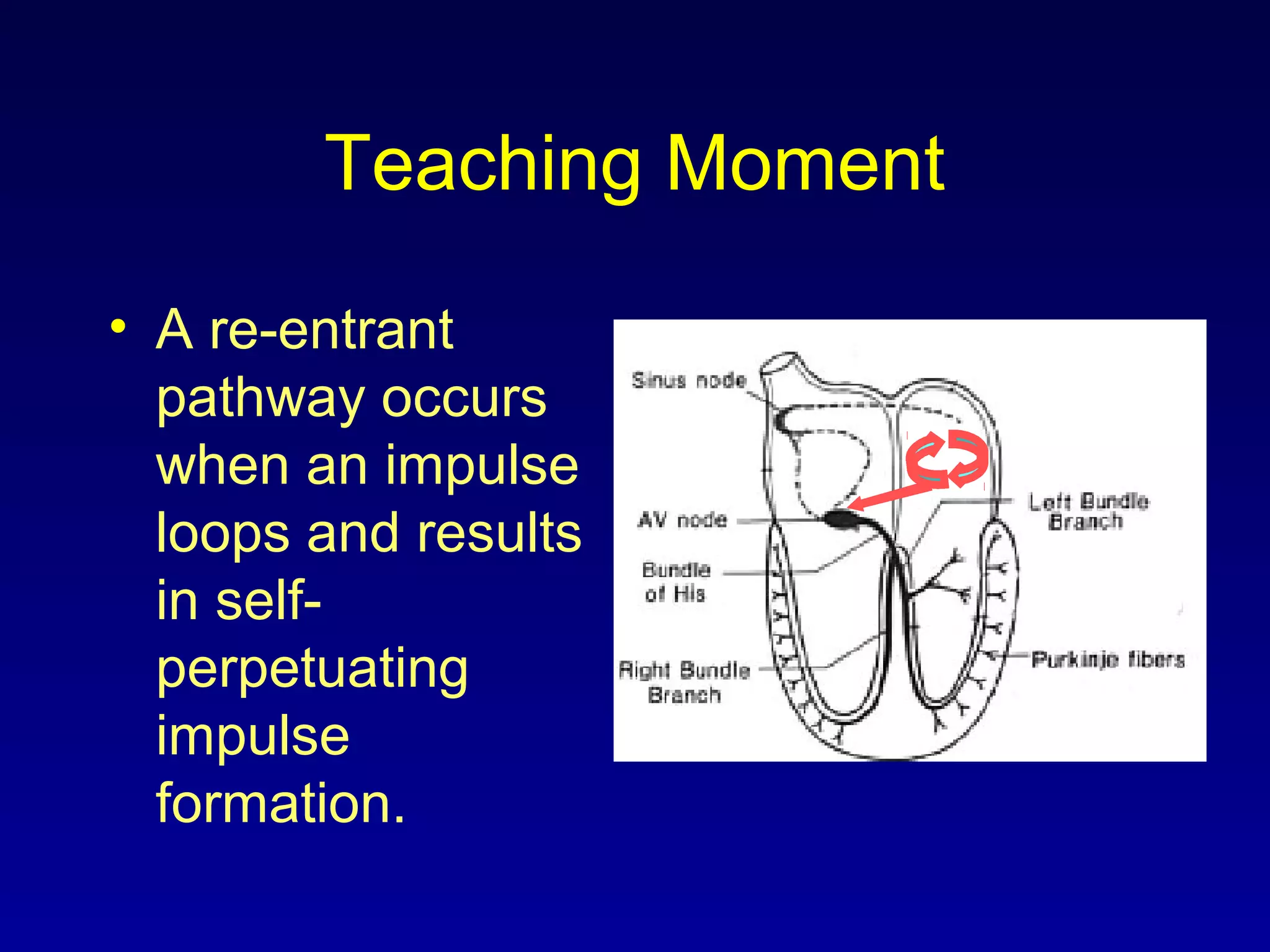
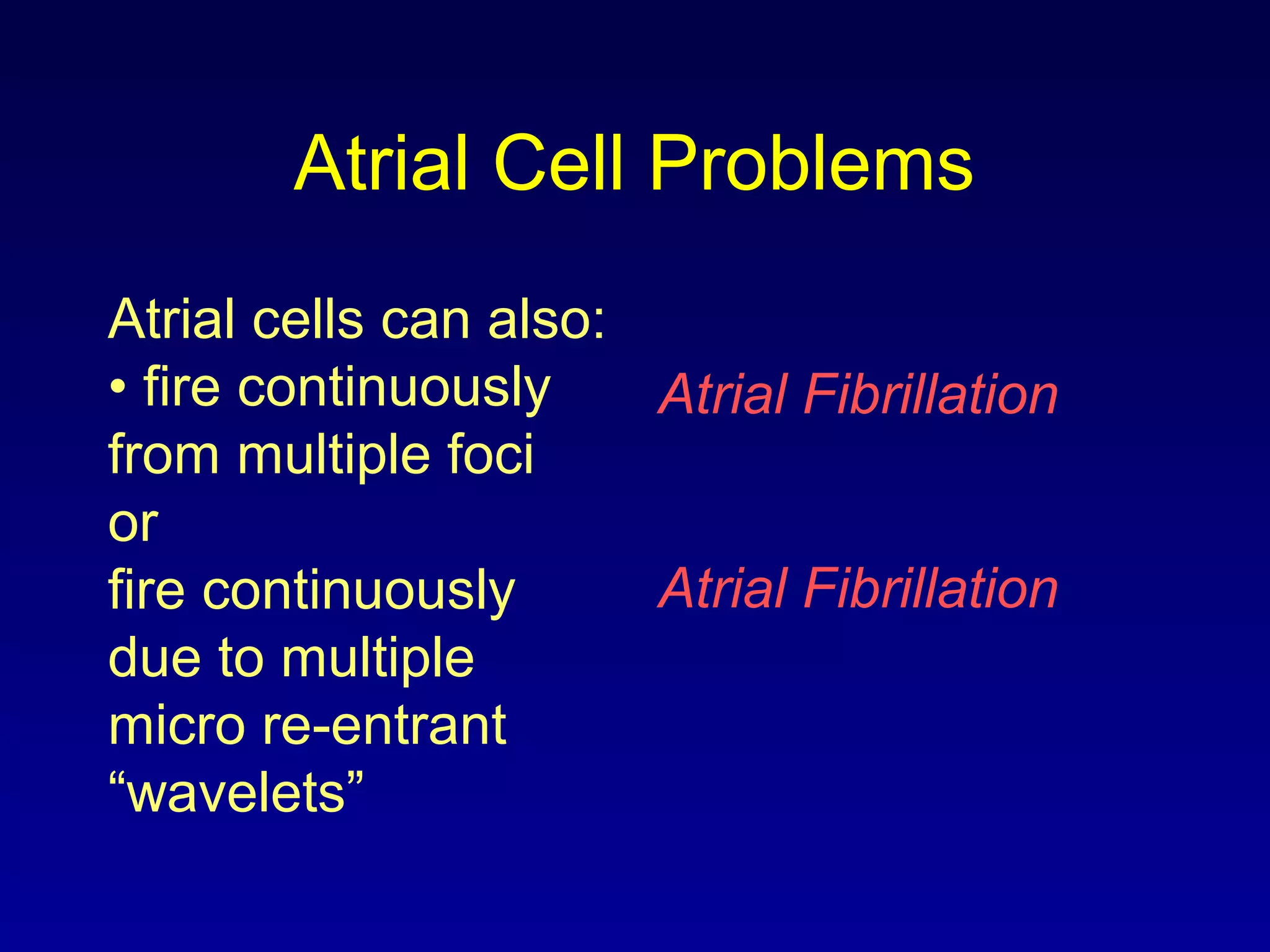
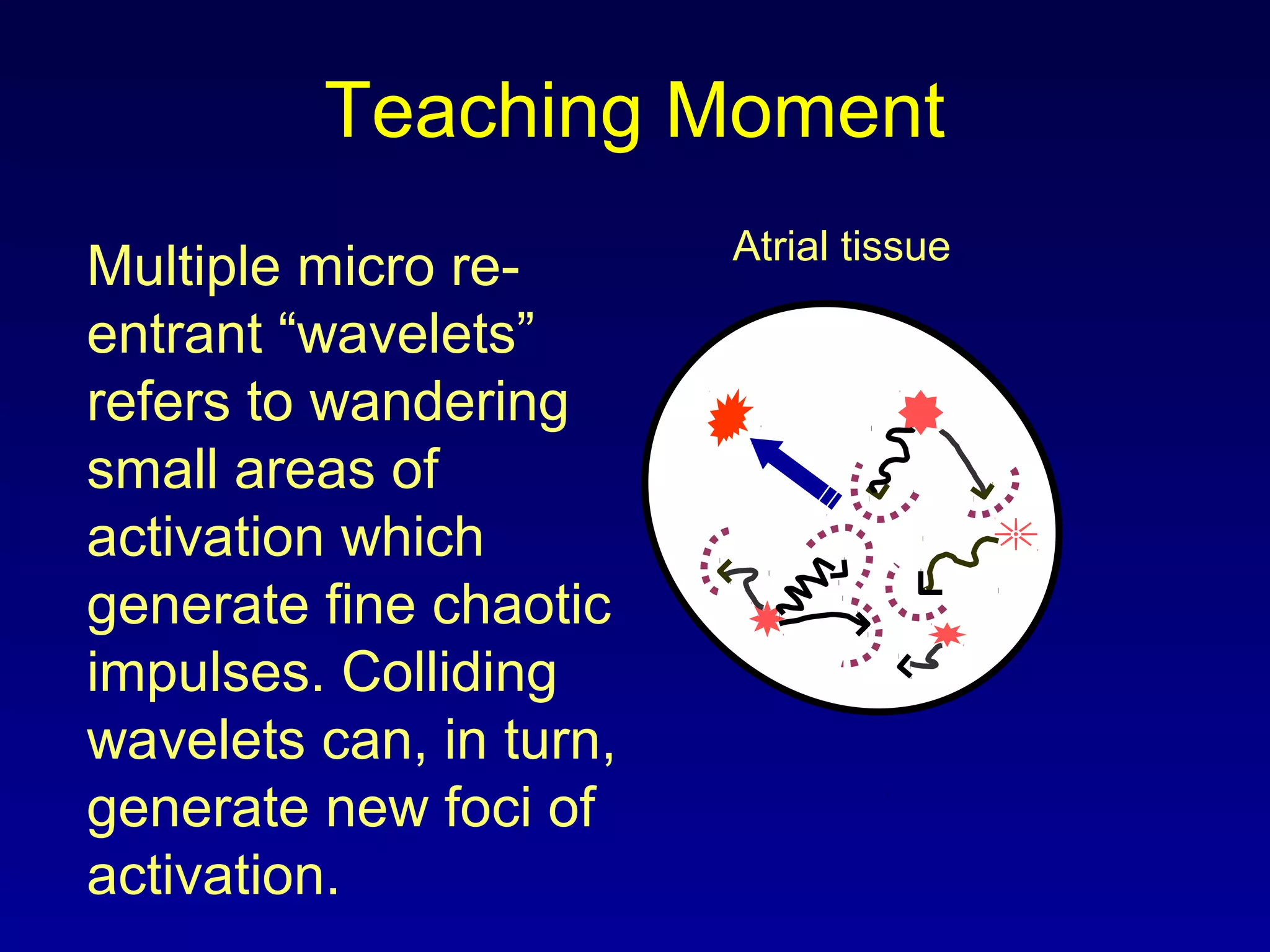
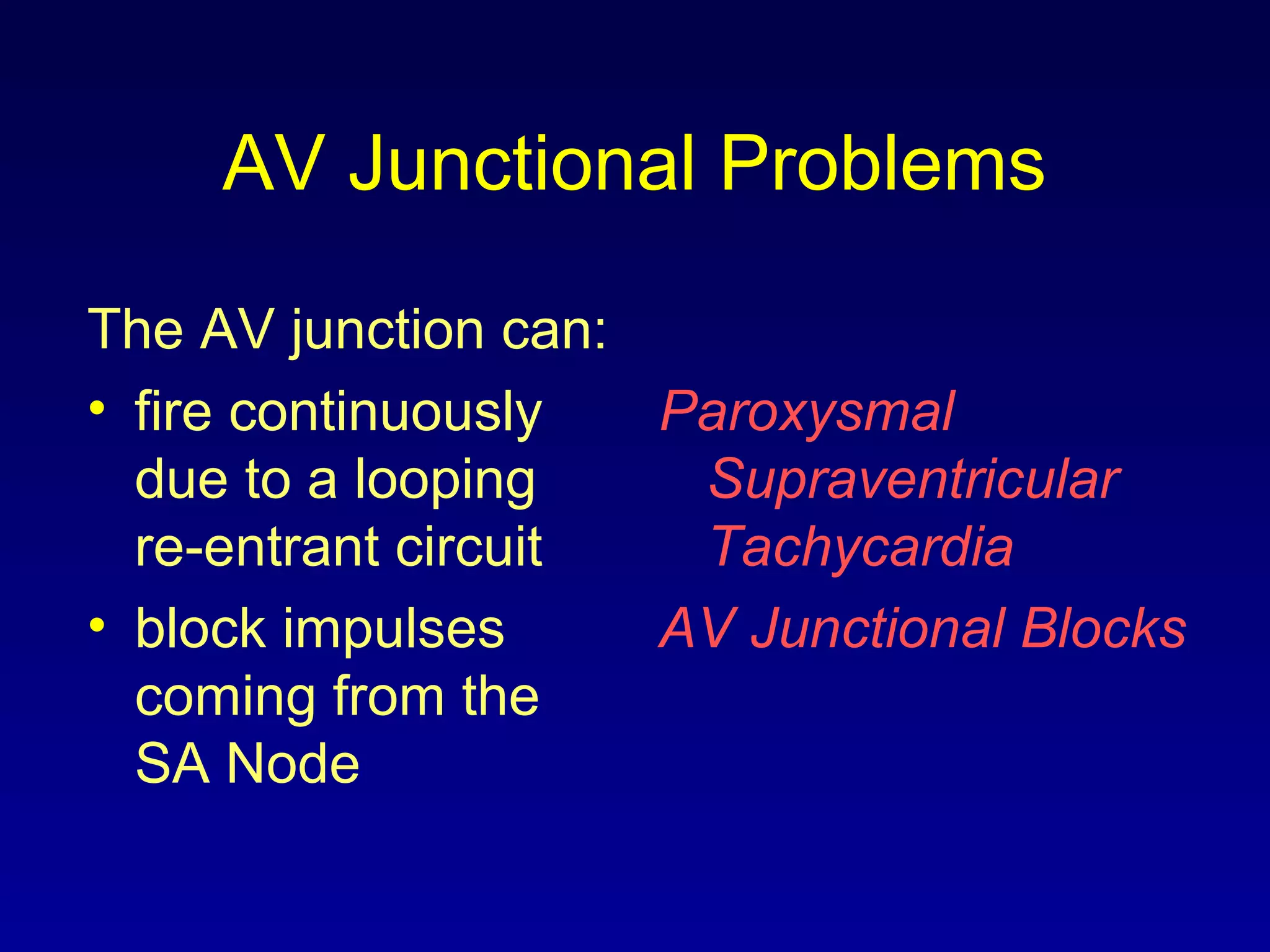
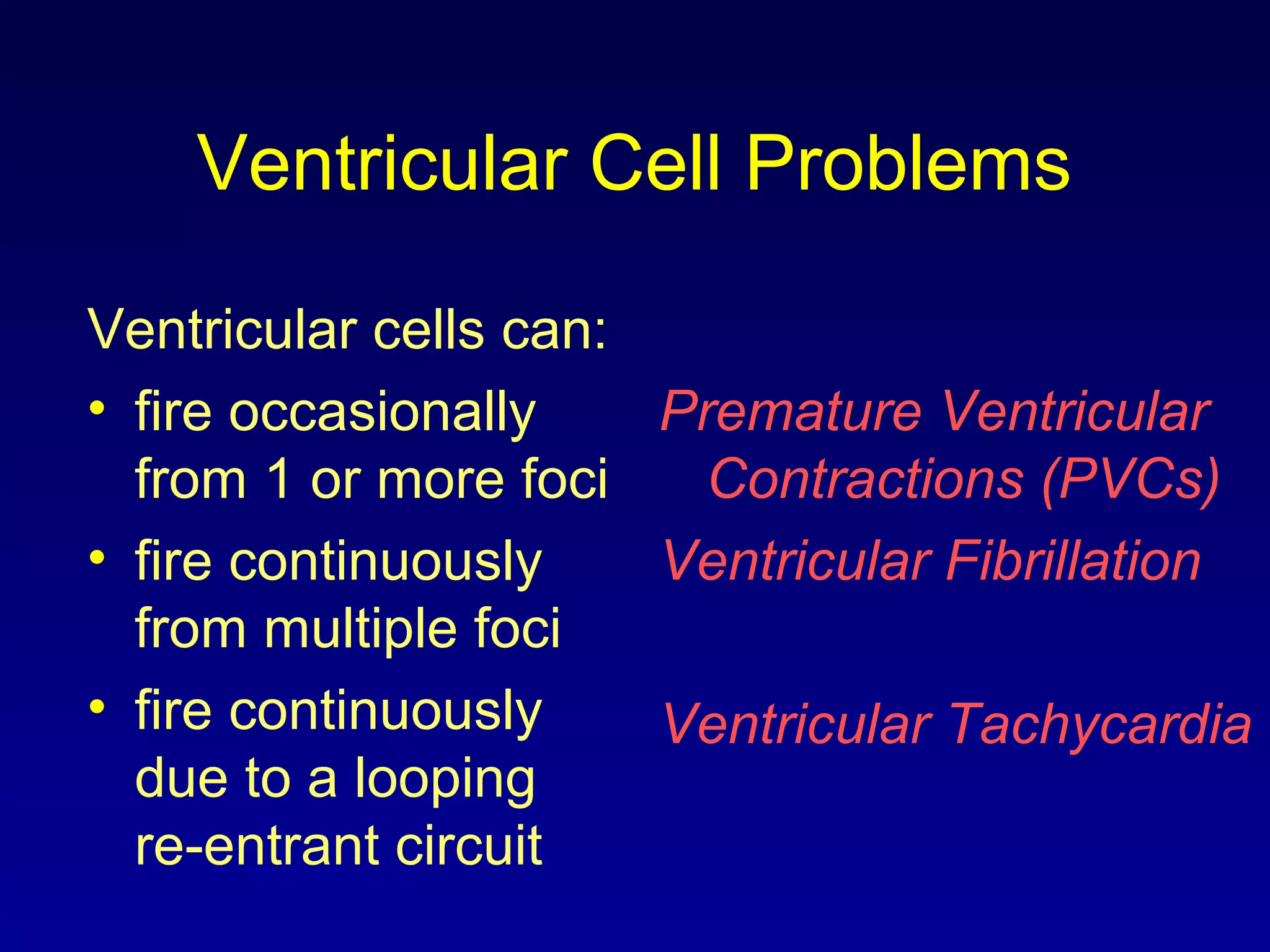
This document provides an overview of a course on ECG rhythm interpretation. The course objectives are to recognize normal sinus rhythm, 13 common rhythm disturbances, and diagnose a myocardial infarction on an ECG. The learning modules cover ECG basics, rhythm analysis, normal sinus rhythm, heart arrhythmias, myocardial infarction diagnosis, and advanced 12-lead interpretation. The document defines normal sinus rhythm and describes parameters for rate, regularity, P waves, and QRS duration. It also explains how arrhythmias can arise from problems in the sinus node, atrial cells, AV junction, or ventricular cells.