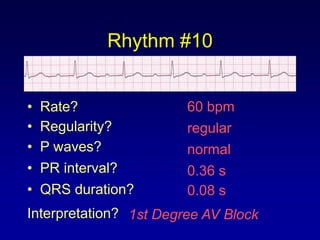
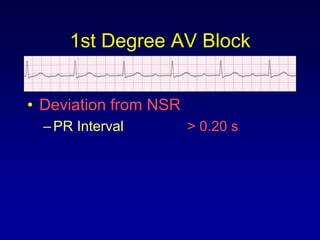
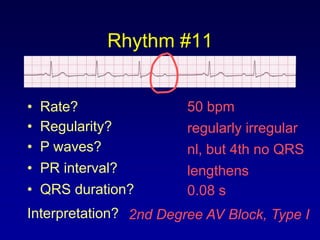
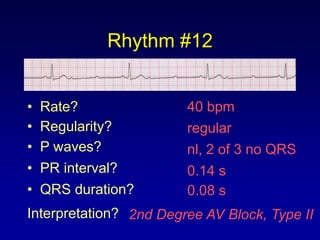
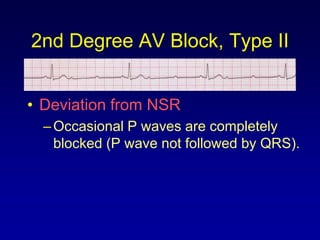
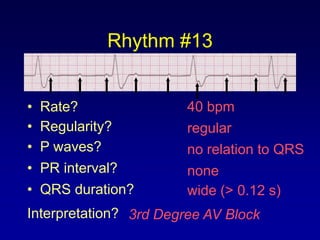
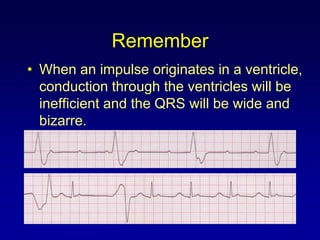
This document provides an overview of AV junctional blocks, including first, second, and third degree blocks. It defines each type of block, describes how they deviate from normal sinus rhythm, and provides their etiologies. Rhythms illustrating each type of block are presented along with their interpretations. It is intended to teach the reader how to recognize and understand different types of AV junctional blocks.