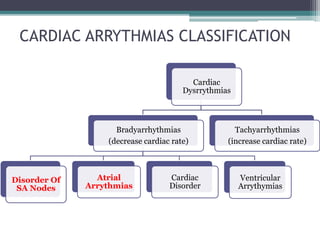
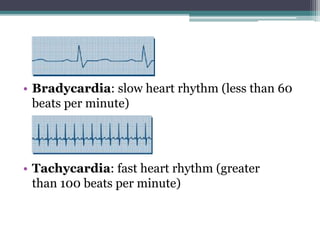
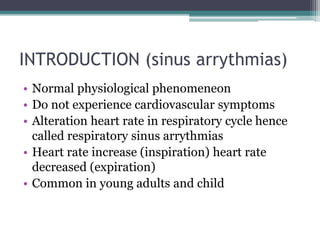
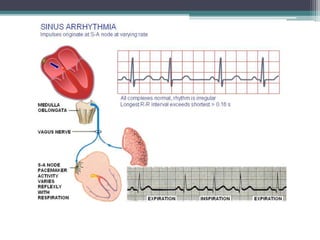
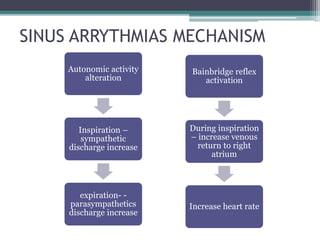
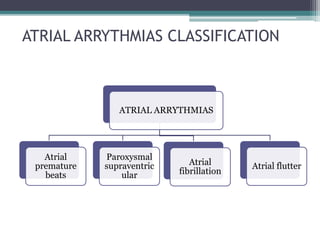
This document discusses sinus and atrial arrhythmias. It classifies cardiac arrhythmias as bradyarrhythmias which decrease heart rate or tachyarrhythmias which increase heart rate. Sinus arrhythmias are a normal phenomenon where the heart rate increases with inspiration and decreases with expiration due to autonomic influences. Atrial arrhythmias include atrial premature beats, paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, atrial flutter, and atrial fibrillation which are abnormalities in the atria and can be caused by ectopic foci or reentry pathways. The mechanisms, ECG patterns, and classifications of these sinus and atrial arrhythmias are explained.