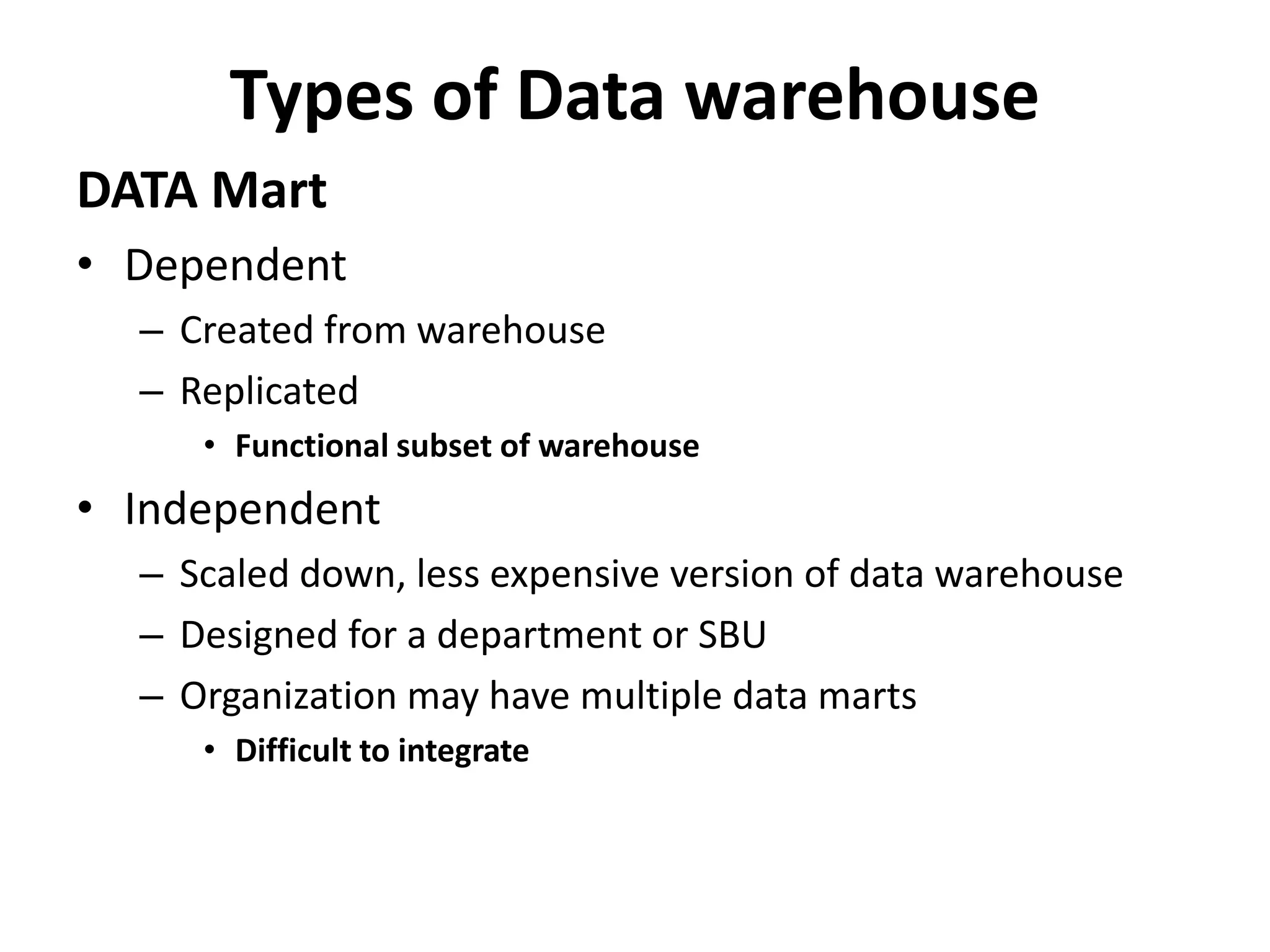
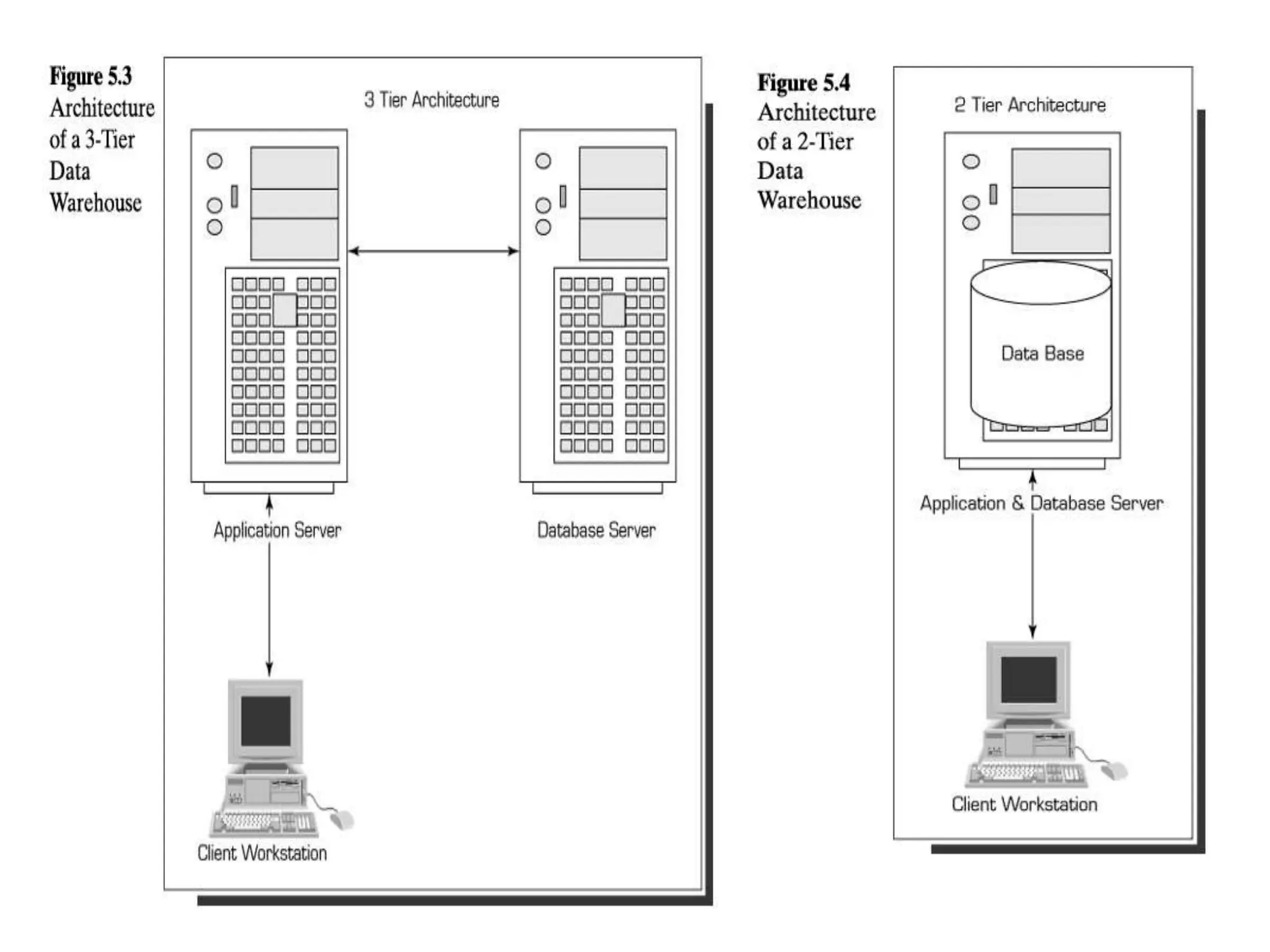
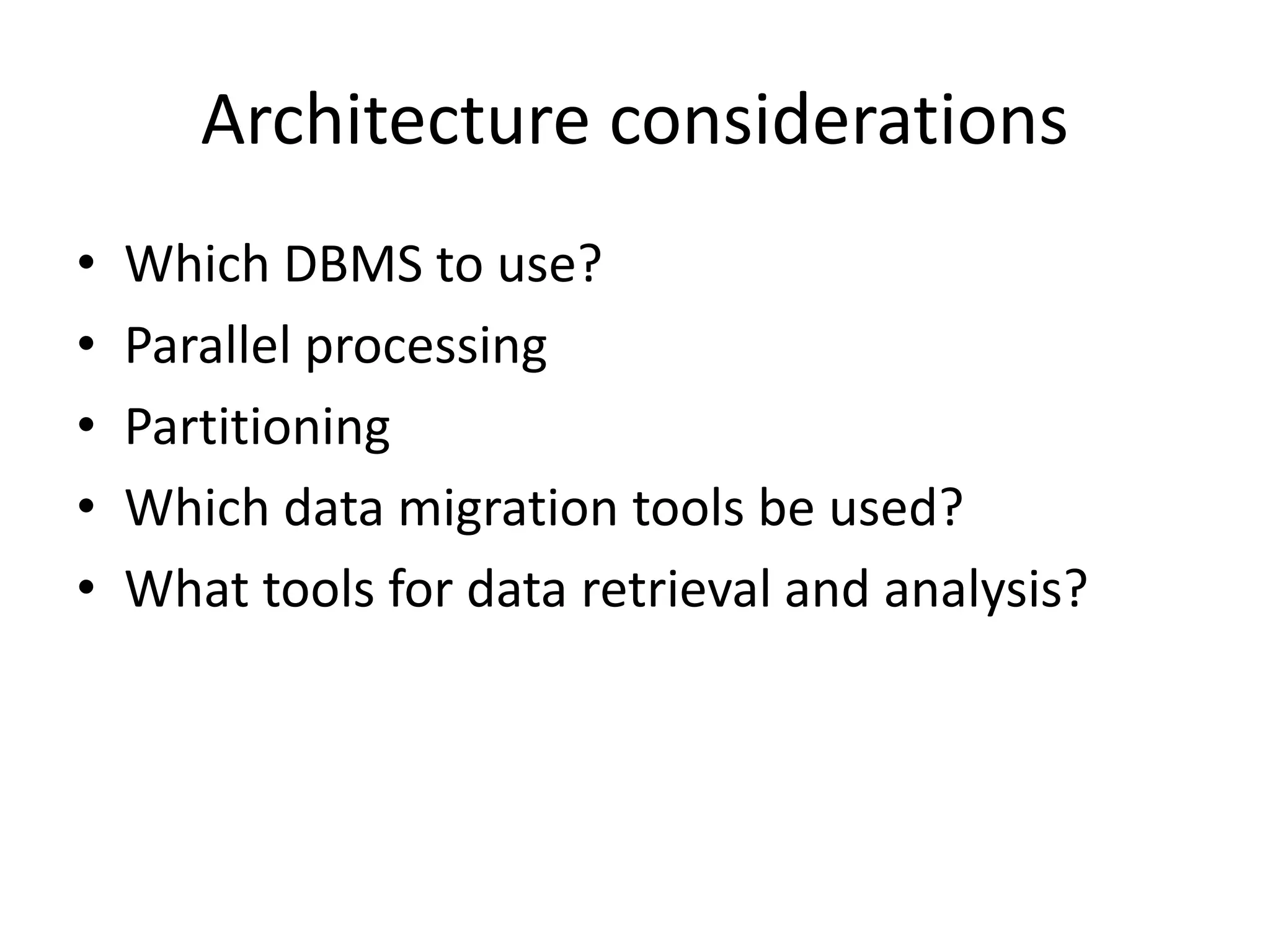
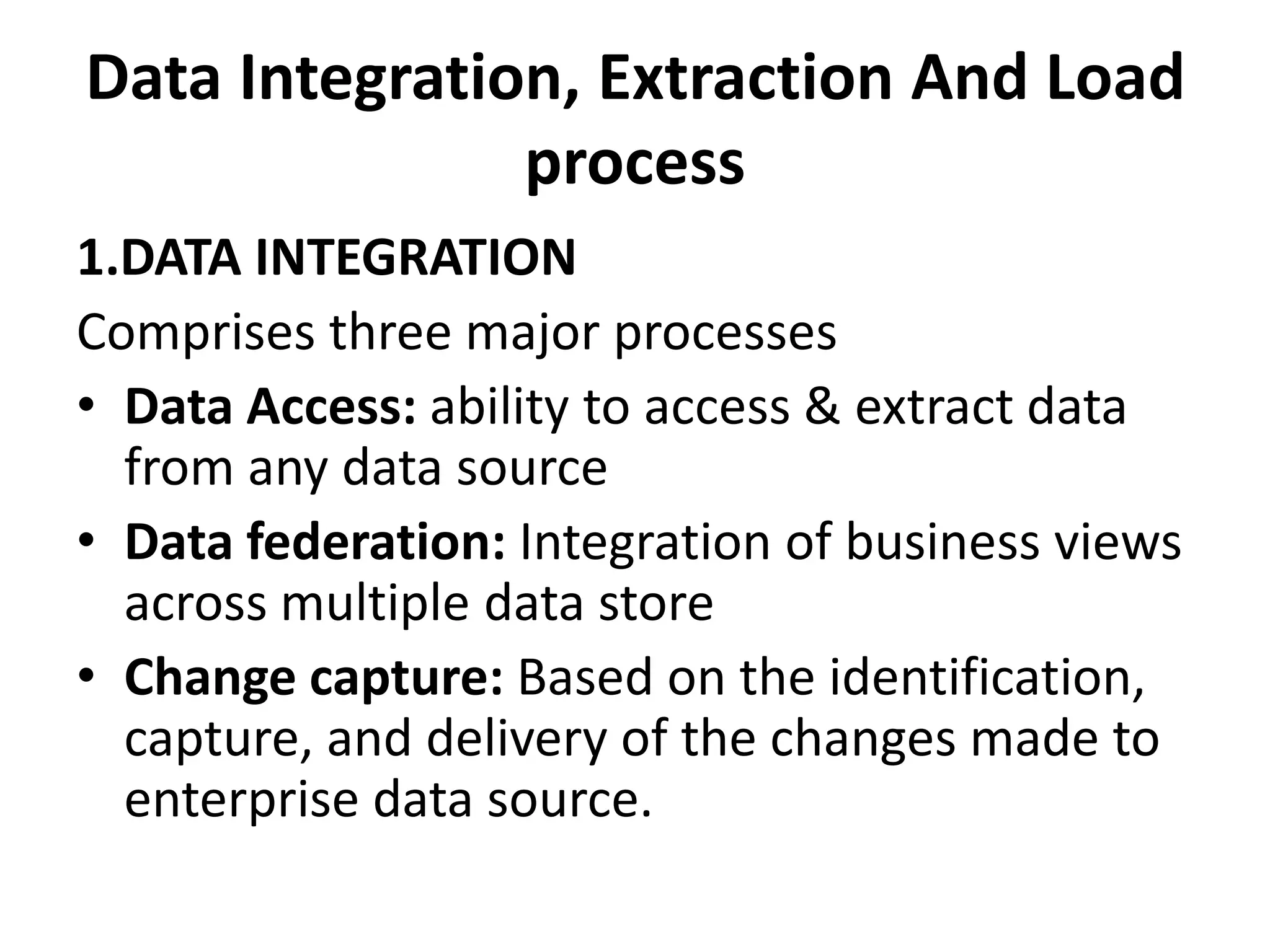
A data warehouse is a collection of data integrated from multiple sources to support decision making. It contains subject-oriented, integrated, time-variant, and non-volatile data stored in a way that makes it readily available for analysis. Data marts can be dependent on the warehouse or independent subsets designed for specific departments. Successful implementation requires identifying data sources and governance, planning data quality and modeling, selecting ETL and database tools, and supporting end users. Key challenges include unrealistic expectations, technical issues, and ensuring ongoing value.