Embed presentation
Download to read offline





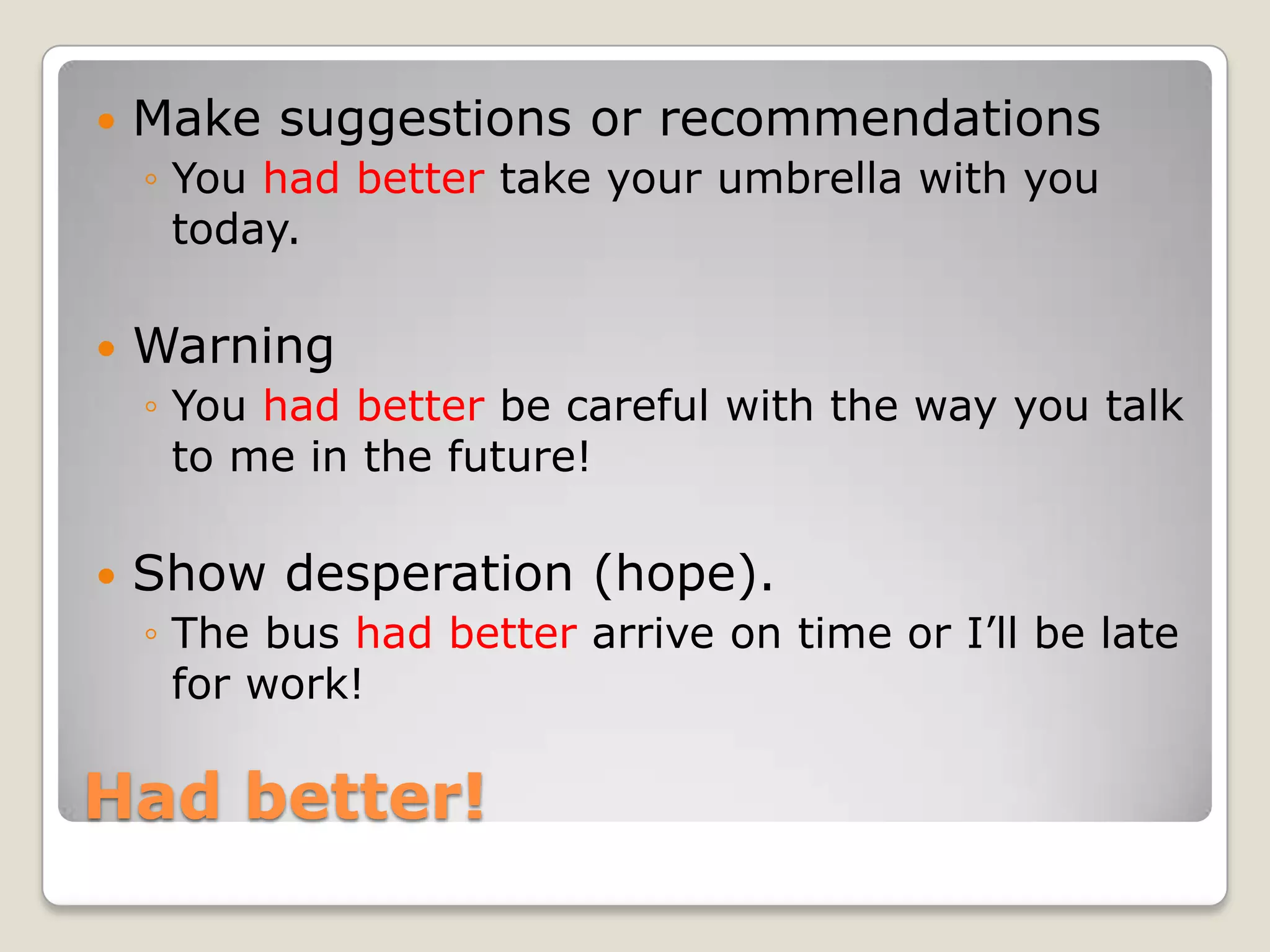

This document discusses modal verbs, which are helping verbs that provide information about the main verb. It defines modal verbs like can, could, may, might, should, ought to, had better, must, and have to. It explains the differences between their meanings and uses, such as ability versus permission for can, formal versus informal for could, possibility for may and might, and obligation from feelings versus outside sources for must and have to. The document also compares the meanings and uses of should and ought to as well as had better. Finally, it provides examples to illustrate levels of severity that can be expressed by these modal verbs.






