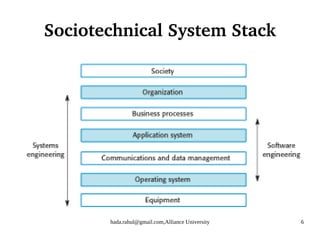
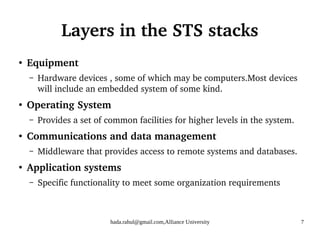
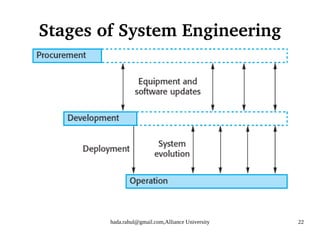
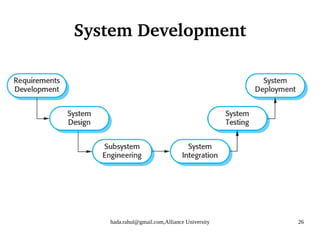
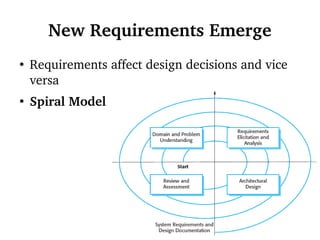
This document discusses socio-technical systems and system engineering. It defines socio-technical systems as systems that include both technical components like hardware and software, as well as human and organizational elements like operational processes and policies. It describes the different layers in a socio-technical system stack from equipment to society. It also discusses characteristics of socio-technical systems like emergent properties and non-determinism. Finally, it outlines the key stages of system engineering like procurement, development, and operation.