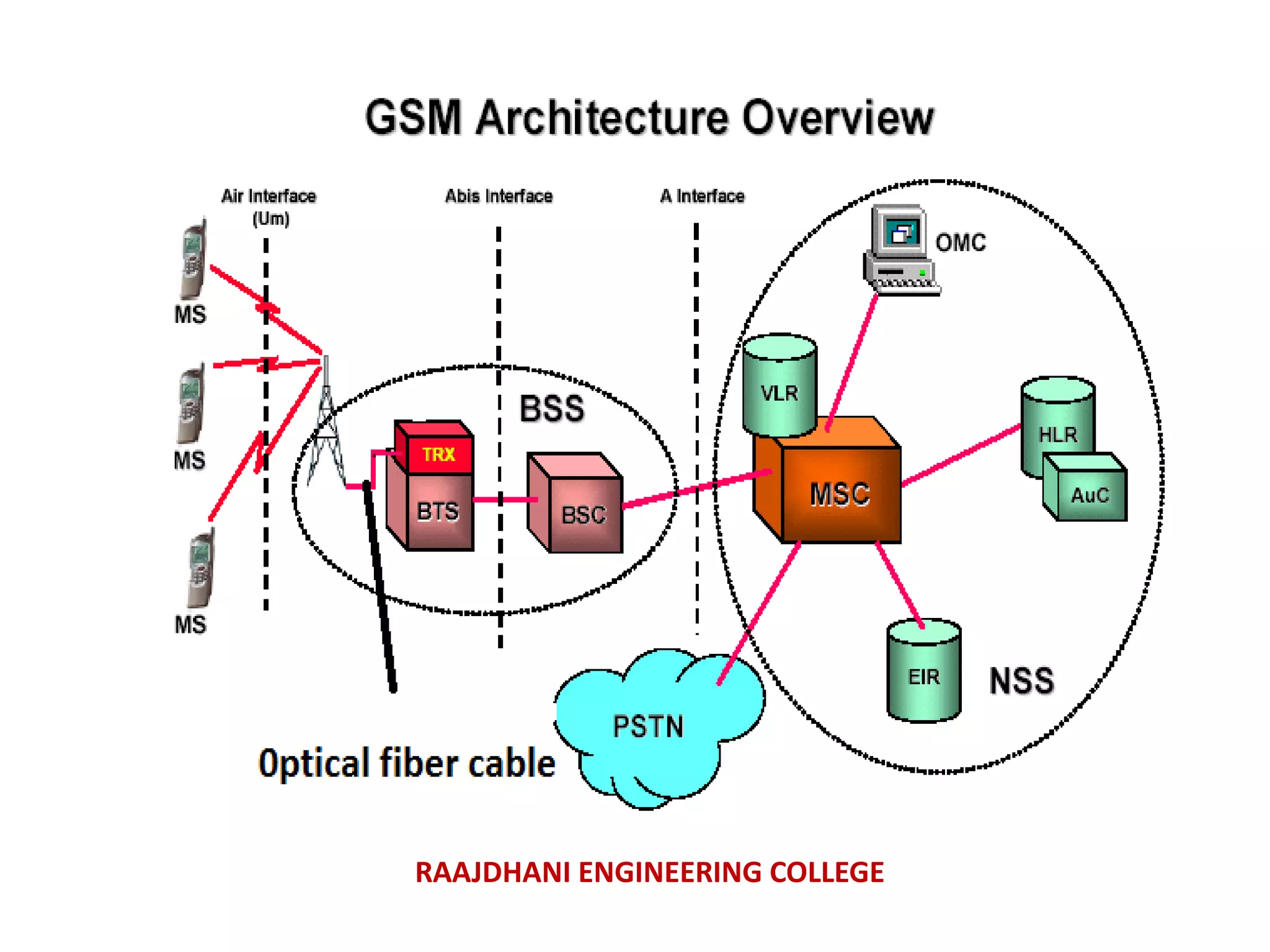
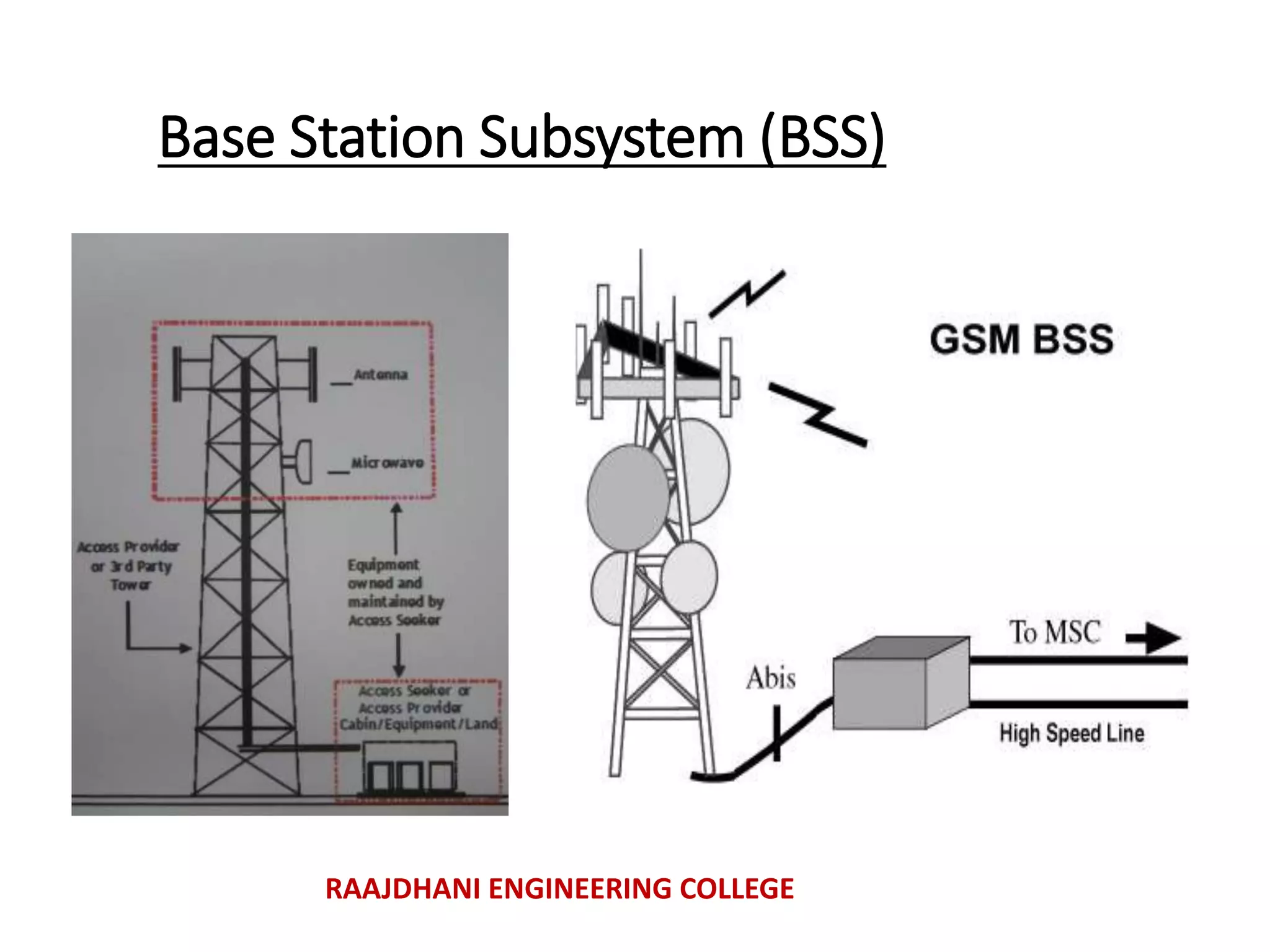
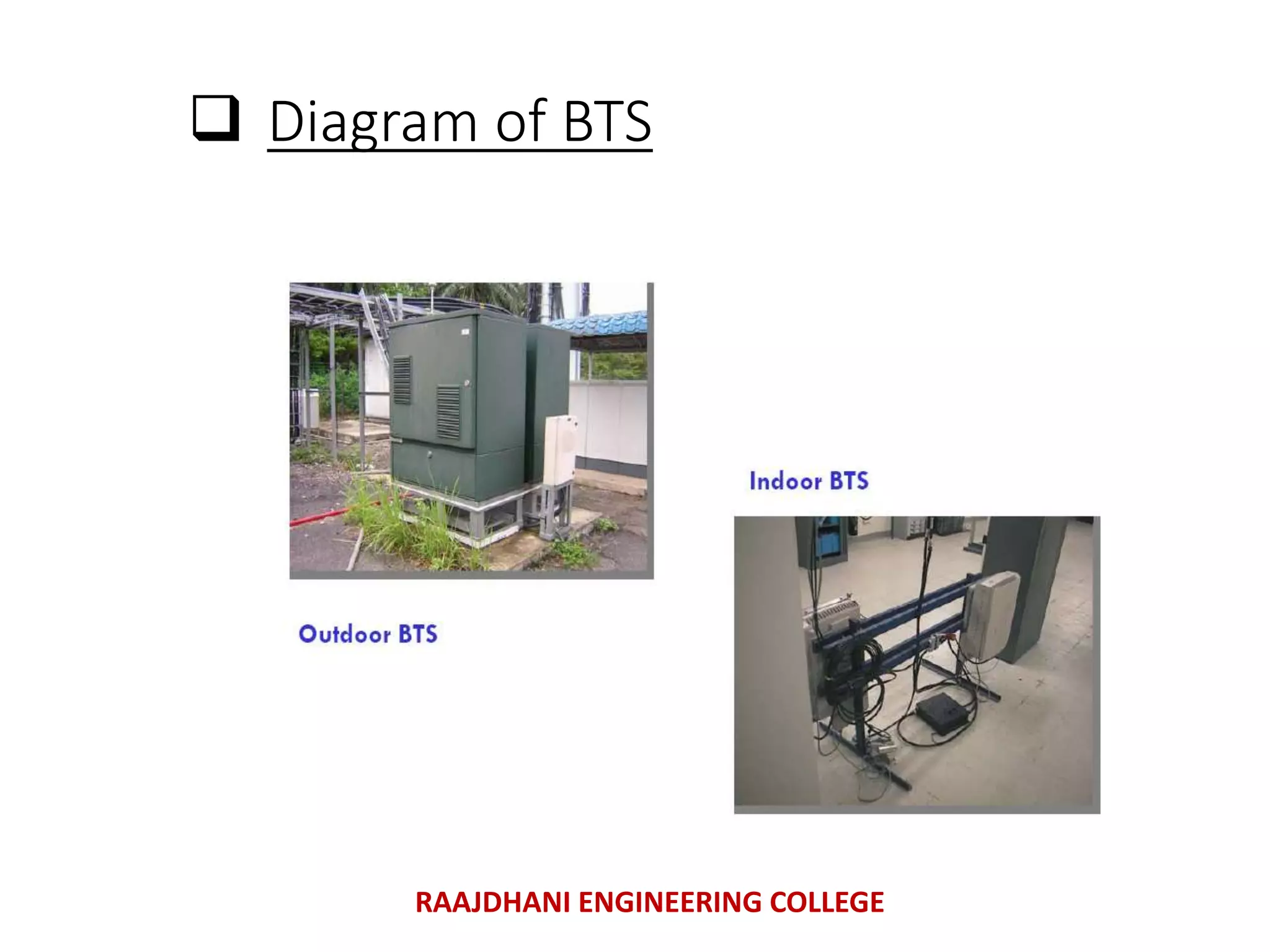
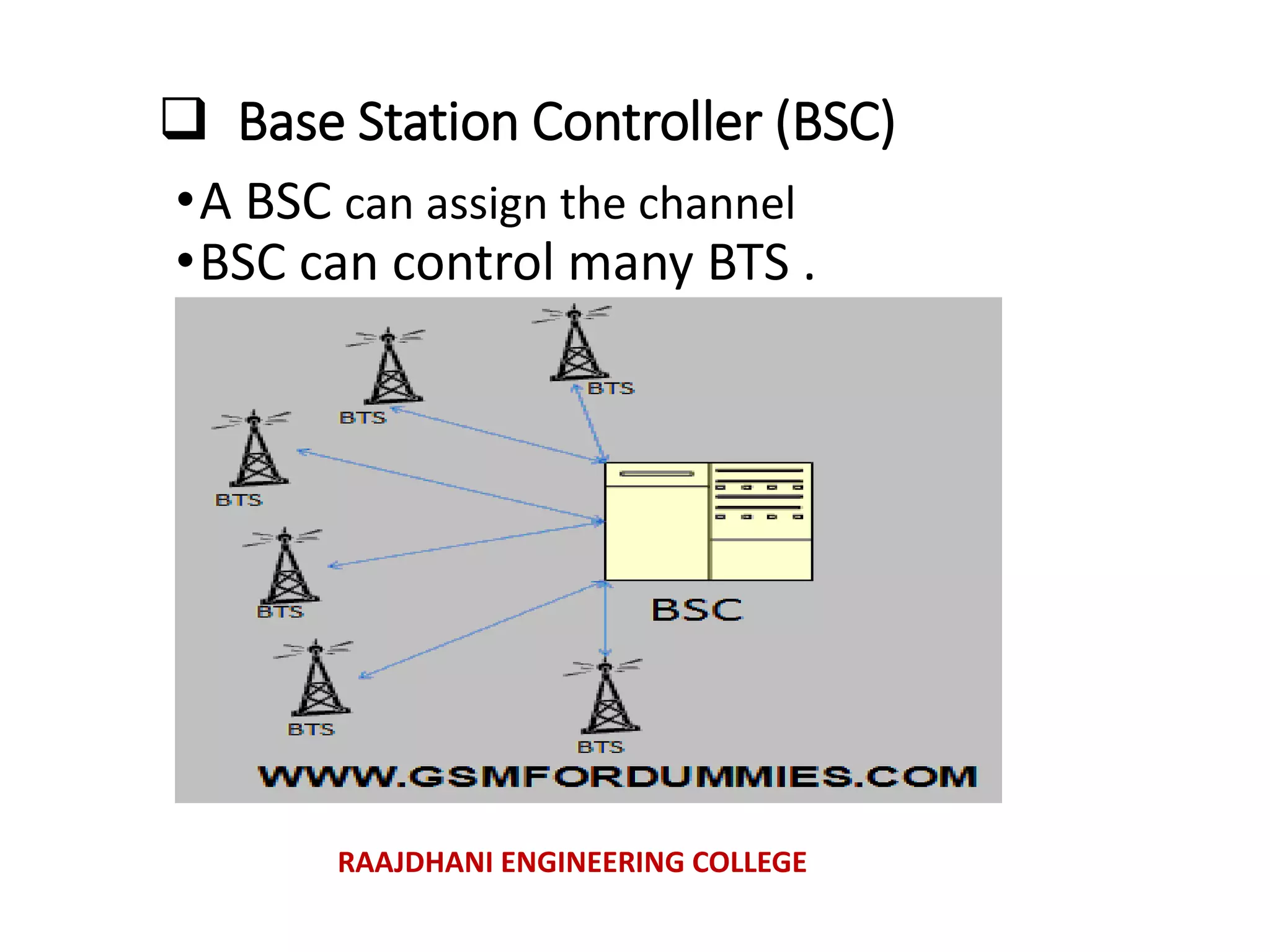
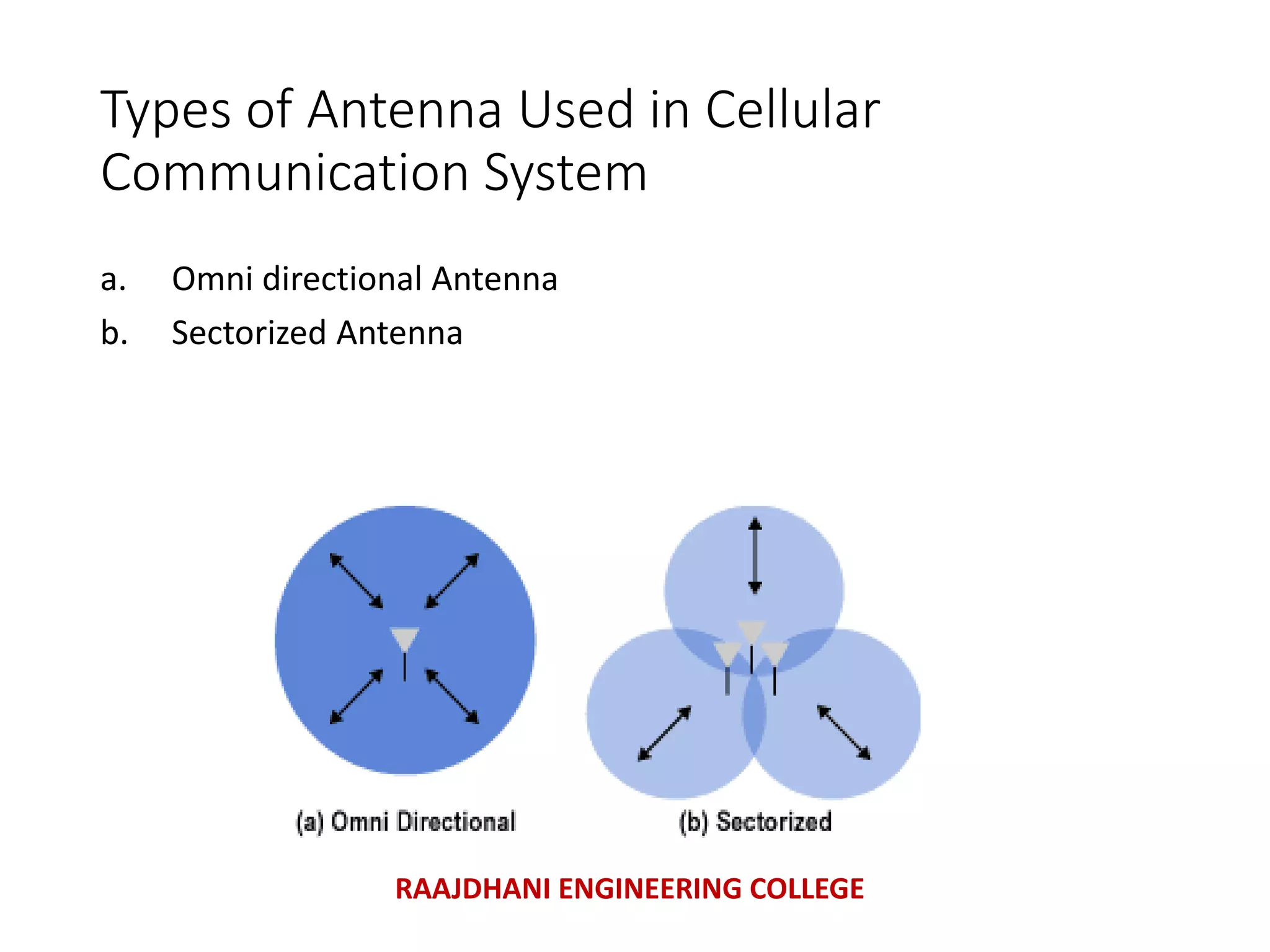
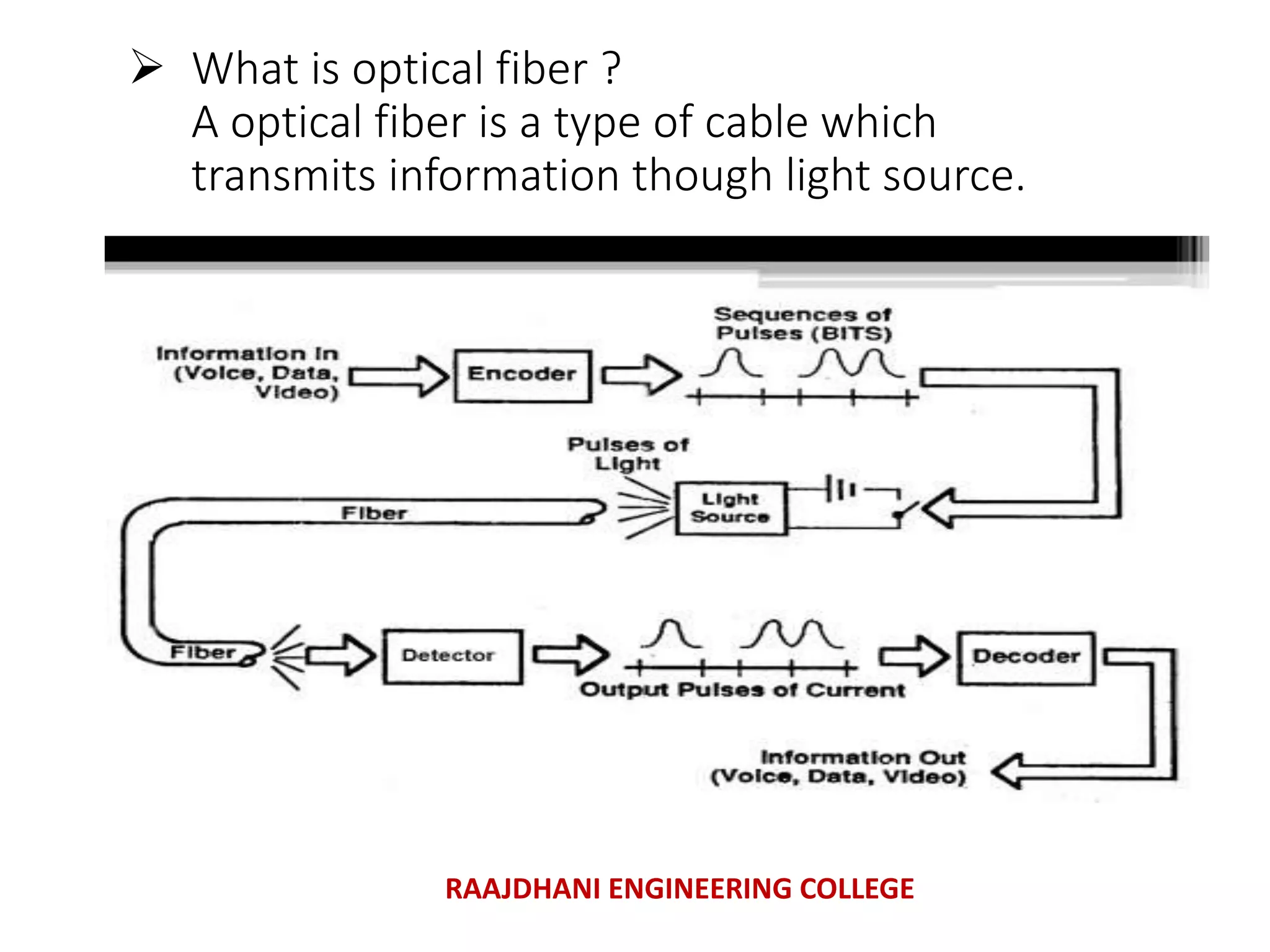
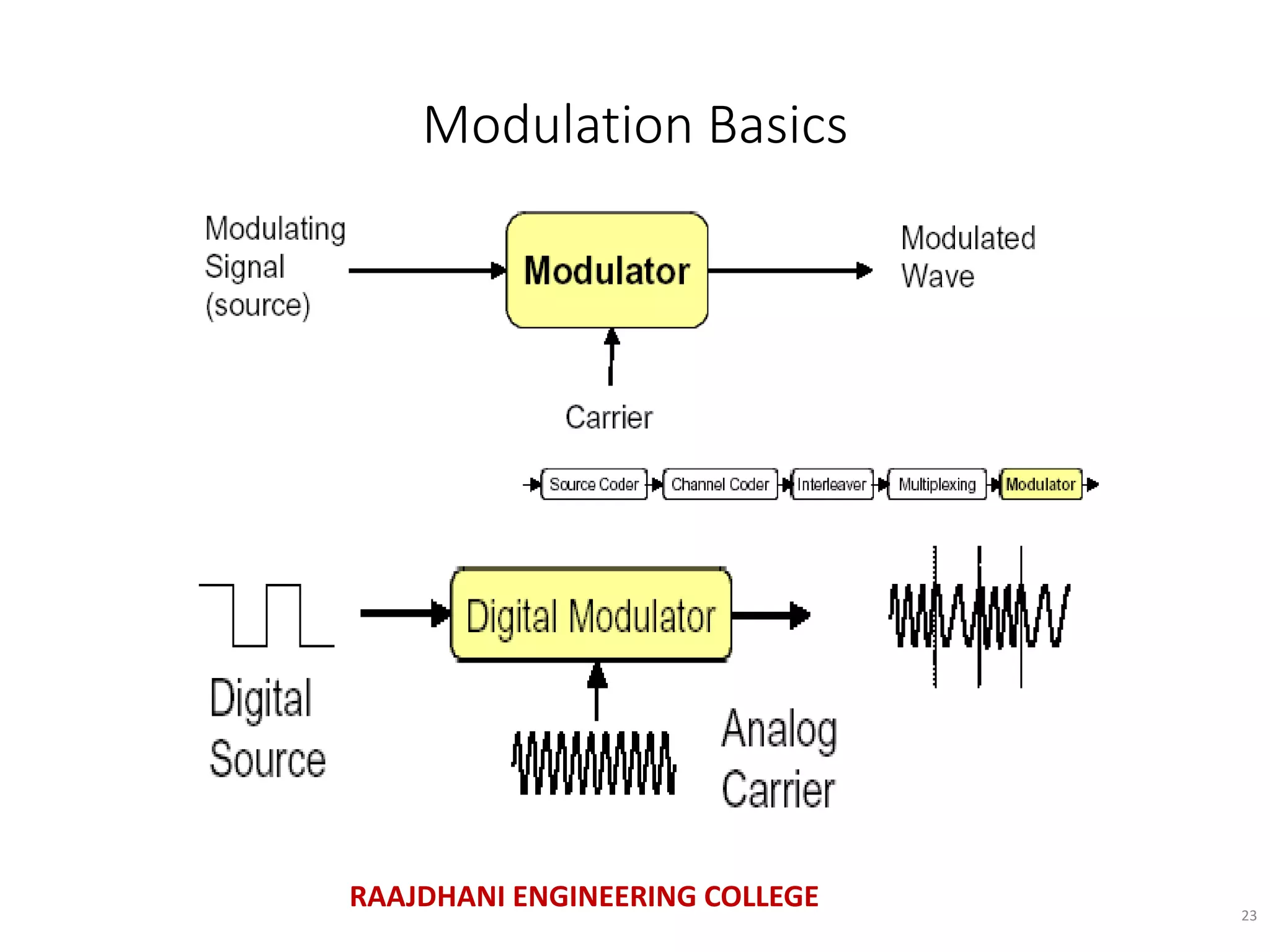
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on mobile communication processes. It describes the key components of a cellular communication system including the mobile switching center (MSC), base station subsystem (BSS), base transceiver station (BTS), and base station controller (BSC). It also discusses the types of antennas used, including omni-directional and sectored antennas. Finally, it provides a brief overview of modulation basics and how optical fibers are used for transmission in cellular networks.