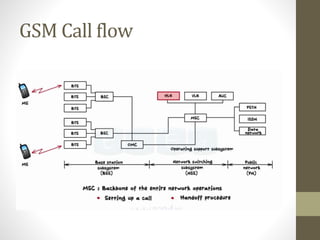
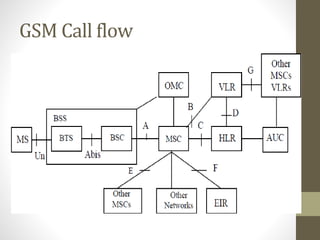
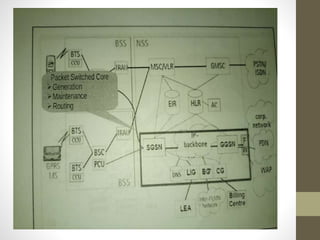
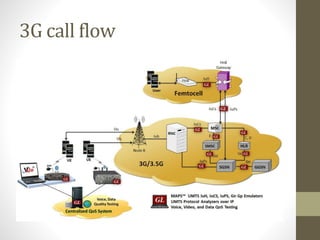
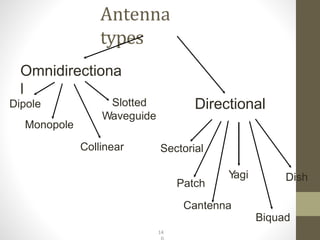
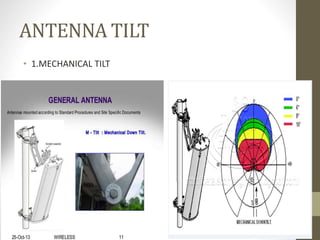
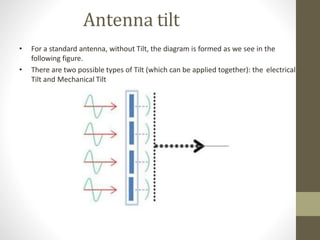
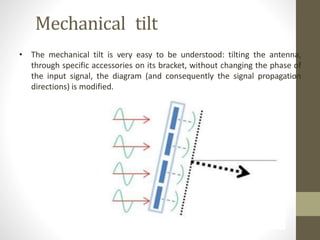
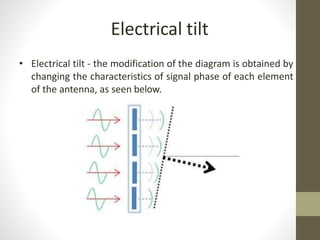
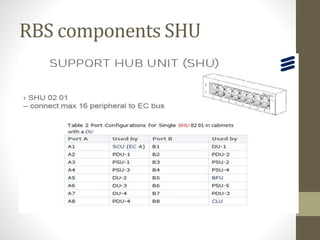
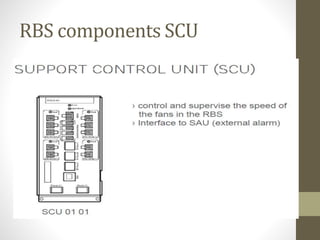
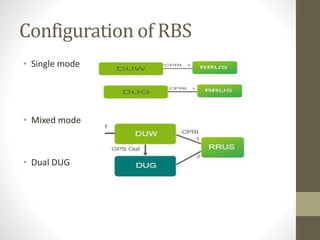
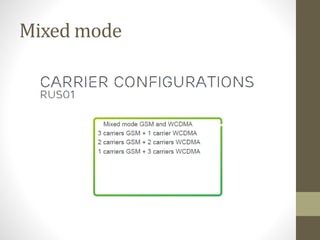
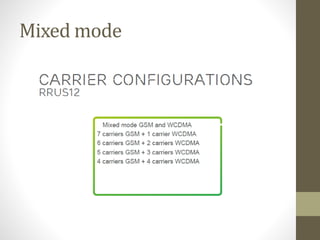
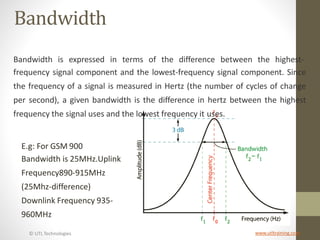
The document provides information about 2G mobile networks. It discusses the evolution from 0G to 2G networks including 1G standards like AMPS, TACS, and NMT. 2G introduced GSM which used digital signaling and TDMA/CDMA. GSM supported SMS but not internet. GPRS (2.5G) introduced packet switching and supported IP and internet. EDGE (2.75G) increased data rates but speeds were still low. The document also describes GSM call flow and components of the BTS including antennas, RRUS, jumpers, fibers, and DUG. It explains 2G configuration in 900MHz and 1800MHz bands and the various cables used.