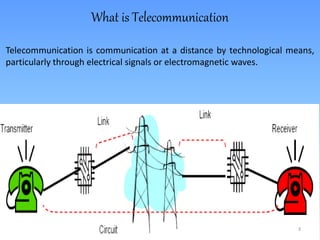
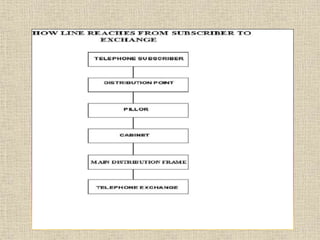
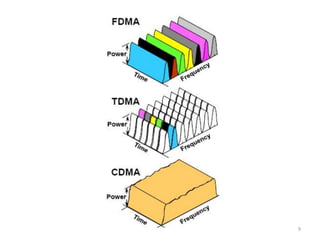
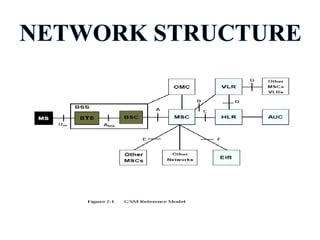
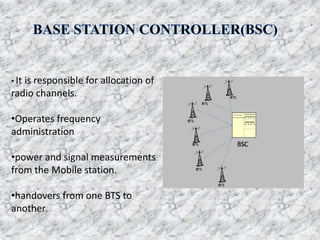
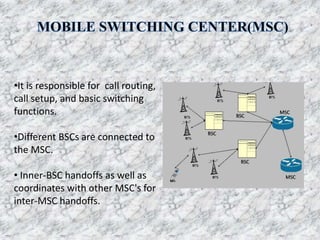
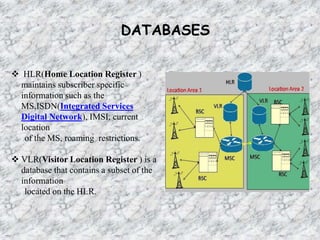
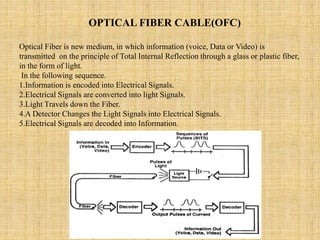
This document provides an overview of Anusha Srivastava's industrial training at the Advanced Level Telecom Training Centre (ALTTC) in Ghaziabad, India. It discusses the history and mission of ALTTC. The document then summarizes key concepts in telecommunications including the basic working of telecom networks, switching, public switched telephone networks, multiple access techniques, GSM network architecture and components, IP addressing, fiber optic transmission systems, CDMA, and references used.