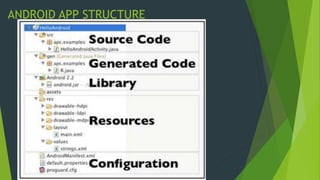
This document discusses three angles for performing mobile application security testing: client side checks, dynamic/runtime checks of local storage, databases and more, and static code analysis. It focuses on static code analysis, explaining that it covers over 50% of the OWASP Mobile Top 10 risks. It provides details on fetching APKs, converting them to source code, manual and automated static code analysis tools like MobSF and QARK, and common issues like improper use of Android intents that can be discovered through static analysis.