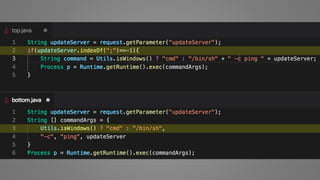
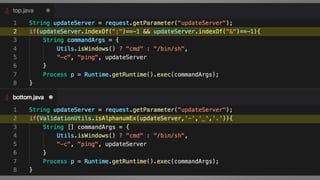
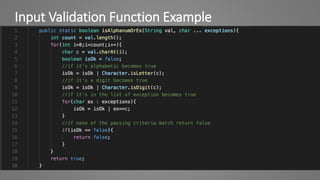
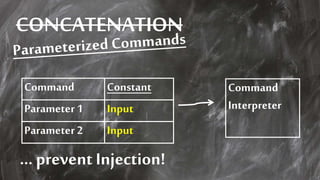
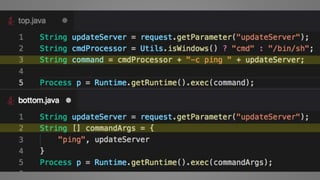
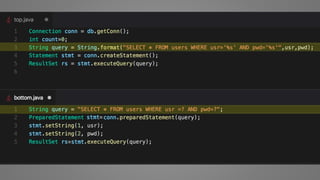
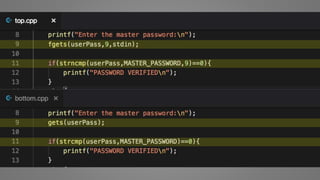
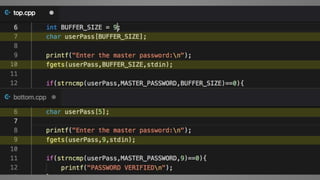
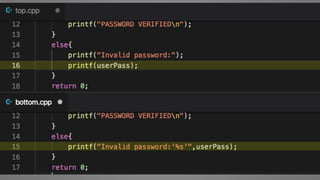
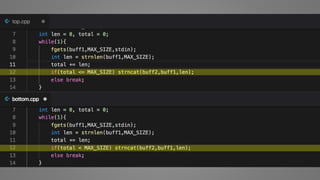
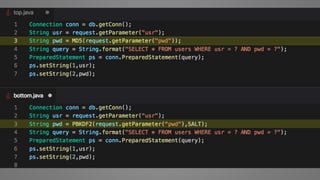
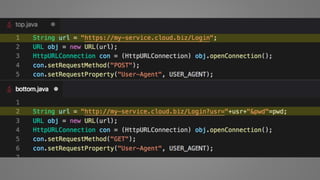
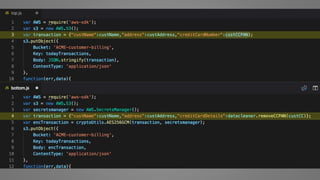
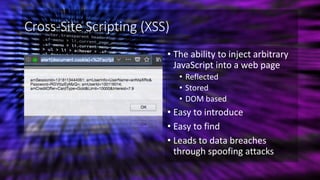
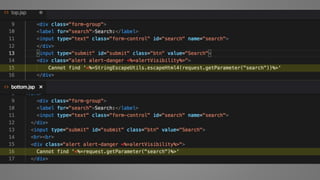
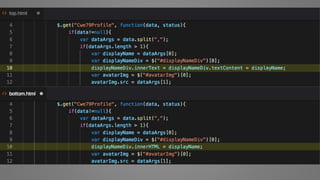
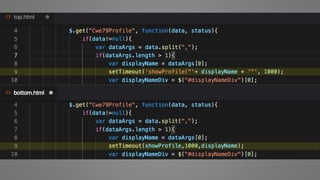
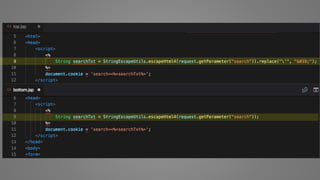
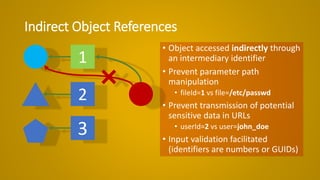
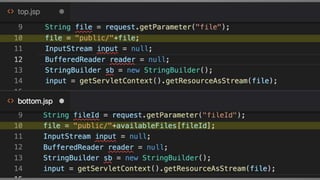
The document outlines essential strategies for input validation, safe memory management, and data encryption to prevent various security vulnerabilities like injection attacks and cross-site scripting. It emphasizes the importance of using parameterized commands, secure functions, and proper data handling practices. The document also highlights the significance of following data privacy regulations and using secure protocols to protect sensitive information.