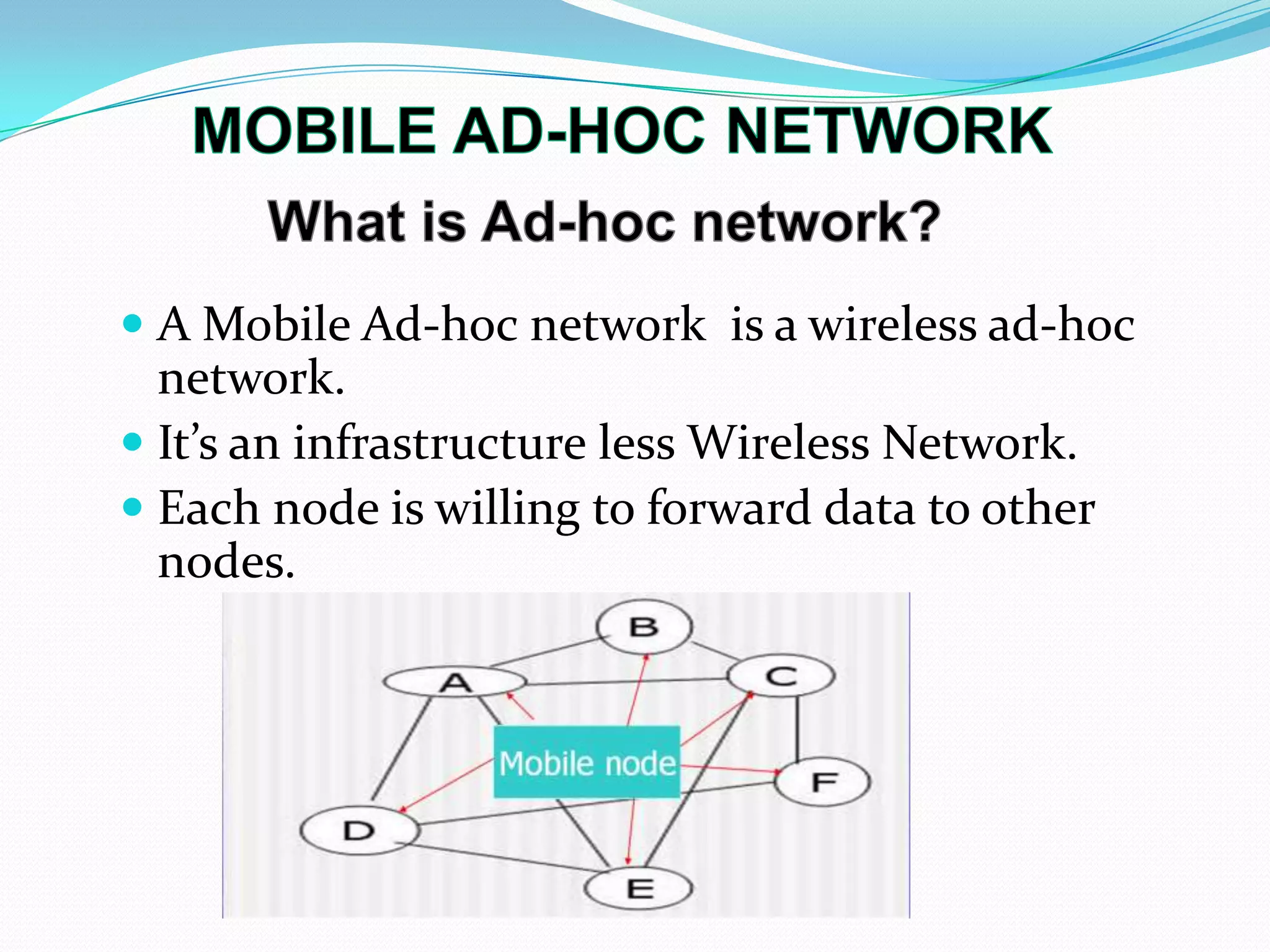
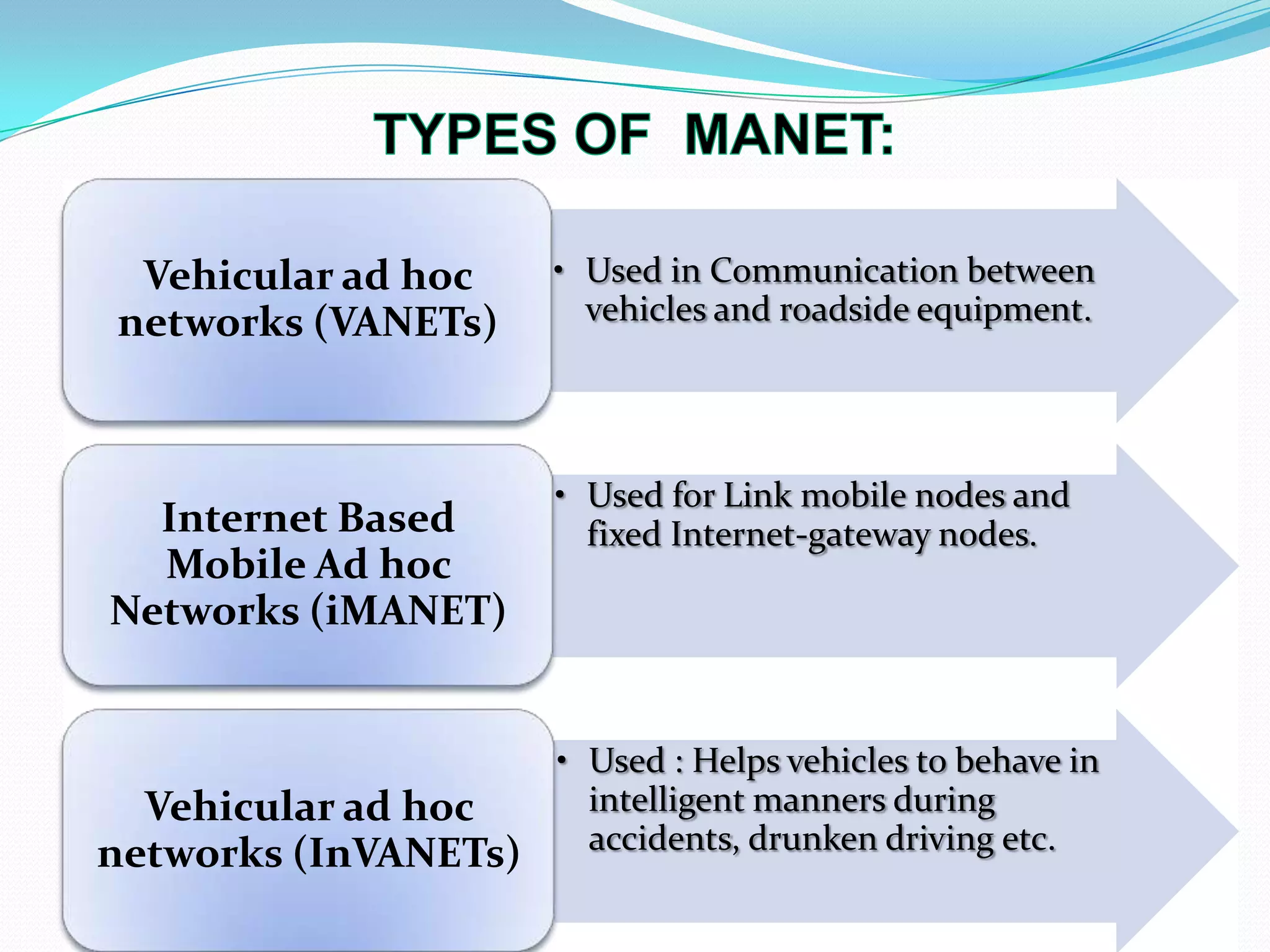
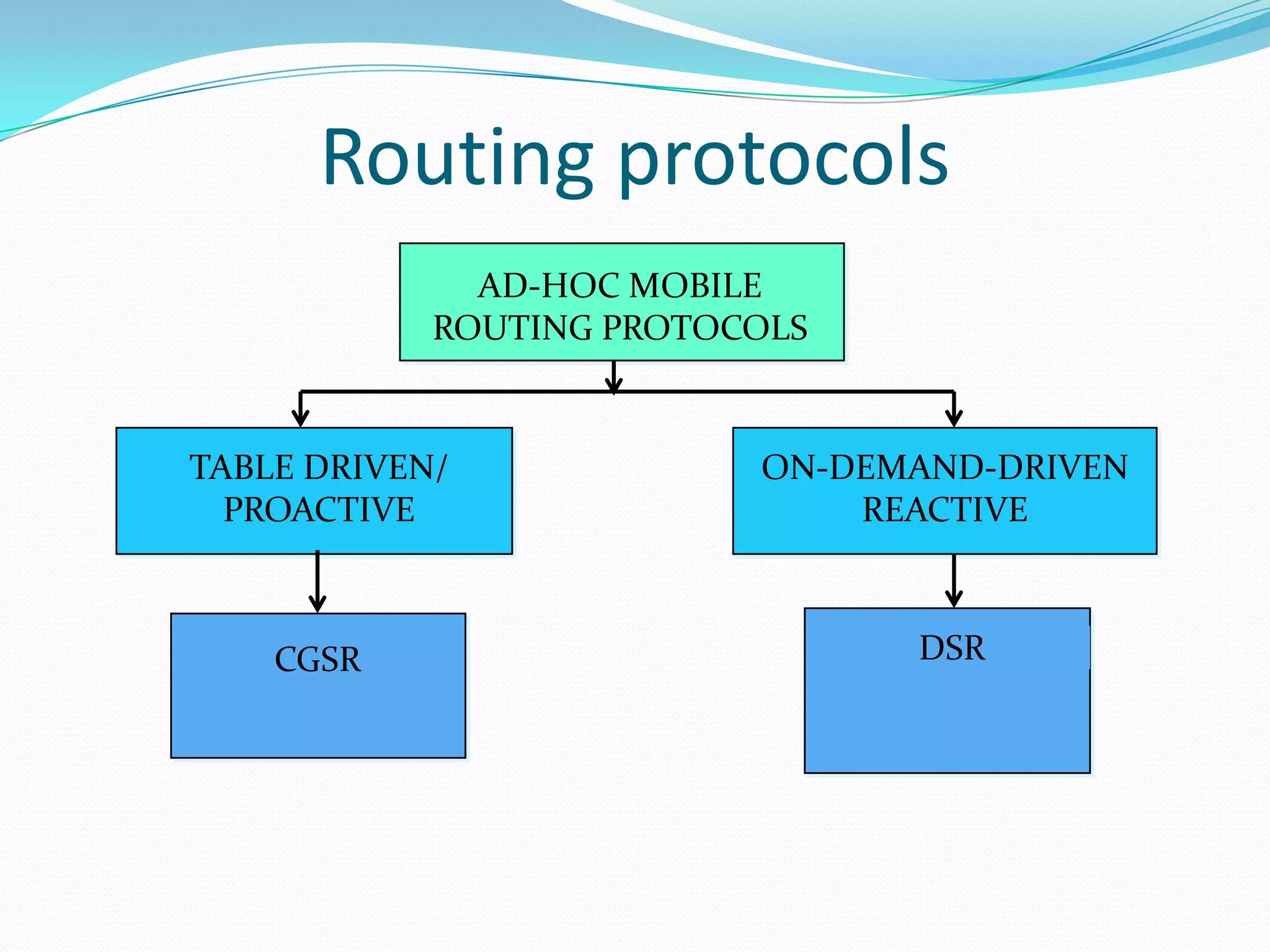
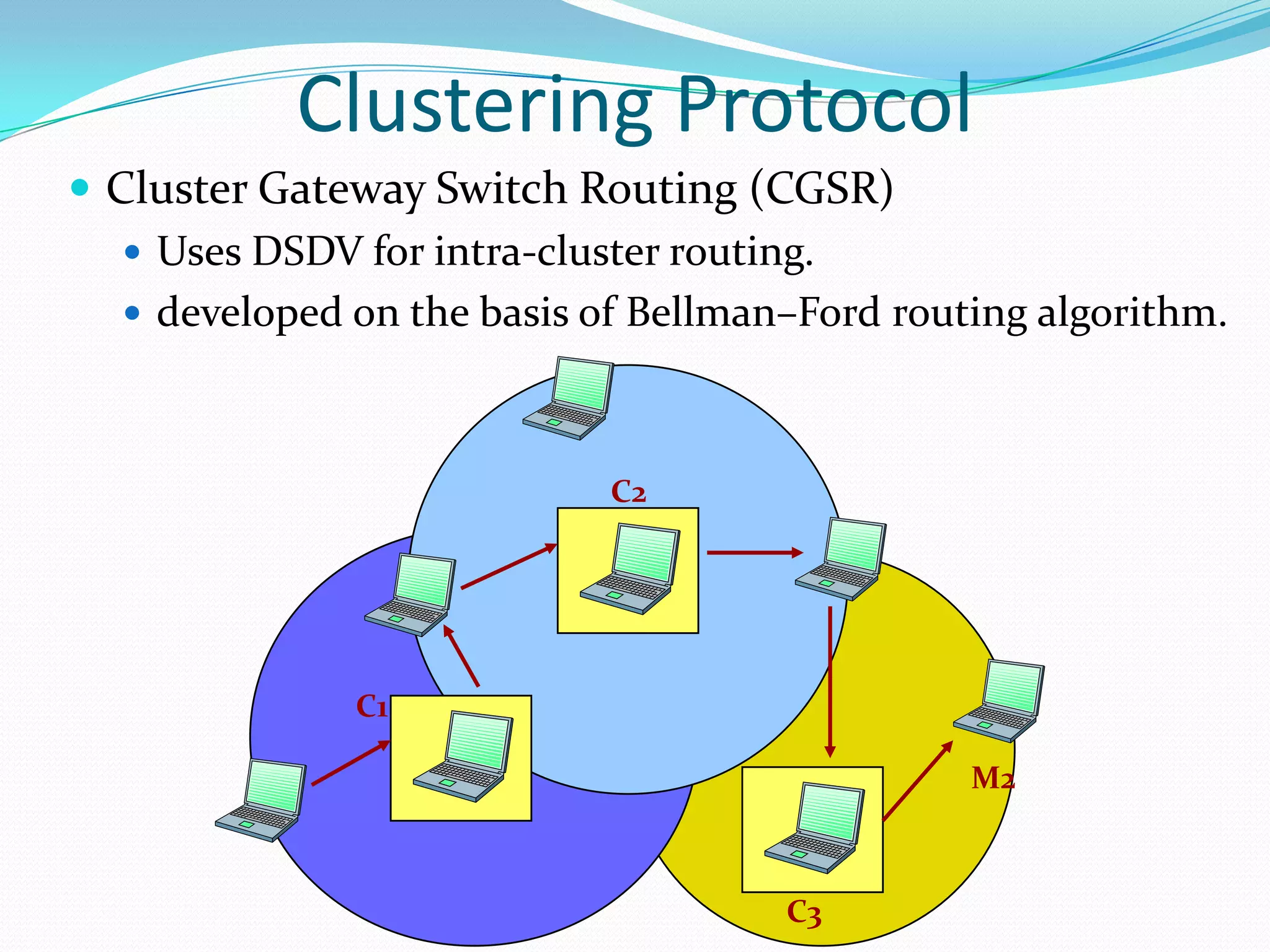
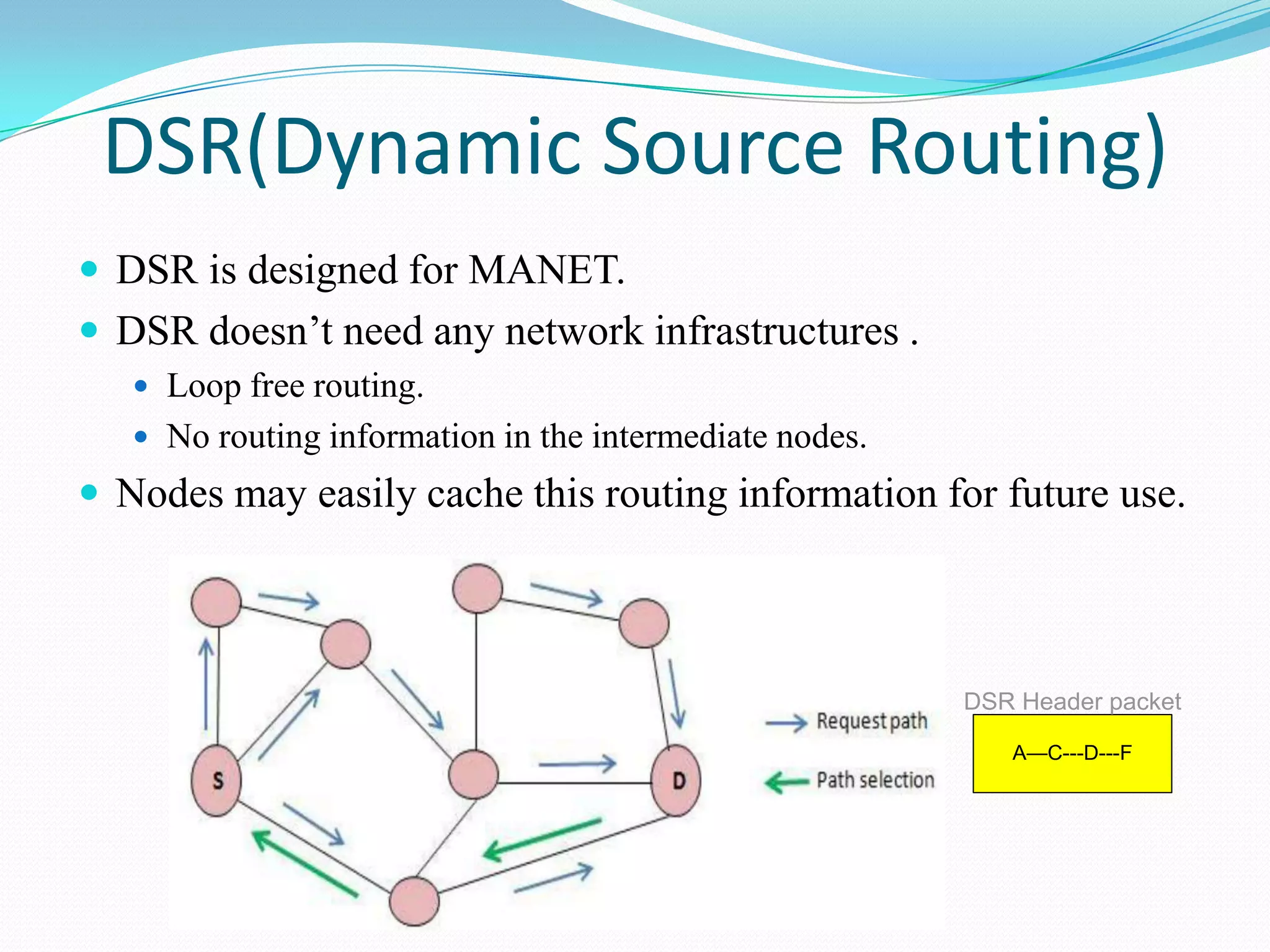
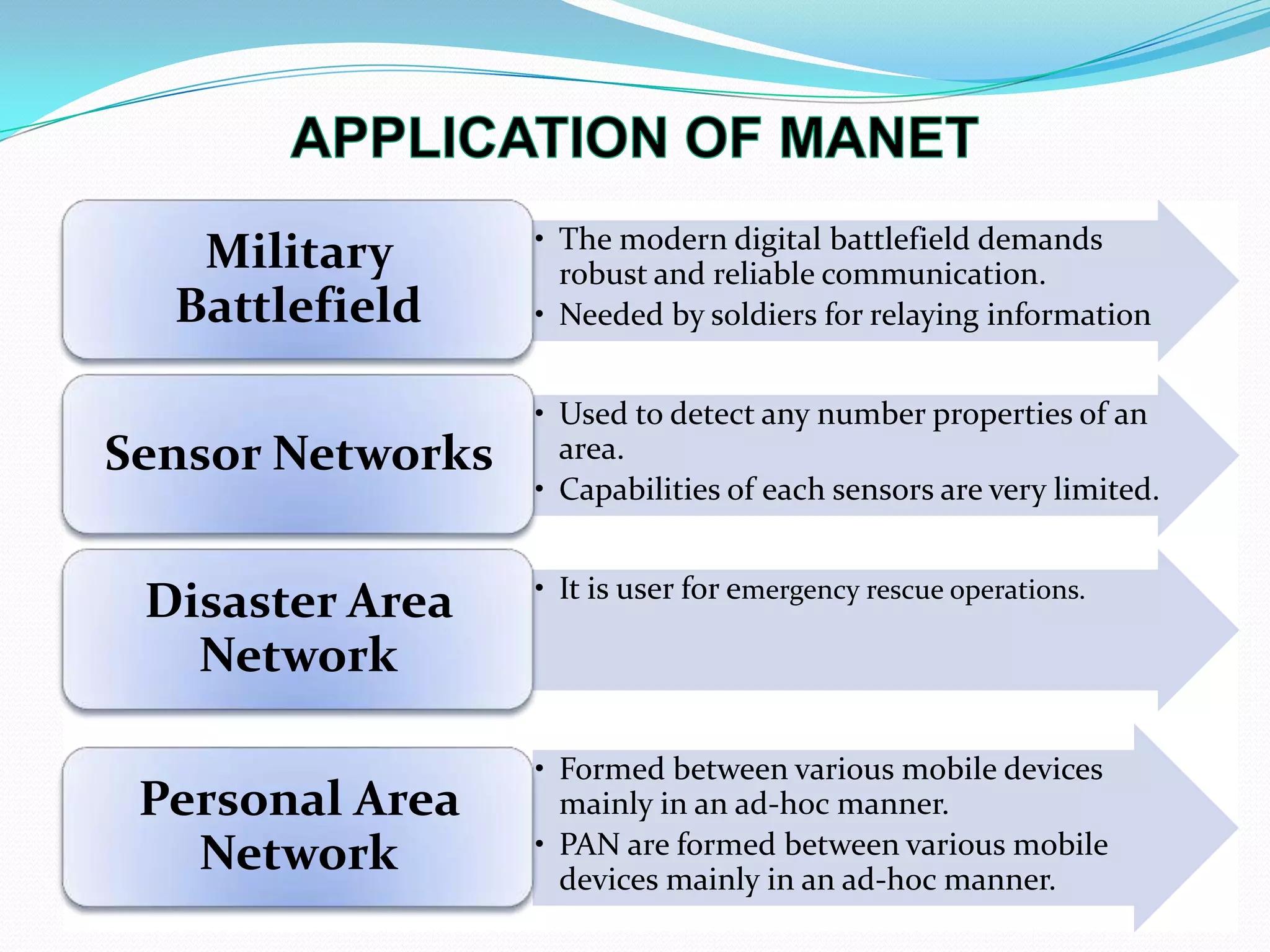
This document discusses mobile ad-hoc networks (MANETs). It defines MANETs as wireless infrastructureless networks where each node is willing to forward data for other nodes. The document outlines the history of MANETs including early packet radio networks. It describes key features like multi-hop routing and the ability for nodes to join or leave the network dynamically. Examples applications discussed include military, disaster recovery, and sensor networks. Finally, the document notes limitations of MANETs such as bandwidth constraints, energy limitations, and security issues.








![Mobile ad-hoc network [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mobilead-hocnetworkautosaved-140510124909-phpapp01/75/Mobile-ad-hoc-network-autosaved-16-2048.jpg)