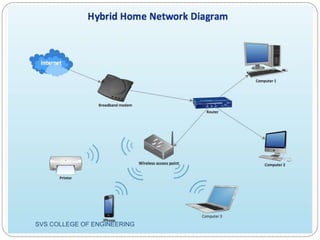
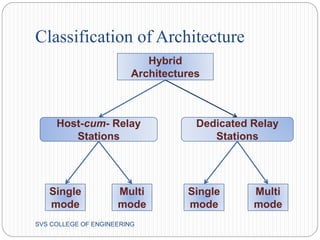
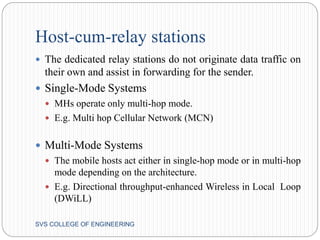
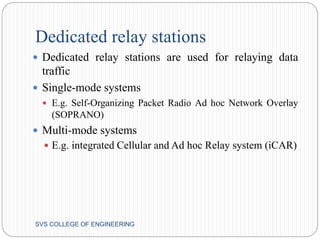
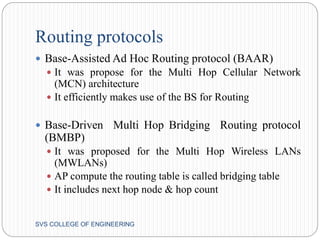
This document discusses hybrid wireless networks (HWNs) and some of their advantages over traditional wireless networks. It outlines the classification of HWN architectures and some routing protocols that have been proposed for different HWN types. Some key challenges of routing in HWNs are scalability, overhead from the presence of base stations and wired backbones, and high routing overhead. The document proposes looking at overhead and scalability issues for routing in HWNs.