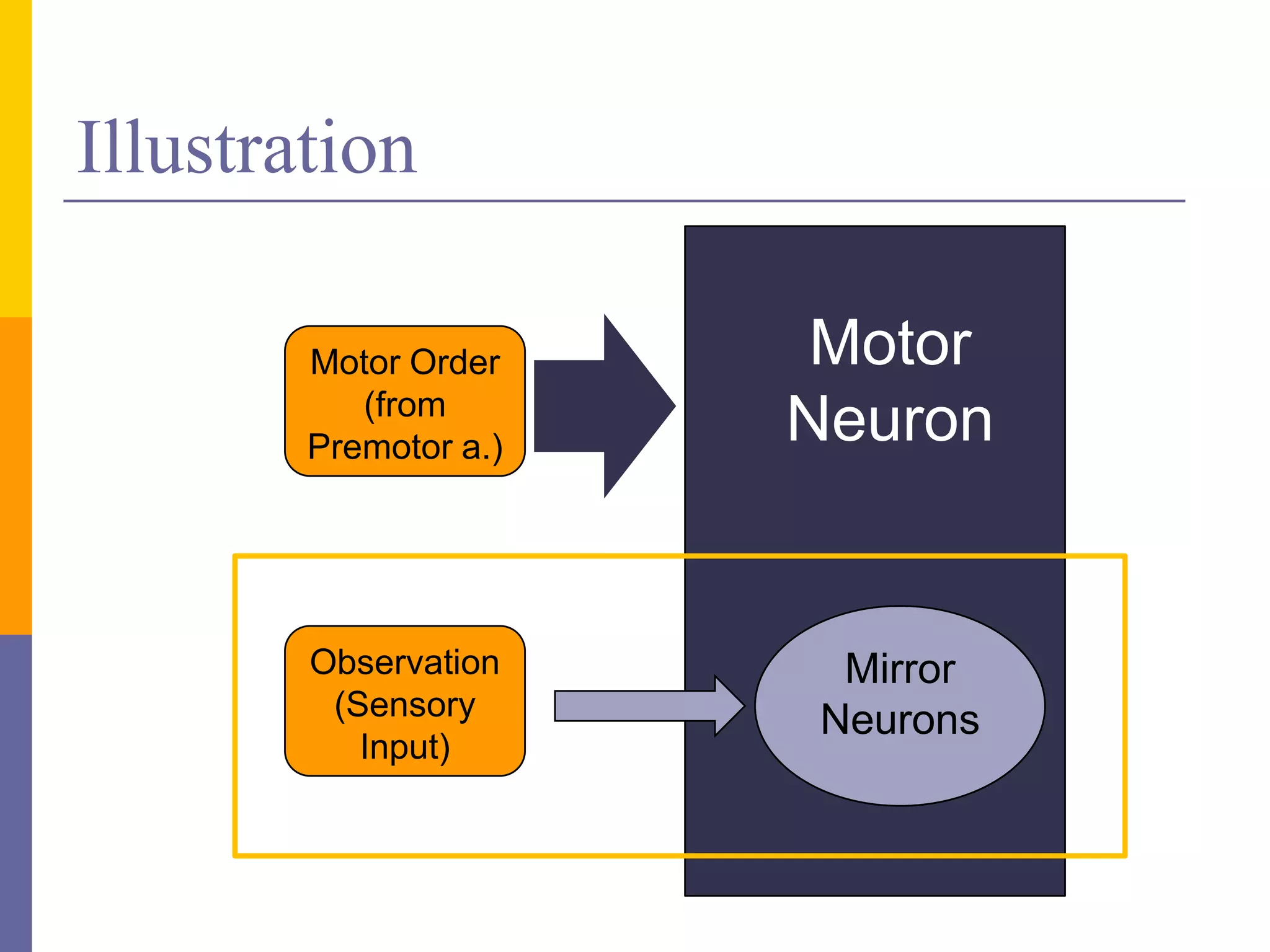
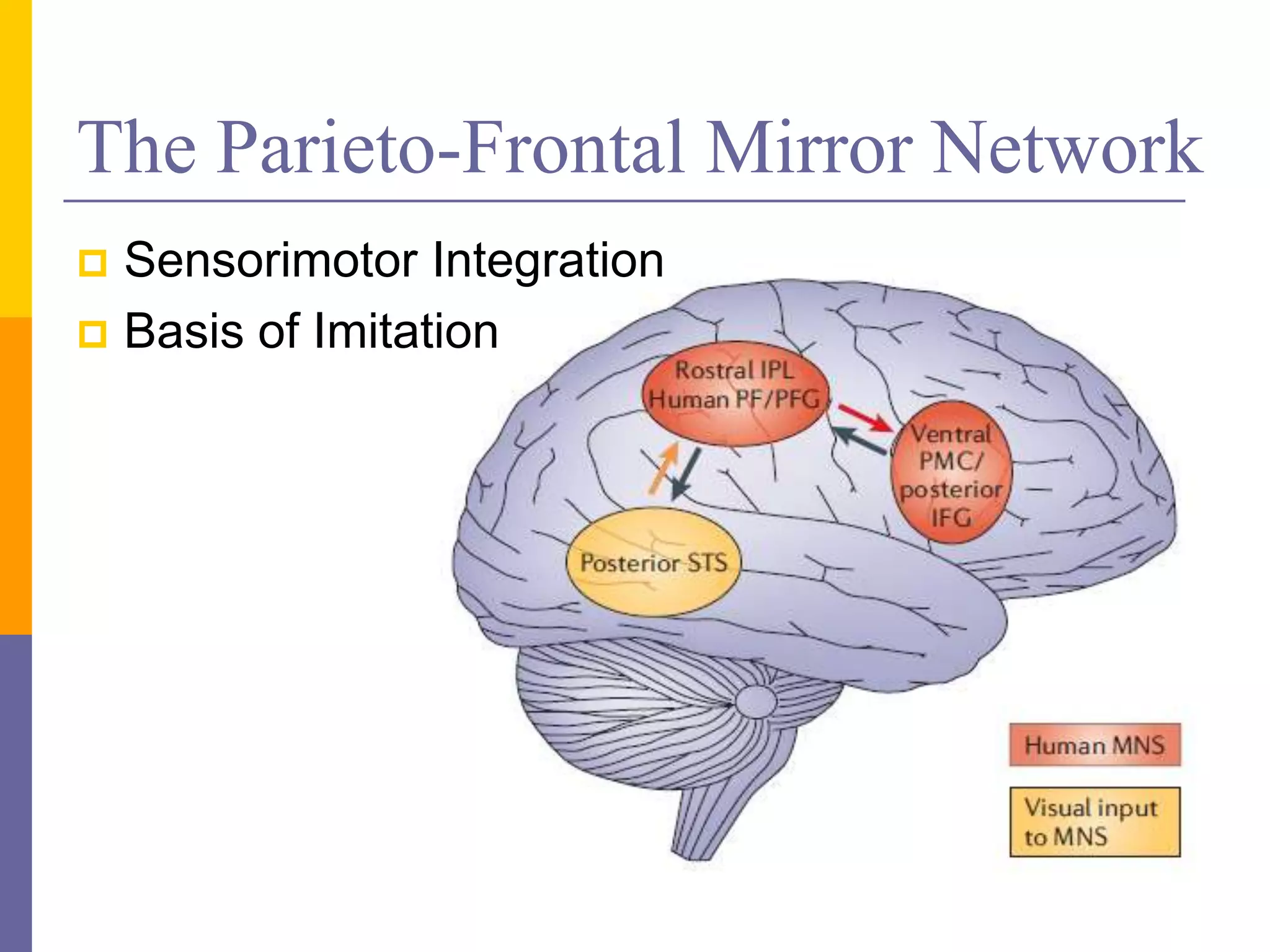
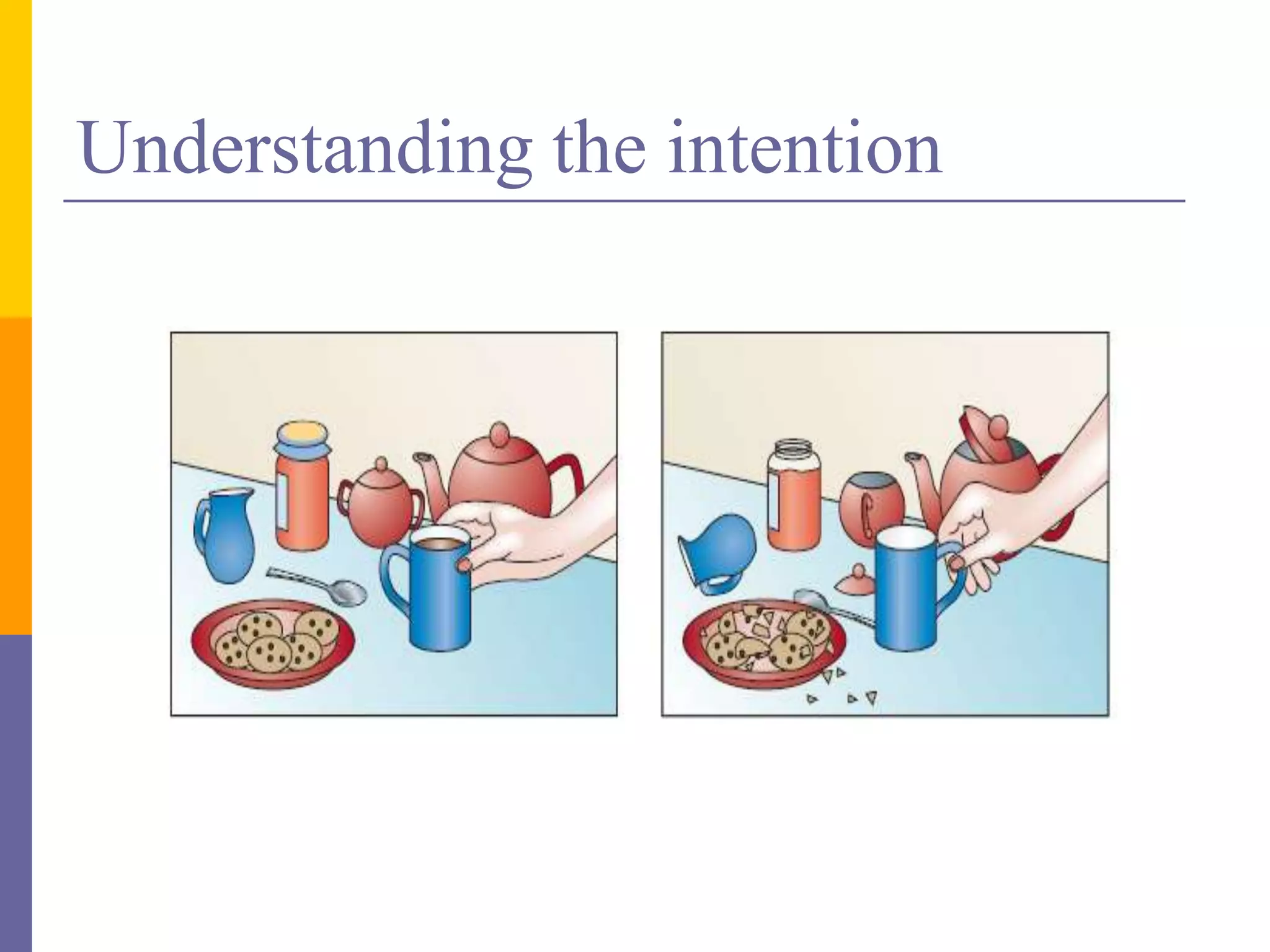
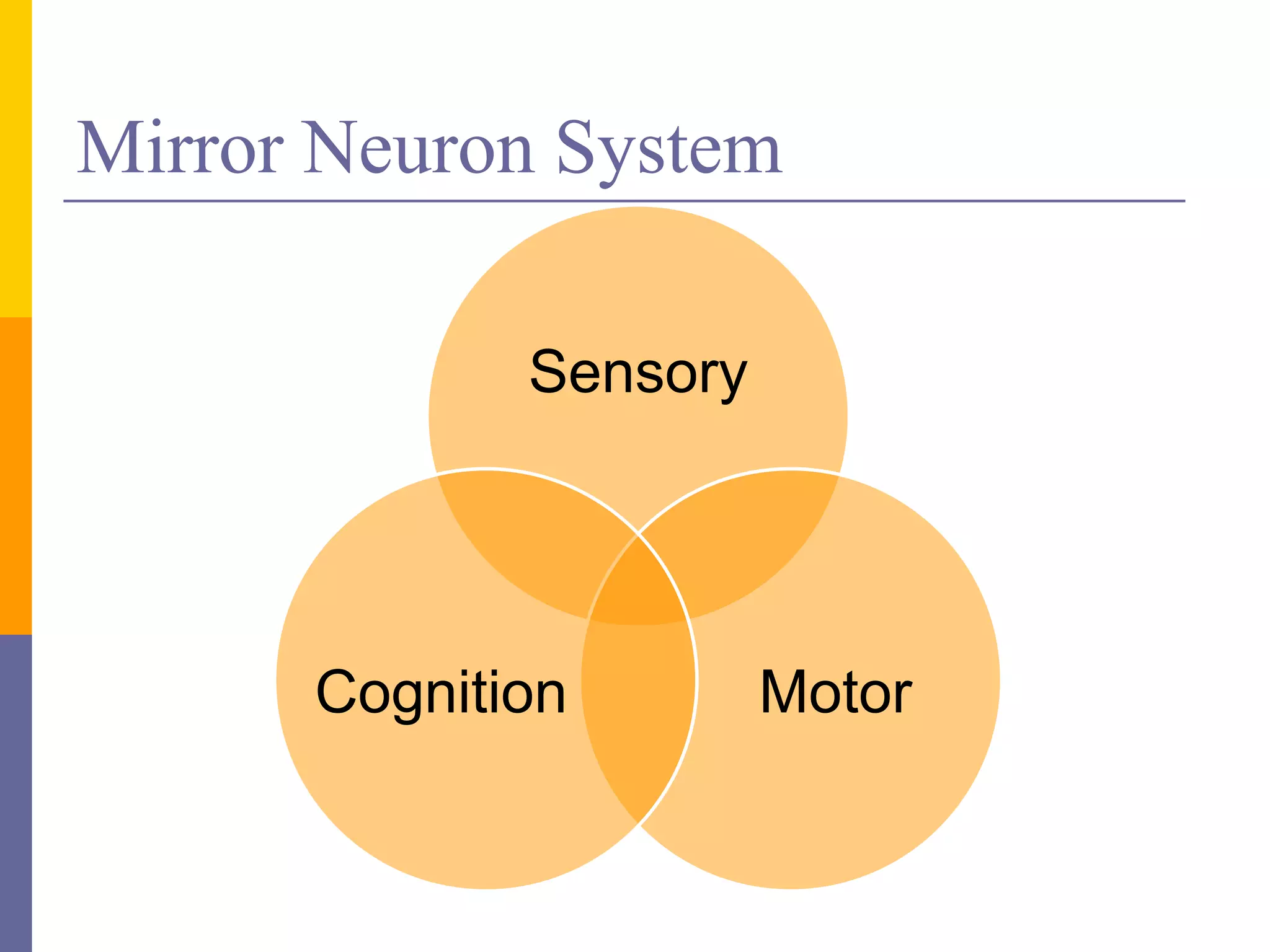
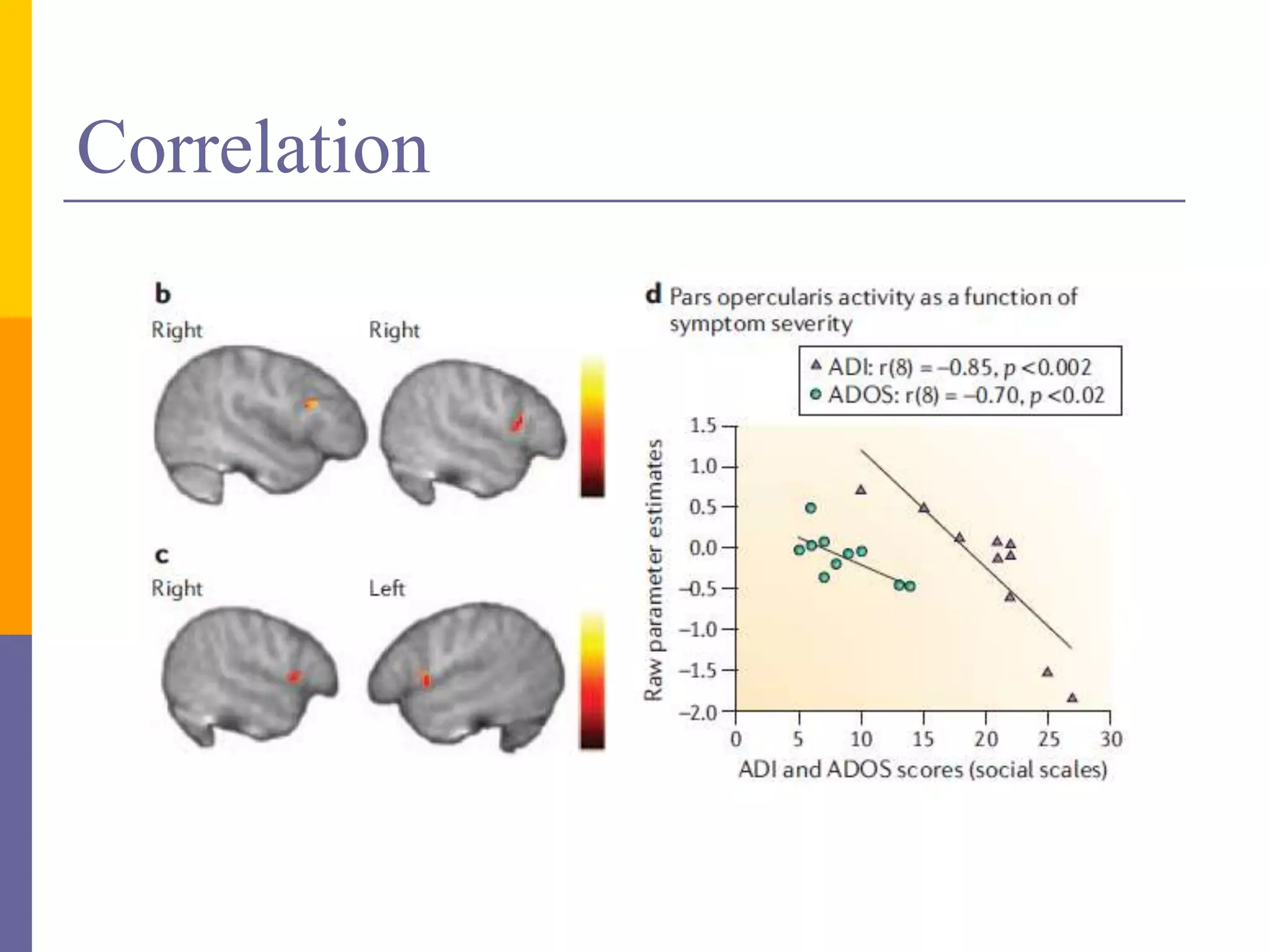
This document discusses mirror neurons and their potential relationship to autism spectrum disorder (ASD). It provides background on mirror neurons, outlining their basic properties and functions such as sensorimotor integration, understanding intentions, and facilitating empathy. The document then hypothesizes that a dysfunction of the mirror neuron system may underlie some characteristics of ASD, including social isolation and lack of empathy. It reviews evidence from EEG studies that found differences in mirror neuron activity in individuals with ASD compared to controls. The document concludes that a dysfunctional mirror neuron system could explain certain ASD symptoms like difficulties understanding intentions and exhibiting poor social skills.