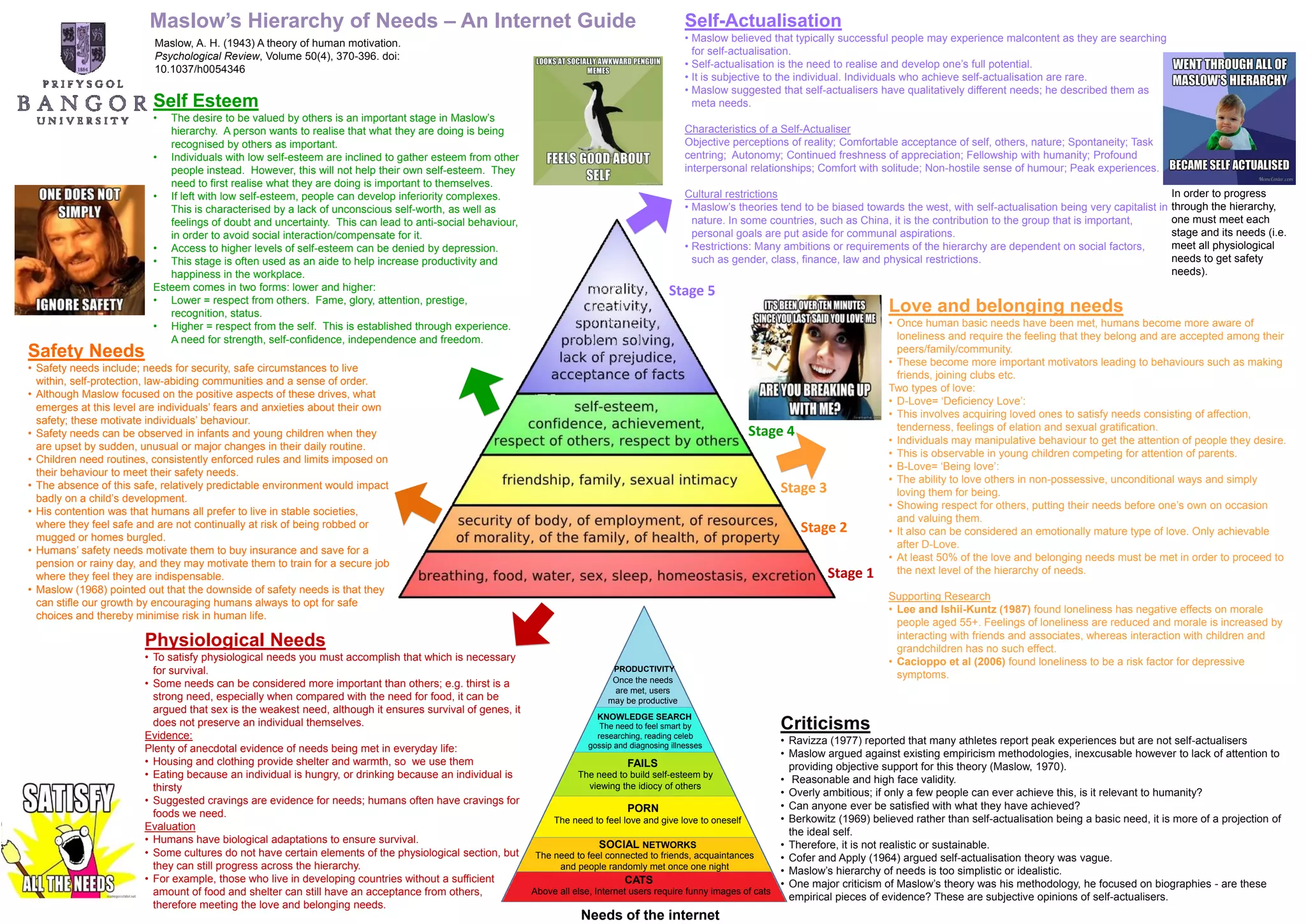
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a theory that proposes humans have five levels of needs: physiological, safety, love/belonging, esteem, and self-actualization. The theory suggests lower level needs must be met before progressing to meet higher level needs. Self-actualization is the highest level where one reaches their full potential, though Maslow believed few achieve this due to cultural and social restrictions. Critics argue self-actualization is not a basic need and Maslow's theory is too simplistic.