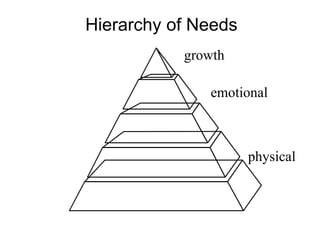
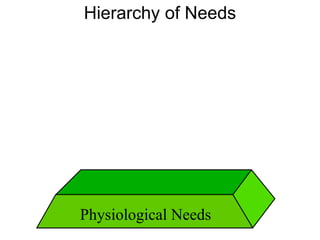
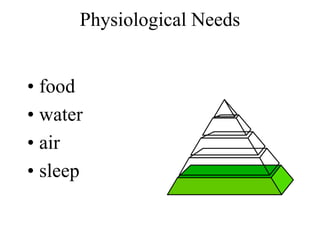
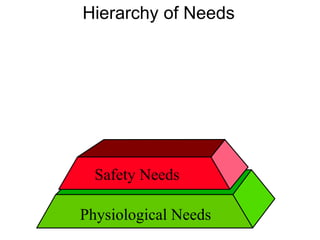
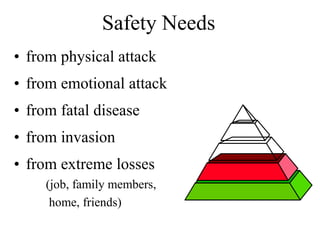
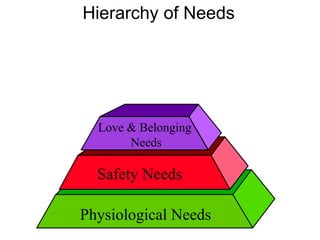
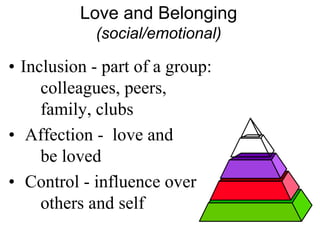
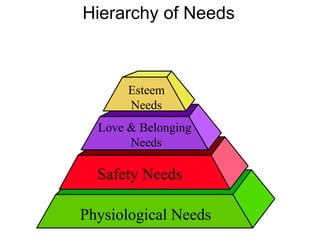
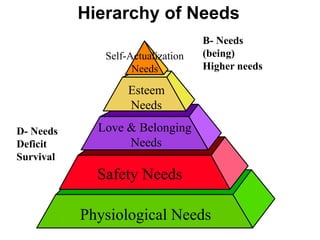
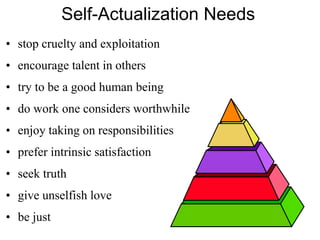
This document discusses Abraham Maslow and his Hierarchy of Needs theory. It provides biographical details about Maslow's life and career as a psychologist. It then explains Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, which posits that people are motivated to fulfill basic physiological needs, safety needs, love and belonging needs, and esteem needs before seeking self-actualization. The hierarchy is depicted visually with examples provided for each level of needs.