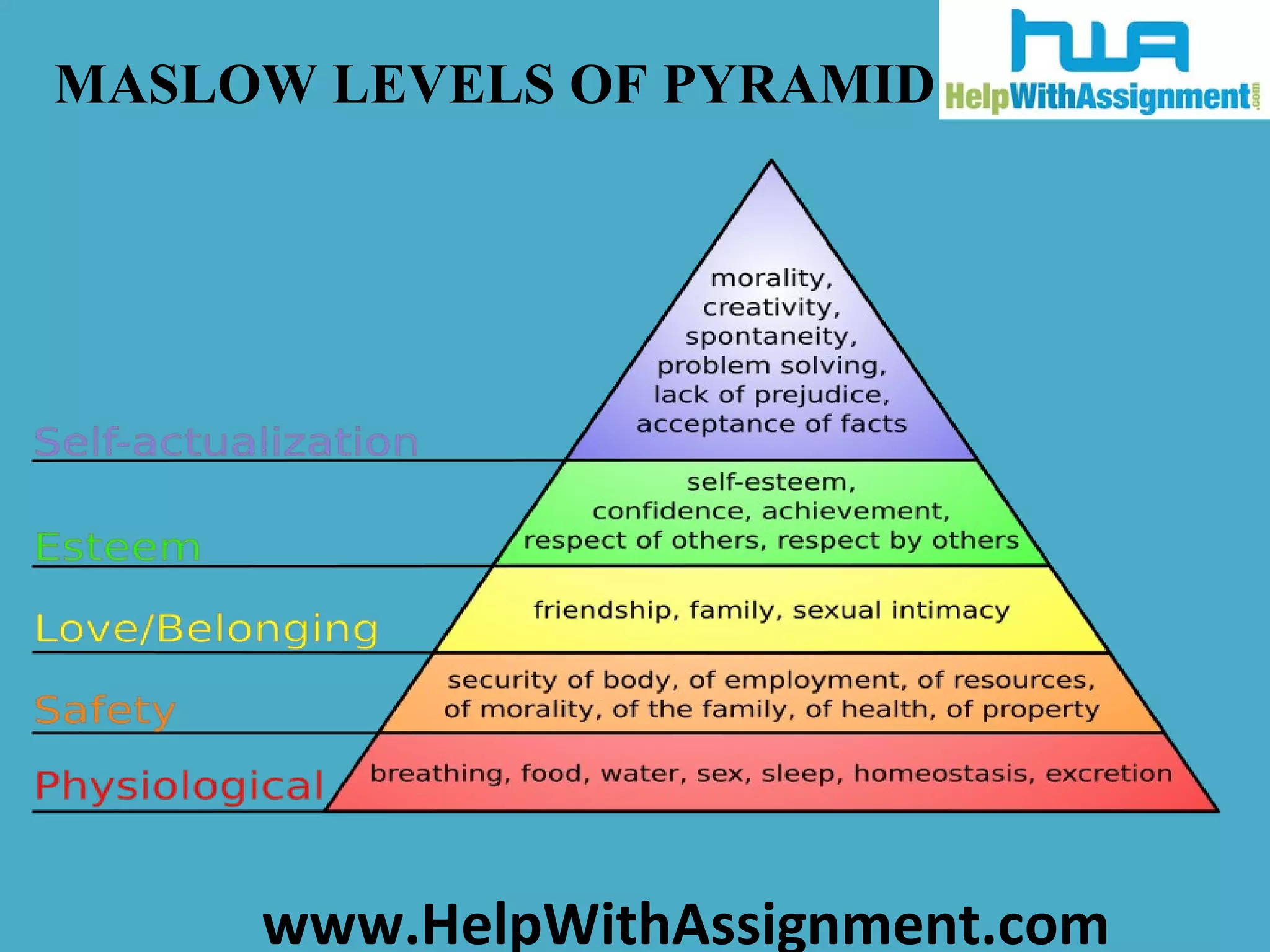
Motivation, derived from Latin meaning 'to move', involves processes that stimulate enthusiasm to pursue actions. Abraham Maslow, a psychologist, developed a hierarchy of needs consisting of five levels: physiological, safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization, where lower needs must be met before higher needs are pursued. However, criticisms of his theory suggest that the relationship between needs and behavior is not strictly hierarchical, as some individuals may strive for higher-level needs despite lacking lower-level needs.