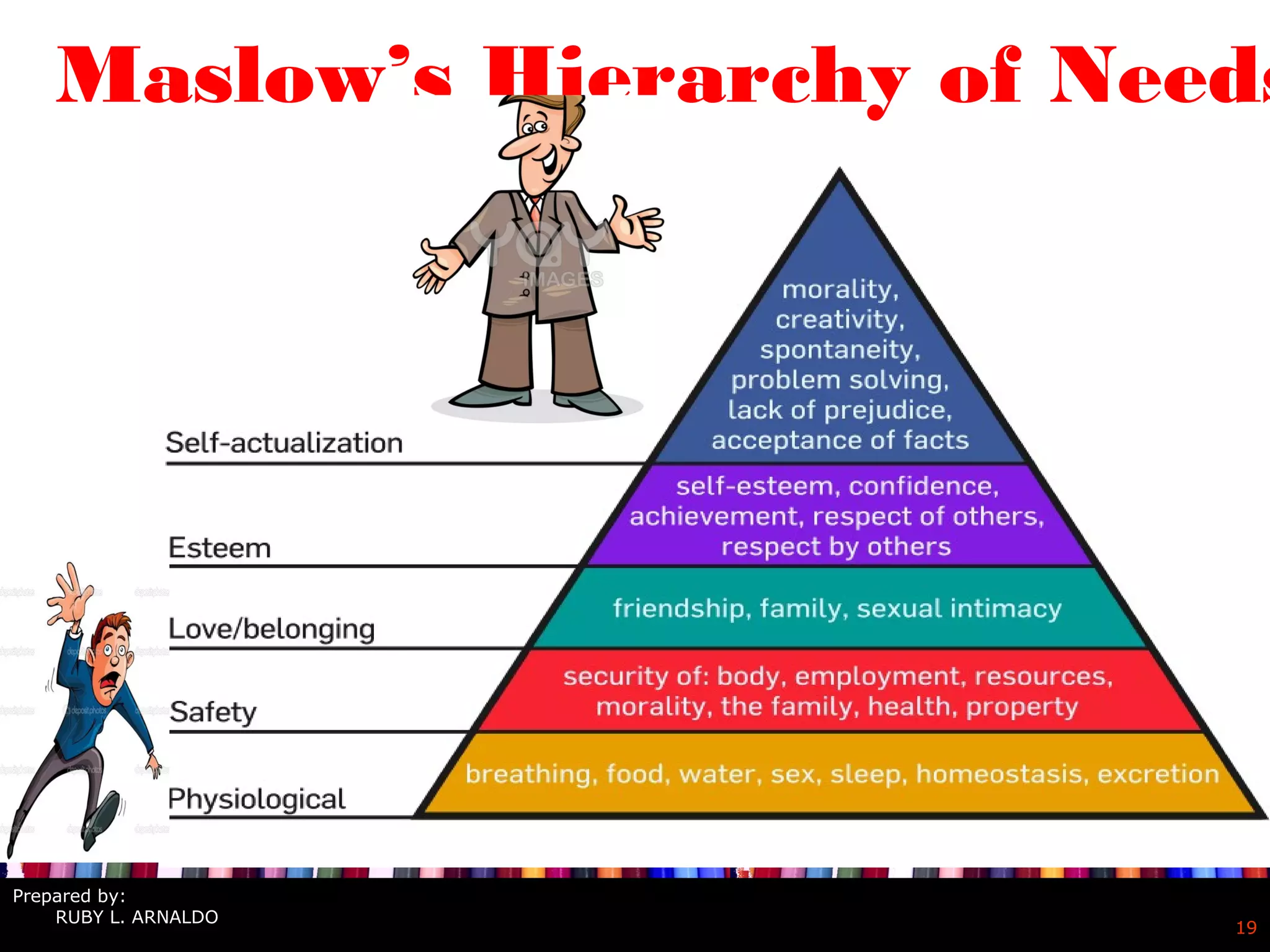
Abraham Maslow was an American psychologist best known for creating Maslow's hierarchy of needs, which proposes that people are motivated to fulfill innate needs beginning with physiological needs and moving up to needs for safety, love, esteem and self-actualization. Maslow's hierarchy suggests that lower level needs must be satisfied before higher level needs can be fulfilled. The theory provides a framework for understanding human motivation and development.