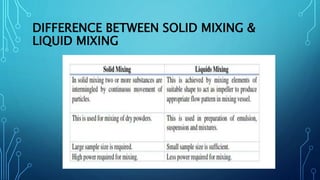
The document discusses mixing in the context of pharmaceutical production. It outlines that the main objective of mixing is to produce a bulk mixture that, when divided into doses, ensures each dose contains the correct proportions. It notes mixing is a critical intermediate step for tablets and capsules. The document also lists factors that affect mixing and different mechanisms for solid, liquid, and semisolid mixing. Specifically, it explains solid mixing involves convective, shear, and diffusive mechanisms while liquid mixing uses bulk transport, turbulent flow, laminar flow, and molecular diffusion.